
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, or the surfaces of intracardiac devices. Endocarditis is characterized by lesions, known as vegetations, which are masses of platelets, fibrin, microcolonies of microorganisms, and scant inflammatory cells. In the subacute form of infective endocarditis, a vegetation may also include a center of granulomatous tissue, which may fibrose or calcify.
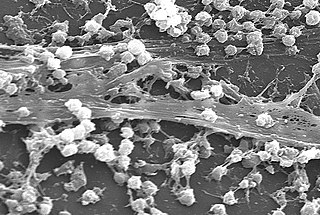
A biofilm is a syntrophic community of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs). The cells within the biofilm produce the EPS components, which are typically a polymeric combination of extracellular polysaccharides, proteins, lipids and DNA. Because they have a three-dimensional structure and represent a community lifestyle for microorganisms, they have been metaphorically described as "cities for microbes".

A central venous catheter (CVC), also known as a central line (c-line), central venous line, or central venous access catheter, is a catheter placed into a large vein. It is a form of venous access. Placement of larger catheters in more centrally located veins is often needed in critically ill patients, or in those requiring prolonged intravenous therapies, for more reliable vascular access. These catheters are commonly placed in veins in the neck, chest, groin, or through veins in the arms.

Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although S. aureus usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. S. aureus is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), is a worldwide problem in clinical medicine. Despite much research and development, no vaccine for S. aureus has been approved.

Platelets or thrombocytes are a blood component whose function is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby initiating a blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm derived from the megakaryocytes of the bone marrow or lung, which then enter the circulation. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates, thrombocytes circulate as intact mononuclear cells.
Bloodstream infections (BSIs) are infections of blood caused by blood-borne pathogens. The detection of microbes in the blood is always abnormal. A bloodstream infection is different from sepsis, which is characterized by severe inflammatory or immune responses of the host organism to pathogens.

A hospital-acquired infection, also known as a nosocomial infection, is an infection that is acquired in a hospital or other healthcare facility. To emphasize both hospital and nonhospital settings, it is sometimes instead called a healthcare-associated infection. Such an infection can be acquired in a hospital, nursing home, rehabilitation facility, outpatient clinic, diagnostic laboratory or other clinical settings. A number of dynamic processes can bring contamination into operating rooms and other areas within nosocomial settings. Infection is spread to the susceptible patient in the clinical setting by various means. Healthcare staff also spread infection, in addition to contaminated equipment, bed linens, or air droplets. The infection can originate from the outside environment, another infected patient, staff that may be infected, or in some cases, the source of the infection cannot be determined. In some cases the microorganism originates from the patient's own skin microbiota, becoming opportunistic after surgery or other procedures that compromise the protective skin barrier. Though the patient may have contracted the infection from their own skin, the infection is still considered nosocomial since it develops in the health care setting. Nosocomial infection tends to lack evidence that it was present when the patient entered the healthcare setting, thus meaning it was acquired post-admission.
Nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis (NBTE) is a form of endocarditis in which small sterile vegetations are deposited on the valve leaflets. Formerly known as marantic endocarditis, which comes from the Greek marantikos, meaning "wasting away". The term "marantic endocarditis" is still sometimes used to emphasize the association with a wasting state such as cancer.
A slime layer in bacteria is an easily removable, unorganized layer of extracellular material that surrounds bacteria cells. Specifically, this consists mostly of exopolysaccharides, glycoproteins, and glycolipids. Therefore, the slime layer is considered as a subset of glycocalyx.

Staphylococcus epidermidis is a Gram-positive bacterium, and one of over 40 species belonging to the genus Staphylococcus. It is part of the normal human microbiota, typically the skin microbiota, and less commonly the mucosal microbiota and also found in marine sponges. It is a facultative anaerobic bacteria. Although S. epidermidis is not usually pathogenic, patients with compromised immune systems are at risk of developing infection. These infections are generally hospital-acquired. S. epidermidis is a particular concern for people with catheters or other surgical implants because it is known to form biofilms that grow on these devices. Being part of the normal skin microbiota, S. epidermidis is a frequent contaminant of specimens sent to the diagnostic laboratory.
Omphalitis of newborn is the medical term for inflammation of the umbilical cord stump in the neonatal newborn period, most commonly attributed to a bacterial infection. Typically immediately after an infant is born, the umbilical cord is cut with a small remnant left behind. Normally the stump separates from the skin within 3–45 days after birth. A small amount of pus-like material is commonly seen at the base of the stump and can be controlled by keeping the stump open to air to dry. Certain bacteria can grow and infect the stump during this process and as a result significant redness and swelling may develop, and in some cases the infection can then spread through the umbilical vessels to the rest of the body. While currently an uncommon anatomical location for infection in the newborn in the United States, it has caused significant morbidity and mortality both historically and in areas where health care is less readily available. In general, when this type of infection is suspected or diagnosed, antibiotic treatment is given, and in cases of serious complications surgical management may be appropriate.

Skin flora, also called skin microbiota, refers to microbiota that reside on the skin, typically human skin.

A staphylococcal infection or staph infection is an infection caused by members of the Staphylococcus genus of bacteria.

Bullous impetigo is a bacterial skin infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus that results in the formation of large blisters called bullae, usually in areas with skin folds like the armpit, groin, between the fingers or toes, beneath the breast, and between the buttocks. It accounts for 30% of cases of impetigo, the other 70% being non-bullous impetigo.

Streptococcal intertrigo is a skin condition that is secondary to a streptococcal bacterial infection. It is often seen in infants and young children and can be characterized by a fiery-red color of the skin, foul odor with an absence of satellite lesions, and skin softening in the neck, armpits or folds of the groin. Newborn children and infants commonly develop intertrigo because of physical features such as deep skin folds, short neck, and flexed posture. Prompt diagnosis by a medical professional and treatment with topical and/or oral antibiotics can effectively relieve symptoms.

Staphylococcus is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical (cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. Staphylococcus species are facultative anaerobic organisms.
Antimicrobial copper-alloy touch surfaces can prevent frequently touched surfaces from serving as reservoirs for the spread of pathogenic microbes. This is especially true in healthcare facilities, where harmful viruses, bacteria, and fungi colonize and persist on doorknobs, push plates, railings, tray tables, tap (faucet) handles, IV poles, HVAC systems, and other equipment. These microbes can sometimes survive on surfaces for more than 30 days.
A biomimetic antifouling coating is a treatment that prevents the accumulation of marine organisms on a surface. Typical antifouling coatings are not biomimetic but are based on synthetic chemical compounds that can have deleterious effects on the environment. Prime examples are tributyltin compounds, which are components in paints to prevent biofouling of ship hulls. Although highly effective at combatting the accumulation of barnacles and other problematic organisms, organotin-containing paints are damaging to many organisms and have been shown to interrupt marine food chains.
Biofilm formation occurs when free floating microorganisms attach themselves to a surface. Although there are some beneficial uses of biofilms, they are generally considered undesirable, and means of biofilm prevention have been developed. Biofilms secrete extracellular polymeric substance that provides a structural matrix and facilitates adhesion for the microorganisms; the means of prevention have thus concentrated largely on two areas: killing the microbes that form the film, or preventing the adhesion of the microbes to a surface. Because biofilms protect the bacteria, they are often more resistant to traditional antimicrobial treatments, making them a serious health risk. For example, there are more than one million cases of catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTI) reported each year, many of which can be attributed to bacterial biofilms. There is much research into the prevention of biofilms.
Antivirulence is the concept of blocking virulence factors. In regards to bacteria, the idea is to design agents that block virulence rather than kill bacteria en masse, as the current regime results in much more selective pressure.










