
Deserts and xeric shrublands are a biome defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. Deserts and xeric shrublands form the largest terrestrial biome, covering 19% of Earth's land surface area. Ecoregions in this habitat type vary greatly in the amount of annual rainfall they receive, usually less than 250 millimetres (10 in) annually except in the margins. Generally evaporation exceeds rainfall in these ecoregions. Temperature variability is also diverse in these lands. Many deserts, such as the Sahara, are hot year-round, but others, such as East Asia's Gobi, become quite cold during the winter.

The Great Basin Desert is part of the Great Basin between the Sierra Nevada and the Wasatch Range. The desert is a geographical region that largely overlaps the Great Basin shrub steppe defined by the World Wildlife Fund, and the Central Basin and Range ecoregion defined by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and United States Geological Survey. It is a temperate desert with hot, dry summers and snowy winters. The desert spans large portions of Nevada and Utah, and extends into eastern California. The desert is one of the four biologically defined deserts in North America, in addition to the Mojave, Sonoran, and Chihuahuan Deserts.

Artemisia tridentata, commonly called big sagebrush, Great Basin sagebrush or simply sagebrush, is an aromatic shrub from the family Asteraceae.

The ecology of California can be understood by dividing the state into a number of ecoregions, which contain distinct ecological communities of plants and animals in a contiguous region. The ecoregions of California can be grouped into four major groups: desert ecoregions, Mediterranean ecoregions, forested mountains, and coastal forests.

Rangelands are grasslands, shrublands, woodlands, wetlands, and deserts that are grazed by domestic livestock or wild animals. Types of rangelands include tallgrass and shortgrass prairies, desert grasslands and shrublands, woodlands, savannas, chaparrals, steppes, and tundras. Rangelands do not include forests lacking grazable understory vegetation, barren desert, farmland, or land covered by solid rock, concrete, or glaciers.
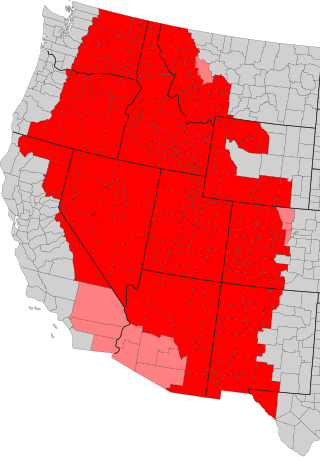
The Intermountain West, or Intermountain Region, is a geographic and geological region of the Western United States. It is located between the Rocky Mountain Front on the east and the Cascade Range and Sierra Nevada on the west.

The Okanagan Desert is the common name for a semi-arid shrubland located in the southern region of the Okanagan Valley in British Columbia and Washington. It is centred around the city of Osoyoos and is the only semi-arid shrubland in Canada. Part of this ecosystem is referred to as the Nk'mip Desert by the Osoyoos Indian Band, though it is identical to the shrublands elsewhere in the region. To the northwest of this area lies an arid shrubland near Kamloops.

The Blue Mountains ecoregion is a Level III ecoregion designated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the Pacific Northwest, mainly in the state of Oregon, with small areas over the state border in Idaho and southeastern Washington. It is also contiguous with the World Wildlife Fund's Blue Mountain forests ecoregion.

The South Central Rockies forests is a temperate coniferous forest ecoregion of the United States located mainly in Wyoming, Idaho, and Montana. It has a considerably drier climate than the North Central Rockies forest.

The Wyoming Basin shrub steppe ecoregion, within the deserts and xeric shrublands biome, is a shrub steppe in the northwestern United States.

The Kazakh semi-desert is an ecoregion in the deserts and xeric shrublands biome, located in Kazakhstan. The climate is semi-arid and continental, with a total annual precipitation of 160 millimetres (6.3 in), and mean temperatures in January averaging −15 °C (5 °F) and in July 23 °C (73 °F). It is a transitional area between the steppes and the deserts of Central Asia and supports flora found in both biomes, predominantly grasses, particularly Stipa species, and shrubs such as Artemisia species. A number of mammals and birds are found in this ecoregion but the habitat is threatened by overgrazing and fragmentation from human encroachment. However, a recent reduction in livestock numbers in Kazakhstan is allowing the native plants a greater opportunity to regenerate.

The Central Asian northern desert is an ecoregion in the deserts and xeric shrublands biome, located in the Central Asian countries of Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan. The annual precipitation ranges from 100 to 150 mm, the winters are cold at −10 to −15 °C and the summers hot at around 25 °C (77 °F). There are a range of habitat types including salt flats, clay desert, rocky desert and some sand desert. The vegetation consists of scanty xeric shrubs including Artemisia and Salsola. The fauna is varied, as well as mammals and birds, there are a large number of reptiles and many species of invertebrate. Some protected areas are included in this ecoregion but other parts are being degraded by conversion to farmland, overgrazing and poaching.

The Great Basin montane forests is an ecoregion of the Temperate coniferous forests biome, as designated by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF).

Artemisia tripartita is a species of flowering plant in the aster family known by the common name threetip sagebrush. It is native to western North America from British Columbia to Nevada and Montana to Colorado. It covers about 8.4 million acres of the Rocky Mountains and Great Basin.

The Eastern Anatolian montane steppe is a temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion. It is located in the Armenian Highlands, covering parts of eastern Turkey, Armenia, Azerbaijan, southern Georgia, and northwestern Iran.

The Colorado Plateau shrublands is an ecoregion of deserts and xeric shrublands in the Western United States.

Okanagan dry forests is a temperate coniferous forest ecoregion in the Pacific Northwest of North America, as defined by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) categorization system. It is closely associated with the Okanagan region of British Columbia and Washington. Only 20% of the ecosystem is still intact, and continues to be under threat for preservation due to land clearing and urban expansion, alongside the increasing threats of fire and extreme weather due to climate change.

The Azerbaijan shrub desert and steppe is a deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion in western Asia. It lies in the lowlands west of the Caspian Sea, and covers portions of Azerbaijan, Georgia, and Iran.

The Mesopotamian shrub desert is a deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion in Western Asia. It extends across portions of Israel, Jordan, Syria, Iraq, and Iran.




















