The United States Coast Guard (USCG) is the maritime security, search and rescue, and law enforcement service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the country's eight uniformed services. The service is a maritime, military, multi-mission service unique among the United States military branches for having a maritime law enforcement mission with jurisdiction in both domestic and international waters and a federal regulatory agency mission as part of its duties. It is the largest coast guard in the world, rivaling the capabilities and size of most navies.
A United States military occupation code, or a military occupational specialty code, is a nine-character code used in the United States Army and United States Marine Corps to identify a specific job. In the United States Air Force, a system of Air Force Specialty Codes (AFSC) is used. In the United States Navy, a system of naval ratings and designators are used along with the Navy Enlisted Classification (NEC) system. A system of ratings is also used in the United States Coast Guard.

The Good Conduct Medal is one of the oldest military awards of the United States Armed Forces. The U.S. Navy's variant of the Good Conduct Medal was established in 1869, the Marine Corps version in 1896, the Coast Guard version in 1923, the Army version in 1941, and the Air Force version in 1963; the Air Force Good Conduct Medal was temporarily discontinued from February 2006 to February 2009, followed by its subsequent reinstatement.

A Reserve Good Conduct Medal refers to any one of the five military conduct awards, four of which are currently issued and one of which was previously issued, by the United States Armed Forces to members of the Reserve and National Guard. The primary difference between the regular Good Conduct Medal and the Reserve Good Conduct Medal is that the regular Good Conduct Medal is only issued for active duty service while the reserve equivalent is bestowed for reserve duties such as drills, annual training, and additional active duty for either training or operational support to the active duty force or, in the case of the Army National Guard and Air National Guard, in support of Title 32 U.S.C. state active duty (SAD) such as disaster response and relief.

The diver insignia are qualification badges of the uniformed services of the United States which are awarded to servicemen qualified as divers. Originally, the diver insignia was a cloth patch decoration worn by United States Navy divers in the upper-portion of the enlisted service uniform's left sleeve during the first part of World War II, when the rating insignia was worn on the right sleeve. When enlisted rating insignia were shifted to the left sleeve in late World War II, the patch shifted to the upper right sleeve. The diving patch was created during World War II, and became a breast insignia in the late 1960s.

A United States Aviator Badge refers to three types of aviation badges issued by the United States Armed Forces, those being for Air Force, Army, and Naval aviation.

The United States Coast Guard Reserve is the reserve component of the United States Coast Guard. It is organized, trained, administered, and supplied under the direction of the Commandant of the Coast Guard through the Assistant Commandant for Reserve (CG-R).
The Recruiting Service Ribbon is a military award of the United States Armed Forces which is issued by every branch of service. The United States Army previously only had the Army Recruiting Badge but this has since changed as of 2023 with the Army Recruiting Ribbon. The Recruiting Service Ribbon recognizes those military service members who have completed a successful tour as a military recruiter in one of the United States Military Recruiting Commands.

A peaked cap, peaked hat, service cap, barracks cover, or combination cap is a form of headgear worn by the armed forces of many nations, as well as many uniformed civilian organisations such as law enforcement agencies and fire departments. It derives its name from its short visor, or peak, which was historically made of polished leather but increasingly is made of a cheaper synthetic substitute.

The United States Navy Reserve (USNR), known as the United States Naval Reserve from 1915 to 2005, is the Reserve Component (RC) of the United States Navy. Members of the Navy Reserve, called Reservists, are categorized as being in either the Selected Reserve (SELRES), the Training and Administration of the Reserve (TAR), the Individual Ready Reserve (IRR), or the Retired Reserve.
The Army of the United States is one of the four major service components of the United States Army, but it has been inactive since the suspension of the draft in 1973 and the U.S. military's transition to a volunteer force. Personnel serving in the United States Army during a major national emergency or armed conflict were enlisted or inducted into the Army of the United States without specifying service in a component. It also includes the "Retired Reserve." Those are retired soldiers who have reached the required years of creditable service, or creditable service and age; regardless of the component, or components they formerly served in.
The Aircrew Badge, commonly known as Wings, is a qualification badge of the United States military that is awarded by all five branches of armed services to personnel who serve as aircrew members on board military aircraft. The badge is intended to recognize the training and qualifications required by aircrew of military aircraft. In order to qualify as an aircrew member and receive the Aircrew Badge, such personnel typically undergo advanced training in aircraft in-flight support roles.
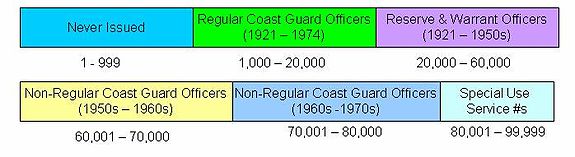
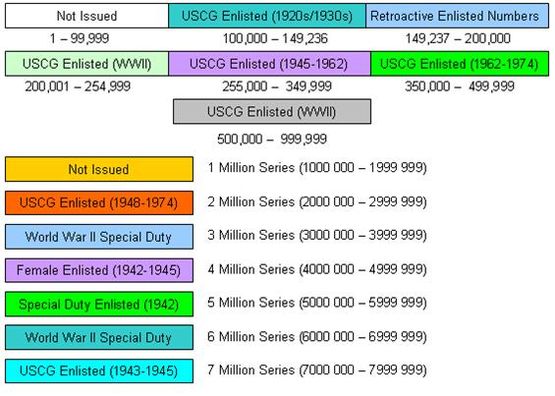
A service number is an identification code used to identify a person within a large group. Service numbers are most often associated with the military; however, they also may be used in civilian organizations. National identification numbers may be seen as types of service numbers.

United States Coast Guard (USCG) Women's Reserve, known as the SPARS, was the women's branch of the United States Coast Guard Reserve. It was established by the United States Congress and signed into law by President Franklin D. Roosevelt on 23 November 1942. This law authorized the acceptance of women into the reserve as commissioned officers and at the enlisted level for the duration of World War II plus six months. Its purpose was to release officers and men for sea duty and to replace them with women at shore stations. Dorothy C. Stratton was appointed director of the SPARS with the rank of lieutenant commander and later promoted to captain.
Service numbers were used by the United States Department of Defense as the primary means of service member identification from 1918 until 1974. Service numbers are public information available under the Freedom of Information Act, unlike social security numbers which are protected by the Privacy Act of 1974.
Service numbers were used by the United States Army from 1918 until 1969. Prior to this time, the Army relied on muster rolls as a means of indexing enlisted service members while officers were usually listed on yearly rolls maintained by the United States War Department. In the nineteenth century, the Army also used pay records as a primary means of identifying service members after discharge.
United States Air Force service numbers were created in the spring of 1948, approximately six months after the Air Force's creation as separate branch of the armed forces.
United States Navy service numbers were created in 1920, one year after the close of the First World War. The creation of Navy service numbers coincided with those of the Marine Corps, as the Marines were under the authority of the Department of the Navy.
United States Marine Corps service numbers were created in 1920, the same year as Navy service numbers, and were modeled after the same design.

An officer is a person who holds a position of authority as a member of an armed force or uniformed service.