Aringay, officially the Municipality of Aringay, is a second class municipality in the province of La Union, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 50,380 people.

San Fernando, officially the City of San Fernando, is a 3rd class component city and capital of the province of La Union, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 125,642 people.

Villasis, officially the Municipality of Villasis, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Pangasinan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 65,047 people.

Badoc, officially the Municipality of Badoc, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Ilocos Norte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 32,530 people.

Pinili, officially the Municipality of Pinili, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Ilocos Norte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 17,626 people.

Vintar, officially the Municipality of Vintar, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Ilocos Norte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 33,339 people.

San Ildefonso, officially the Municipality of San Ildefonso, is a 5th class municipality in the province of Ilocos Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 8,190 people.

San Vicente, officially the Municipality of San Vicente, is a 5th class municipality in the province of Ilocos Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 13,118 people.

Santo Domingo, officially the Municipality of Santo Domingo, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Ilocos Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 29,041 people.

Sinait, officially the Municipality of Sinait, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Ilocos Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 25,998 people.

Burgos, officially the Municipality of Burgos, is a 5th class municipality in the province of La Union, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 9,006 people, making it the least populated municipality in the province.

Luna, officially the Municipality of Luna, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of La Union, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 37,318 people.

Pugo, officially the Municipality of Pugo, is a 5th class municipality in the province of La Union, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 19,337 people.

Rosario, officially the Municipality of Rosario, is a 1st class municipality in the province of La Union, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 60,278 people.

San Juan, officially the Municipality of San Juan, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of La Union, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 40,507 people.

Santol, officially the Municipality of Santol, is a 4th class municipality in the province of La Union, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 14,166 people.

Sudipen , officially the Municipality of Sudipen, is a 4th class municipality in the province of La Union, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 17,187 people.

Manaoag, officially the Municipality of Manaoag, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Pangasinan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 76,045 people.

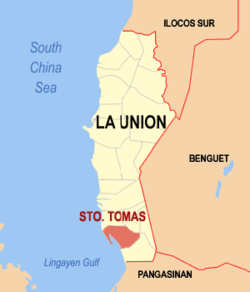
Santo Tomas, officially the Municipality of Santo Tomas, is a 5th class municipality in the province of Pangasinan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 14,878 people, making it the least populated municipality in the province.

Saguday, officially the Municipality of Saguday, is a 5th class municipality in the province of Quirino, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 17,137 people, making it the least populated municipality in the province.