
The Saab Toad, or Paddan in Swedish, was a development car Saab Automobile made in 1966 to test out the new chassis, drive train and engine for the Saab 99.

The Saab Toad, or Paddan in Swedish, was a development car Saab Automobile made in 1966 to test out the new chassis, drive train and engine for the Saab 99.
On 2 April 1964, Gudmund's day in Sweden, after several years of planning, the Saab board started Project Gudmund. [1] [2] [3] This was a project to develop a new and larger car to replace the Saab 96. This new car became the Saab 99, designed by Sixten Sason, [2] and unveiled in Stockholm on 22 November 1967. [1] [4]

The reason for this project was to preserve secrecy during development of the new model, the Saab 99, which was the company's first radically new body shape since the first cars made in 1947. The Toad used the body of a Saab 96, which was long enough for the purpose but had to be widened by 20 centimetres (7.9 in). [5] This was achieved by cutting the body in half lengthwise and inserting 20 cm of steel spacer. The windscreen (windshield) and rear window clearly showed the seam.
The bonnet (hood) and grille required widening in a different way, to prevent changing the appearance of the centrally-placed features, as the picture shows. Under the bonnet, the inline four engine for the future Saab 99 was mounted, developed by Triumph in coordination with Saab.
It was rightly believed that the wider body would not be noticed on Sweden's roads, where so many SAAB 96 cars were an everyday sight. This deception was successful, for a while, until test drivers allowed a grey Toad to be followed by a similarly-colored SAAB 96, making the different proportions obvious to any observer. [6]
Four Saab Toads were made, but only one remains, in dark gray paintwork. It is currently on display in the SAAB museum in Trollhättan, Sweden. [5] [7]

Further development was carried out on the SAAB Daihatsu, a test car with the new body but badged "Daihatsu", to prevent its identification by journalists as a developmental SAAB. This vehicle is on display in the SAAB Museum in Trollhättan.[ citation needed ]

Saab AB, with subsidiaries collectively known as the Saab Group, is a Swedish aerospace and defense company primarily operating from Sweden. The company is headquartered in Stockholm, but its development and manufacturing operations are undertaken in Linköping.

The Saab 900 is a mid-sized automobile produced by Swedish manufacturer Saab from 1978 until 1998 in two generations: the first from 1978 to 1994, and the second from 1994 to 1998.

The Saab 9-3 is a compact executive car initially developed and manufactured by the Swedish automaker Saab.

The Saab 90 is a family car produced by Saab from September 1984 to 1987. It was manufactured at a facility in Uusikaupunki (Nystad), Finland, at that time owned by a joint venture with Finnish Valmet called Saab-Valmet. The 90 was a continuation of the Saab 99 and it was basically a Saab 99 from the B-pillar forward with the rear of a Saab 900 sedan. The 90, while easier to build than the 99, was still considerably more labour-intensive than the more modern 900.

The Saab 99 is a car produced by Swedish manufacturer Saab from 1968 to 1984; their first foray into a larger class than the Saab 96. While considered a large family car in Scandinavia, it was marketed as a niche compact executive car in most other markets. It was manufactured both in Sweden and Finland and was succeeded by the Saab 900, although the 99 continued to be produced alongside its successor. The Saab 90, an updated, less complex version using many 900 parts took over from the 99 in late 1984.

The Saab 9-5 is an executive car that was produced by the Swedish automobile maker Saab from 1997 to 2012.

The Saab 96 is an automobile manufactured and marketed by Swedish automaker Saab from 1960 to January 1980, replacing the Saab 93. The 96 featured aerodynamic two-door bodywork, four-passenger seating and at first a two-stroke, three-cylinder engine, later a four-stroke V4.

The Saab 98 was an automobile built by Saab in 1974 which never reached full production. Originally it was called X14, designed by Björn Envall as a combi coupé based on the Saab 95 and using its floorpan. The prototype was assembled by Sergio Coggiola, who had already done work on the Saab Sonett III.

