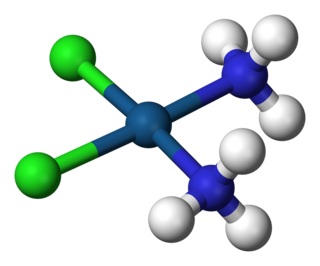
A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the coordination centre, and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals, are coordination complexes.

In organic chemistry, an oxime is an organic compound belonging to the imines, with the general formula RR’C=N−OH, where R is an organic side-chain and R' may be hydrogen, forming an aldoxime, or another organic group, forming a ketoxime. O-substituted oximes form a closely related family of compounds. Amidoximes are oximes of amides with general structure R1C(=NOH)NR2R3.

In organic chemistry, Fehling's solution is a chemical reagent used to differentiate between water-soluble carbohydrate and ketone functional groups, and as a test for reducing sugars and non-reducing sugars, supplementary to the Tollens' reagent test. The test was developed by German chemist Hermann von Fehling in 1849.

In organic chemistry, a Schiff base is a compound with the general structure R1R2C=NR3. They can be considered a sub-class of imines, being either secondary ketimines or secondary aldimines depending on their structure. Anil refers to a common subset of Schiff bases: imines derived from anilines. The term can be synonymous with azomethine which refers specifically to secondary aldimines.

Copper(II) nitrate describes any member of the family of inorganic compounds with the formula Cu(NO3)2(H2O)x. The hydrates are blue solids. Anhydrous copper nitrate forms blue-green crystals and sublimes in a vacuum at 150-200 °C. Common hydrates are the hemipentahydrate and trihydrate.
Classical qualitative inorganic analysis is a method of analytical chemistry which seeks to find the elemental composition of inorganic compounds. It is mainly focused on detecting ions in an aqueous solution, therefore materials in other forms may need to be brought to this state before using standard methods. The solution is then treated with various reagents to test for reactions characteristic of certain ions, which may cause color change, precipitation and other visible changes.
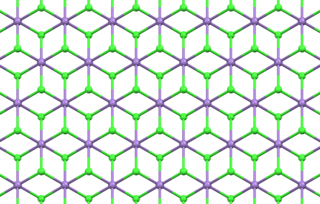
Manganese(II) chloride is the dichloride salt of manganese, MnCl2. This inorganic chemical exists in the anhydrous form, as well as the dihydrate (MnCl2·2H2O) and tetrahydrate (MnCl2·4H2O), with the tetrahydrate being the most common form. Like many Mn(II) species, these salts are pink, with the paleness of the color being characteristic of transition metal complexes with high spin d5 configurations.
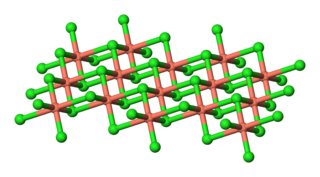
Copper(II) chloride, also known as cupric chloride, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuCl2. The monoclinic yellowish-brown anhydrous form slowly absorbs moisture to form the orthorhombic blue-green dihydrate CuCl2·2H2O, with two water molecules of hydration. It is industrially produced for use as a co-catalyst in the Wacker process.
Hydrometallurgy is a technique within the field of extractive metallurgy, the obtaining of metals from their ores. Hydrometallurgy involve the use of aqueous solutions for the recovery of metals from ores, concentrates, and recycled or residual materials. Processing techniques that complement hydrometallurgy are pyrometallurgy, vapour metallurgy, and molten salt electrometallurgy. Hydrometallurgy is typically divided into three general areas:

