
Salmonidae is a family of ray-finned fish that constitutes the only currently extant family in the order Salmoniformes, consisting of 11 extant genera and over 200 species collectively known as "salmonids" or "salmonoids". The family includes salmon, trout, char, graylings, freshwater whitefishes, taimens and lenoks, all coldwater mid-level predatory fish that inhabit the subarctic and cool temperate waters of the Northern Hemisphere. The Atlantic salmon, whose Latin name became that of its genus Salmo, is also the eponym of the family and order names.

The Arctic char or Arctic charr is a cold-water fish in the family Salmonidae, native to alpine lakes, as well as Arctic and subarctic coastal waters in the Holarctic.

The Dolly Varden trout is a species of salmonid ray-finned fish native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. Despite the name "trout", it belongs to the genus Salvelinus (chars), which includes 51 recognized species, the most prominent being the brook, lake and bull trout as well as the Arctic char. Although many populations are semi-anadromous, riverine and lacustrine populations occur throughout its range. It is considered by taxonomists as part of the Salvelinus alpinus complex, as many populations of bull trout, Dolly Varden trout and Arctic char overlap.
Salvelinus curilus is a species of anadromous fish in the salmon family. It inhabits the waters of Russian Far East in the Kurile Islands, Sakhalin, Primorye and also Korea and Japan. It has mostly been considered a subspecies of the Dolly Varden trout Salvelinus malma, with the name Salvelinus malma krascheninnikova, and referred to as the southern Dolly Varden or Asian southern form Dolly Varden trout.

Salvelinus is a genus of salmonid fish often called char or charr; some species are called "trout". Salvelinus is a member of the subfamily Salmoninae within the family Salmonidae. The genus has a northern circumpolar distribution, and most of its members are typically cold-water fish that primarily inhabit fresh waters. Many species also migrate to the sea.

Triodia is a genus of moths of the family Hepialidae. There are seven described species found in northern and western Eurasia.

Lenoks, otherwise known as Asiatic trout or Manchurian trout, are salmonid fish of the genus Brachymystax, native to rivers and lakes in Mongolia, Kazakhstan, wider Siberia, Northern China and Korea.
Salvethymus svetovidovi, also called the long-finned charr, is a species of salmonid fish. It is endemic to Elgygytgyn Lake in Chukotka, Far East of Russia, together with another species, the small-mouth char Salvelinus elgyticus. A third char species in the same lake is Salvelinusboganidae, the Boganid char.
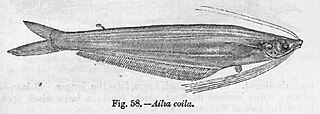
Ailia coila, also known as the Gangetic ailia is a species of catfish in the family Ailiidae native to India, Bangladesh, Nepal and Pakistan. This species grows to a length of 30 centimetres (12 in) TL.

Eysarcoris is a genus of shield bugs belonging to the family Pentatomidae, subfamily Pentatominae, and typical of the tribe Eysarcorini.
Salvelinus inframundus, also known as Orkney charr is a cold-water fish in the family Salmonidae which is endemic to Scotland.

Salvelinus killinensis, also known as Haddy charr is a variety of charr found in certain lakes in Scotland.

Salvelinus willughbii, also known as the Windermere char, is a cold-water fish in the family Salmonidae. Its binomial species name commemorates Francis Willughby. Willughby and John Ray had described this fish and its relatives in two Welsh lakes in 1662, recognising these charr as differing from other salmon-like species.

The Sommen charr is a population or subspecies of Arctic charr found in Lake Sommen. It is one of twenty-two species of fish found in the lake.
Solanum acaule is a species of wild potato in the family Solanaceae, native to Peru, Bolivia, northern Chile, and northwestern Argentina. The complete chloroplast genome of S. acaule was constructed by de novo assembly using Illumina paired-end (PE) sequencing data. The chloroplast genome of S. acaule is circular and has a length of 155,570 bp and typical quadripartite consisting of 86,020 bp of large single copy, 18,364 bp of small single copy, and 25,593 bp of a pair of inverted repeat regions. A total of 158 genes were annotated including 105 protein-coding genes, 45 tRNA genes, and eight rRNA genes. Maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis of the sequence with 31 species in the Solanaceae revealed that S. acaule is fully resolved in a large clade with nine other Solanum species including S. tuberosum. It is being extensively studied for its resistance to Phytophthora infestans, Potato leafroll virus, Potato virus X, Potato virus Y, potato cyst nematodes, and frost, in an effort to improve the domestic potato Solanum tuberosum.

The Kamchatka grayling is a grayling in the salmon family Salmonidae. The fish grows up to 50 cm (20 in). It is found in freshwater habitats of the Russian Far East, including the Kamchatka Peninsula, eastern part of Magadan Oblast and northwards to the southern Chukchi Peninsula.
Thymallus flavomaculatus, also known as yellow-spotted grayling, is a species of brackish-water fish in the salmon family. It is found in Khabarovsk and Primorsky Krai of the Russian Far East, as well as the Sea of Japan and the Sea of Okhotsk. They usually live near or on the bottom of the water body.
Salvelinus albus, also known as white char, is a species of freshwater fish in the salmon family. It is endemic to the Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia, including the Lake Kronotskoye drainage basin.

Salvelinus neiva, also known as neiva, is a freshwater species of fish in the salmon family. It is endemic to the Okhota river basin of the Russian far east and mountain lakes nearby.
Salvelinus jacuticus, commonly known as Yakutian char, is a species of freshwater fish in the salmon family. It is endemic to the mountain lakes in the Lena Delta, Russia. It was reported that the population of the species declined due to overfishing and the rise of temperature in the arctic region.