The Saab Sonett is an automobile manufactured by Swedish automaker Saab between 1955 and 1957 and again between 1966 and 1974. The Sonett share its engines and other mechanical components with the Saab 93, 95 and 96 of the same era. It was mainly intended for the lucrative American export market and was only offered intermittently in the Swedish domestic market for the 1968 and 1972 model years.

The Saab Monster was an experimental car made by Saab in 1959. This project was part of Saab's work in motorsport and the need to derive more power from their two-stroke powerplant.

The Saab Catherina is a 1964 prototype automobile, commissioned by the Swedish automaker Saab, designed by Sixten Sason and made at the workshops of the Aktiebolaget Svenska Järnvägsverkstäderna in Katrineholm, Sweden. It is a red, two-seat sports car with a targa top.

Saab Automobile AB was a car manufacturer that was founded in Sweden in 1945 when its parent company, Saab AB, began a project to design a small automobile. The first production model, the Saab 92, was launched in 1949. In 1968 the parent company merged with Scania-Vabis, and ten years later the Saab 900 was launched, in time becoming Saab's best-selling model. In the mid-1980s the new Saab 9000 model also appeared.

The Saab MFI 13 was a February 1965 prototype for the Saab 97 automobile, later known as Sonett II. It was built at the Malmö Flygindustri as they had some experience with plastic manufacturing. The body of the prototype was made of steel though. A second prototype was designed by Sixten Sason and delivered a month later by ASJ in Arlöv.

Ursaab, also known as 92001 and X9248, was the first of four prototype cars made by Saab AB, which at that time was solely an aeroplane manufacturer, leading to production of the first Saab car, the Saab 92 in 1949. The car is now in the Saab Car Museum in Trollhättan. The name "Ursaab" means "original Saab".

The Saab 9-4X is a mid-size luxury crossover SUV that was introduced at the 2010 LA Auto Show. It is based on the all-wheel-drive GM Theta Premium platform, which also forms the basis for the Cadillac SRX. Production of the 9-4X began in 2011, at General Motors' Ramos Arizpe Assembly in Mexico, but halted before the end of that year as a result of the bankruptcy of Saab, leaving a total of 814 assembled.
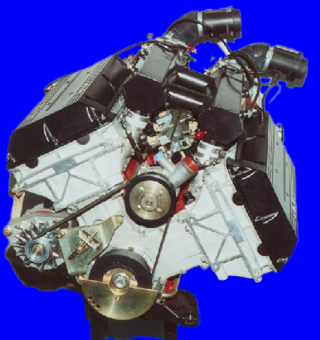
The Saab V8 is a V8 engine developed for Saab Automobile by Saab-Valmet. Only five prototype engines were built, with one being extensively road tested. The V8 engine was never put into production.

The Saab 21R was a Swedish fighter/attack aircraft developed and produced by Svenska Aeroplan AB (SAAB). It was a jet-powered development of the piston-engined SAAB 21 and was the first jet aircraft to be produced by Saab. The R-suffix stands for reaktion (reaction), referencing reaktionsdrift or reaktionsmotor. Along with the Soviet Yakovlev Yak-15, the 21R was one of only two jet fighters to have been successfully converted from piston-powered aircraft.

Trollhättan Assembly is an automobile factory in Trollhättan, Sweden. The factory opened in 1947 under the ownership of Saab AB, then passing to Saab Automobile. From 1989 to 2010, the factory was partially (1989–1999), then completely (2000–2010) owned by General Motors. In 2010, Saab was sold to Spyker Cars. The plant ended production in 2011 and restarted in 2013, after the NEVS purchase of Saab Automobile. The Trollhättan complex, including the assembly, is now the sole site of all Saab engineering and manufacturing activities. After NEVS announced its closure in March 2023, the factory was sold to Stenhaga Invest AB, with both Polestar and EV Electra showing interest in buying the factory.
NEVS AB was a Swedish electric car manufacturer which acquired the assets of Saab Automobile from a bankruptcy estate in 2012. After facing numerous financial difficulties, the company was closed in March 2023, with both Polestar and EV Electra interested in buying the former Trollhättan factory.

The Saab Car Museum is an automobile museum in Trollhättan, Sweden. It covers the history of the Saab brand of automobiles manufactured by Saab under various owners since 1947.