Liquid–liquid extraction, also known as solvent extraction and partitioning, is a method to separate compounds or metal complexes, based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids, usually water (polar) and an organic solvent (non-polar). There is a net transfer of one or more species from one liquid into another liquid phase, generally from aqueous to organic. The transfer is driven by chemical potential, i.e. once the transfer is complete, the overall system of chemical components that make up the solutes and the solvents are in a more stable configuration. The solvent that is enriched in solute(s) is called extract. The feed solution that is depleted in solute(s) is called the raffinate. Liquid–liquid extraction is a basic technique in chemical laboratories, where it is performed using a variety of apparatus, from separatory funnels to countercurrent distribution equipment called as mixer settlers. This type of process is commonly performed after a chemical reaction as part of the work-up, often including an acidic work-up.
The uranyl ion is an oxycation of uranium in the oxidation state +6, with the chemical formula UO2+
2. It has a linear structure with short U–O bonds, indicative of the presence of multiple bonds between uranium and oxygen. Four or more ligands may be bound to the uranyl ion in an equatorial plane around the uranium atom. The uranyl ion forms many complexes, particularly with ligands that have oxygen donor atoms. Complexes of the uranyl ion are important in the extraction of uranium from its ores and in nuclear fuel reprocessing.
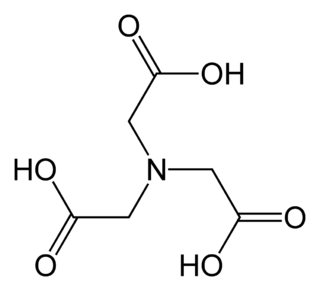
Nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) is the aminopolycarboxylic acid with the formula N(CH2CO2H)3. It is a colourless solid. Its conjugate base nitrilotriacetate is used as a chelating agent for Ca2+, Co2+, Cu2+, and Fe3+.

A coordination polymer is an inorganic or organometallic polymer structure containing metal cation centers linked by ligands. More formally a coordination polymer is a coordination compound with repeating coordination entities extending in 1, 2, or 3 dimensions.

Hexafluorophosphate is an anion with chemical formula of [PF6]−. It is an octahedral species that imparts no color to its salts. [PF6]− is isoelectronic with sulfur hexafluoride, SF6, and the hexafluorosilicate dianion, [SiF6]2−, and hexafluoroantimonate [SbF6]−. In this anion, phosphorus has a valence of 5. Being poorly nucleophilic, hexafluorophosphate is classified as a non-coordinating anion.
In organic chemistry, the Baudisch reaction is a process for the synthesis of nitrosophenols using metal ions. Although the products are of limited value, the reaction is of historical interest as an example of metal-promoted functionalization of aromatic substrates.
In coordination chemistry, a stability constant is an equilibrium constant for the formation of a complex in solution. It is a measure of the strength of the interaction between the reagents that come together to form the complex. There are two main kinds of complex: compounds formed by the interaction of a metal ion with a ligand and supramolecular complexes, such as host–guest complexes and complexes of anions. The stability constant(s) provide(s) the information required to calculate the concentration(s) of the complex(es) in solution. There are many areas of application in chemistry, biology and medicine.
In chemistry, binding selectivity is defined with respect to the binding of ligands to a substrate forming a complex. Binding selectivity describes how a ligand may bind more preferentially to one receptor than another. A selectivity coefficient is the equilibrium constant for the reaction of displacement by one ligand of another ligand in a complex with the substrate. Binding selectivity is of major importance in biochemistry and in chemical separation processes.
Equilibrium chemistry is concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid–base, host–guest, metal–complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria.
Coordination cages are three-dimensional ordered structures in solution that act as hosts in host–guest chemistry. They are self-assembled in solution from organometallic precursors, and often rely solely on noncovalent interactions rather than covalent bonds. Coordinate bonds are useful in such supramolecular self-assembly because of their versatile geometries. However, there is controversy over calling coordinate bonds noncovalent, as they are typically strong bonds and have covalent character. The combination of a coordination cage and a guest is a type of inclusion compound. Coordination complexes can be used as "nano-laboratories" for synthesis, and to isolate interesting intermediates. The inclusion complexes of a guest inside a coordination cage show intriguing chemistry as well; often, the properties of the cage will change depending on the guest. Coordination complexes are molecular moieties, so they are distinct from clathrates and metal-organic frameworks.

Copper forms a rich variety of compounds, usually with oxidation states +1 and +2, which are often called cuprous and cupric, respectively. Copper compounds, whether organic complexes or organometallics, promote or catalyse numerous chemical and biological processes.














