
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species.

Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a species of yeast. The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been originally isolated from the skin of grapes. It is one of the most intensively studied eukaryotic model organisms in molecular and cell biology, much like Escherichia coli as the model bacterium. It is the microorganism behind the most common type of fermentation. S. cerevisiae cells are round to ovoid, 5–10 μm in diameter. It reproduces by budding.

Candida is a genus of yeasts. It is the most common cause of fungal infections worldwide and the largest genus of medically important yeast.

Torulaspora delbrueckii is a ubiquitous yeast species with both wild and anthropic habitats. The type strain of T. delbrueckii is CBS 1146T, equivalent to CLIB 230 or ATCC 10662, etc.. The type strain of T. delbrueckii CBS 1146 T was sequenced in 2009, and is composed of 8 chromosomes in addition to a mitochondrial genome.
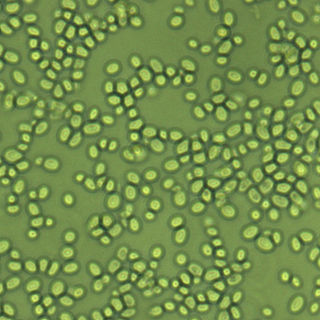
Nakaseomyces glabratus is a species of haploid yeast of the genus Nakaseomyces, previously known as Candida glabrata. Despite the fact that no sexual life cycle has been documented for this species, N. glabratus strains of both mating types are commonly found. C. glabrata is generally a commensal of human mucosal tissues, but in today's era of wider human immunodeficiency from various causes, N. glabratus is often the second or third most common cause of candidiasis as an opportunistic pathogen. Infections caused by N. glabratus can affect the urogenital tract or even cause systemic infections by entrance of the fungal cells in the bloodstream (Candidemia), especially prevalent in immunocompromised patients.
Saccharomyces bayanus is a yeast of the genus Saccharomyces, and is used in winemaking and cider fermentation, and to make distilled beverages. Saccharomyces bayanus, like Saccharomyces pastorianus, is now accepted to be the result of multiple hybridisation events between three pure species, Saccharomyces uvarum, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Saccharomyces eubayanus. Notably, most commercial yeast cultures sold as pure S. bayanus for wine making, e.g. Lalvin EC-1118 strain, have been found to contain S. cerevisiae cultures instead
A killer yeast is a yeast, such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is able to secrete one of a number of toxic proteins which are lethal to susceptible cells. These "killer toxins" are polypeptides that kill sensitive cells of the same or related species, often functioning by creating pores in target cell membranes. These yeast cells are immune to the toxic effects of the protein due to an intrinsic immunity. Killer yeast strains can be a problem in commercial processing because they can kill desirable strains. The killer yeast system was first described in 1963. Study of killer toxins helped to better understand the secretion pathway of yeast, which is similar to those of more complex eukaryotes. It also can be used in treatment of some diseases, mainly those caused by fungi.

The Ustilaginaceae are a family of smut fungi in the order Ustilaginomycetes. Collectively, the family contains 17 genera and 607 species.
Saccharomyces paradoxus is a wild yeast and the closest known species to the baker's yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. It is used in population genomics and phylogenetic studies to compare its wild characteristics to laboratory yeasts.
Saccharomyces eubayanus, a cryotolerant type of yeast, is most likely the parent of the lager brewing yeast, Saccharomyces pastorianus.
Saccharomyces kudriavzevii, is a species of yeast in the Saccharomyces sensu stricto complex. Its type strain is NCYC 2889T. It is used in production of alcoholic beverages, including pinot noir wine, and hybrids of it are used in beer brewing. It is isolated widely from the bark of oak trees.
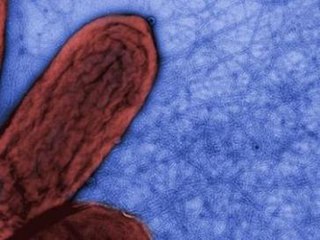
Geobacter sulfurreducens is a gram-negative metal and sulphur-reducing proteobacterium. It is rod-shaped, aerotolerant anaerobe, non-fermentative, has flagellum and type four pili, and is closely related to Geobacter metallireducens. Geobacter sulfurreducens is an anaerobic species of bacteria that comes from the family of bacteria called Geobacteraceae. Under the genus of Geobacter, G. sulfurreducens is one out of twenty different species. The Geobacter genus was discovered by Derek R. Lovley in 1987. G. sulfurreducens was first isolated in Norman, Oklahoma, USA from materials found around the surface of a contaminated ditch.
Helicobacter canadensis is a bacterium in the Helicobacteraceae family, Campylobacterales order, first isolated from humans with diarrhea. Its genome has been sequenced.
Candida zemplinina is a yeast species that is osmotolerant, psychrotolerant and ferments sweet botrytized wines. Its type strain is 10-372T.
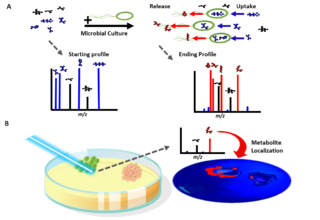
Exometabolomics, also known as 'metabolic footprinting', is the study of extracellular metabolites and is a sub-field of metabolomics.

Pdr1p is a transcription factor found in yeast and is a key regulator of genes involved in general drug response. It induces the expression of ATP-binding cassette transporter, which can export toxic substances out of the cell, allowing cells to survive under general toxic chemicals. It binds to DNA sequences that contain certain motifs called pleiotropic drug response element (PDRE). Pdr1p is encoded by a gene called PDR1 on chromosome VII.
ERG5 or Sterol 22-desaturase is a cytochrome P450 enzyme in the ergosterol biosynthesis pathway of fungi Saccharomyces cerevisiae, with the CYP Symbol CYP61A1. CYP61A1 is one of only three P450 enzyme found in baker's yeast, the other two are CYP51F1 and CYP56A1. The ortholog in Schizosaccharomyces pombe, was named CYP61A3 for historical reasons, and is only one of two P450 enzyme found with CYP51F1. ERG5 catalyzes the C22-C23 double bond formation on the sterol side chain of ergostatrienol to convert it into ergostatetraenol, then the C24 double bond of ergostatetrenol will be hydrogenation reduced into ergosterol by ERG4.
Fungal genomes are among the smallest genomes of eukaryotes. The sizes of fungal genomes range from less than 10 Mbp to hundreds of Mbp. The average genome size is approximately 37 Mbp in Ascomycota, 47 Mbp in Basidiomycota and 75 Mbp in Oomycota. The sizes and gene numbers of the smallest genomes of free-living fungi such as those of Wallemia ichthyophaga, Wallemia mellicola or Malassezia restricta are comparable to bacterial genomes. The genome of the extensively researched yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae contains approximately 12 Mbp and was the first completely sequenced eukaryotic genome. Due to their compact size fungal genomes can be sequenced with less resources than most other eukaryotic genomes and are thus important models for research. Some fungi exist as stable haploid, diploid, or polyploid cells, others change ploidy in response to environmental conditions and aneuploidy is also observed in novel environments or during periods of stress.
Saccharomycodes ludwigii is a yeast species best known for being a contaminant in alcohol and fruit juice production. It is highly resistant to typical environmental stressors such as high temperature, high sugar concentration, and high sulfur dioxide concentration. It is often referred to as the "winemaker's nightmare," as it contaminates products by outcompeting desirable yeast species. However, S. ludwigii strains are currently being tested in the growing low-alcohol beer industry.








