The Kara Sea is a marginal sea, separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and from the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya archipelago. Ultimately the Kara, Barents and Laptev Seas are all extensions of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia.

The Barents Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian territorial waters. It was known earlier among Russians as the Northern Sea, Pomorsky Sea or Murman Sea ; the current name of the sea is after the historical Dutch navigator Willem Barentsz.

The Laptev Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, the Taimyr Peninsula, Severnaya Zemlya and the New Siberian Islands. Its northern boundary passes from the Arctic Cape to a point with co-ordinates of 79°N and 139°E, and ends at the Anisiy Cape. The Kara Sea lies to the west, the East Siberian Sea to the east.

The East Siberian Sea is a marginal sea in the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the Arctic Cape to the north, the coast of Siberia to the south, the New Siberian Islands to the west and Cape Billings, close to Chukotka, and Wrangel Island to the east. This sea borders on the Laptev Sea to the west and the Chukchi Sea to the east.

The Chukchi Sea, sometimes referred to as the Chuuk Sea, Chukotsk Sea or the Sea of Chukotsk, is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is bounded on the west by the Long Strait, off Wrangel Island, and in the east by Point Barrow, Alaska, beyond which lies the Beaufort Sea. The Bering Strait forms its southernmost limit and connects it to the Bering Sea and the Pacific Ocean. The principal port on the Chukchi Sea is Uelen in Russia. The International Date Line crosses the Chukchi Sea from northwest to southeast. It is displaced eastwards to avoid Wrangel Island as well as the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug on the Russian mainland.

Arctica, or Arctida was an ancient continent which formed approximately 2.565 billion years ago in the Neoarchean era. It was made of Archaean cratons, including the Siberian Craton, with its Anabar/Aldan shields in Siberia, and the Slave, Wyoming, Superior, and North Atlantic cratons in North America. Arctica was named by Rogers 1996 because the Arctic Ocean formed by the separation of the North American and Siberian cratons. Russian geologists writing in English call the continent "Arctida" since it was given that name in 1987, alternatively the Hyperborean craton, in reference to the hyperboreans in Greek mythology.

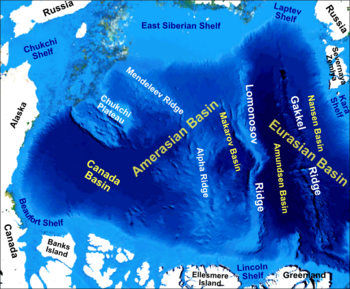
The Lomonosov Ridge is an unusual underwater ridge of continental crust in the Arctic Ocean. It spans 1,800 kilometres (1,100 mi) between the New Siberian Islands over the central part of the ocean to Ellesmere Island of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The ridge divides the Arctic Basin into the Eurasian Basin and the Amerasian Basin. The width of the Lomonosov Ridge varies from 60 to 200 kilometres. It rises 3,300 to 3,700 metres above the 4,200-metre (13,800 ft) deep seabed. The minimum depth of the ocean above the ridge is less than 400 metres (1,300 ft). Slopes of the ridge are relatively steep, broken up by canyons, and covered with layers of silt. It is an aseismic ridge.

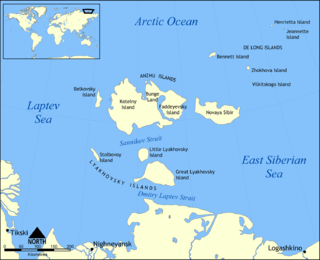
Kotelny Island is part of the Anzhu Islands subgroup of the New Siberian Islands located between the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea in the Russian Arctic. It is administratively and municipally part of Bulunsky District of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia).
Exploration for petroleum in the Arctic is expensive and challenging both technically and logistically. In the offshore, sea ice can be a major factor. There have been many discoveries of oil and gas in the several Arctic basins that have seen extensive exploration over past decades but distance from existing infrastructure has often deterred development. Development and production operations in the Arctic offshore as a result of exploration have been limited, with the exception of the Barents and Norwegian seas. In Alaska, exploration subsequent to the discovery of the Prudhoe Bay oilfield has focussed on the onshore and shallow coastal waters.
The Arctic consists of land, internal waters, territorial seas, exclusive economic zones (EEZs) and international waters above the Arctic Circle. All land, internal waters, territorial seas and EEZs in the Arctic are under the jurisdiction of one of the eight Arctic coastal states: Canada, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and the United States. International law regulates this area as with other portions of Earth.

The Mendeleev Ridge is a broad ridge in the Arctic Ocean from the East Siberian Sea area of the Siberian Shelf to the central areas of the ocean. It is attached to the Alpha Ridge of the Amerasian Basin. It is named after Dmitri Mendeleyev.The Ridge was discovered in 1948 by Soviet high latitude expeditions. The name was approved by the Sub-Committee on Geographical Names and Nomenclature of Ocean Bottom Features in April 1987.
The continental shelf of Russia is a continental shelf adjacent to the Russian Federation. Geologically, the extent of the shelf is defined as the entirety of the continental shelves adjacent to Russia's coast. In international law, however, the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea more narrowly defines the extent of the shelf as the seabed and subsoil of the submarine areas over which a state exercises sovereign rights.

The Eurasian Basin, or Eurasia Basin, is one of the two major basins into which the Arctic Basin of the Arctic Ocean is split by the Lomonosov Ridge. The Eurasia Basin may be seen as an extension of the North Atlantic Basin through Fram Strait. It is further split by the mid-ocean Gakkel Ridge into the Nansen Basin and the Amundsen Basin. The latter basin is the deepest one of the Arctic Ocean and the geographic North Pole is located there.

The Amerasia Basin, or Amerasian Basin, is one of the two major basins from which the Arctic Ocean can be subdivided. The triangular-shaped Amerasia Basin broadly extends from the Canadian Arctic Islands to the East Siberian Sea, and from Alaska to the Lomonosov Ridge. The basin can be further subdivided based on bathymetric features; these include the Canada Basin, the Makarov Basin, the Podvodnikov Basin, the Alpha-Mendeleev Ridge, and the Chukchi Plateau.

The Arctic realm is one of the planet's twelve marine realms, as designated by the WWF and Nature Conservancy. It includes the coastal regions and continental shelves of the Arctic Ocean and adjacent seas, including the Arctic Archipelago, Hudson Bay, and the Labrador Sea of northern Canada, the seas surrounding Greenland, the northern and eastern coasts of Iceland, and the eastern Bering Sea.

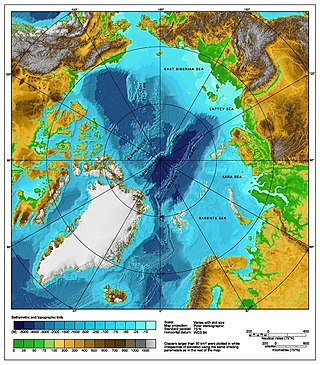
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately 14,060,000 km2 (5,430,000 sq mi) and is known as one of the coldest of oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Mediterranean Sea. It has also been described as an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It is also seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing World Ocean.
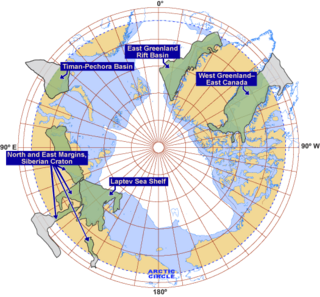
The Barents Basin or East Barents Basin is a sedimentary basin underlying the eastern half of the Barents Sea. Lying off Russia on the continental shelf between the Kola Peninsula and Novaya Zemlya, it produces oil and gas.