
Medieval fortification refers to medieval military methods that cover the development of fortification construction and use in Europe, roughly from the fall of the Western Roman Empire to the Renaissance. During this millennium, fortifications changed warfare, and in turn were modified to suit new tactics, weapons and siege techniques.

A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or by well-prepared assault. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static, defensive position. Consequently, an opportunity for negotiation between combatants is common, as proximity and fluctuating advantage can encourage diplomacy.

A Roman siege tower or breaching tower is a specialized siege engine, constructed to protect assailants and ladders while approaching the defensive walls of a fortification. The tower was often rectangular with four wheels with its height roughly equal to that of the wall or sometimes higher to allow archers or crossbowmen to stand on top of the tower and shoot arrows or quarrels into the fortification. Because the towers were wooden and thus flammable, they had to have some non-flammable covering of iron or fresh animal skins.

A battering ram is a siege engine that originated in ancient times and was designed to break open the masonry walls of fortifications or splinter their wooden gates. In its simplest form, a battering ram is just a large, heavy log carried by several people and propelled with force against an obstacle; the ram would be sufficient to damage the target if the log were massive enough and/or it were moved quickly enough. Later rams encased the log in an arrow-proof, fire-resistant canopy mounted on wheels. Inside the canopy, the log was swung from suspensory chains or ropes.

A trebuchet is a type of catapult that uses a rotating arm with a sling attached to the tip to launch a projectile. It was a common powerful siege engine until the advent of gunpowder. The design of a trebuchet allows it to launch projectiles of greater weights and further distances than that of a traditional catapult.

A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick city walls and other fortifications in siege warfare. Some are immobile, constructed in place to attack enemy fortifications from a distance, while others have wheels to enable advancing up to the enemy fortification. There are many distinct types, such as siege towers that allow foot soldiers to scale walls and attack the defenders, battering rams that damage walls or gates, and large ranged weapons that attack from a distance by launching projectiles. Some complex siege engines were combinations of these types.

A sickle, bagging hook, reaping-hook or grasshook is a single-handed agricultural tool designed with variously curved blades and typically used for harvesting or reaping grain crops, or cutting succulent forage chiefly for feeding livestock. Falx was a synonym, but was later used to mean any of a number of tools that had a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge.

Early thermal weapons, which used heat or burning action to destroy or damage enemy personnel, fortifications or territories, were employed in warfare during the classical and medieval periods.
Roman siege engines were, for the most part, adapted from Hellenistic siege technology. Relatively small efforts were made to develop the technology; however, the Romans brought an unrelentingly aggressive style to siege warfare that brought them repeated success. Up to the first century BC, the Romans utilized siege weapons only as required and relied for the most part on ladders, towers and rams to assault a fortified town. Ballistae were also employed, but held no permanent place within a legion's roster, until later in the republic, and were used sparingly. Julius Caesar took great interest in the integration of advanced siege engines, organizing their use for optimal battlefield efficiency.

The falx was a weapon with a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge used by the Thracians and Dacians. The name was later applied to a siege hook used by the Romans.
Vallum is either the whole or a portion of the fortifications of a Roman camp. The vallum usually comprised an earthen or turf rampart (Agger) with a wooden palisade on top, with a deep outer ditch (fossa). The name is derived from vallus, and properly means the palisade which ran along the outer edge of the top of the agger, but is usually used to refer to the whole fortification.

The sambuca was a ship-borne siege engine which was invented by Heracleides of Tarentum and was first used unsuccessfully by Marcus Claudius Marcellus during the Roman siege of Syracuse in 213 BC.

Major innovations in the history of weapons have included the adoption of different materials – from stone and wood to different metals, and modern synthetic materials such as plastics – and the developments of different weapon styles either to fit the terrain or to support or counteract different battlefield tactics and defensive equipment.

The siege of Yodfat was a 47-day siege by Roman forces of the Jewish town of Yodfat which took place in 67 CE, during the Great Revolt. Led by Roman General Vespasian and his son Titus, both future emperors, the siege ended with the sacking of the town, the deaths of most of its inhabitants and the enslavement of the rest. It was the second bloodiest battle of the revolt, surpassed only by the Siege of Jerusalem, and the longest except for Jerusalem and Masada. The siege was chronicled by Josephus, who had personally commanded the Jewish forces at Yodfat and was subsequently captured by the Romans.

A hook is a tool consisting of a length of material, typically metal, that contains a portion that is curved/bent back or has a deeply grooved indentation, which serves to grab, latch or in any way attach itself onto another object. The hook's design allows traction forces to be relayed through the curved/indented portion to and from the proximal end of the hook, which is either a straight shaft or a ring for attachment to a thread, rope or chain, providing a reversible attachment between two objects.

The Ming dynasty continued to improve on gunpowder weapons from the Yuan and Song dynasties as part of its military. During the early Ming period larger and more cannons were used in warfare. In the early 16th century Turkish and Portuguese breech-loading swivel guns and matchlock firearms were incorporated into the Ming arsenal. In the 17th century Dutch culverin were incorporated as well and became known as hongyipao. At the very end of the Ming dynasty, around 1642, Chinese combined European cannon designs with indigenous casting methods to create composite metal cannons that exemplified the best attributes of both iron and bronze cannons. While firearms never completely displaced the bow and arrow, by the end of the 16th century more firearms than bows were being ordered for production by the government, and no crossbows were mentioned at all.
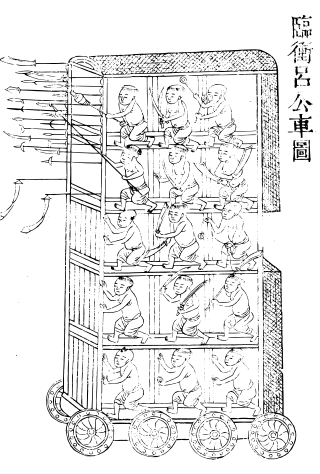
This is an overview of Chinese siege weapons.
The siege of Petra was fought in 550 AD, between the Byzantines under general Bessas, and the Sasanian Persian garrison of Petra in the buffer state of Lazica. The strategic fortress had previously been held by the Byzantines before it was seized in 541 by the Sasanian king Khosrow I, and his Lazi allies. This conquest gave the Sassanian Empire access to the Black Sea and marked the beginning of the Lazic War. After a failed attempt to recapture Petra in 549, the Byzantine emperor Justinian I sent an army under Bessas to retake the fortress. The Byzantine historian Procopius described the resulting siege in vivid detail.

Warfare in Sumer predominantly consisted of small-scale conflicts between nearby city-states. Sumerian armies consisted of bronze-armoured soldiers armed with various weapons, including spears, swords and sickle-swords, engaging each other in phalanx-like formations. When besieging cities, battering rams and sappers would be used to breach the defences; on the open battlefield, chariots were also used. Most wars were fought because of inter-city rivalries, or for wealth, resources, and prestige. Military victories were later glorified in Mesopotamian art — a major source of historical information.
Siegecraft originated in Ancient Greece. This type of siege originated from the moment in which the stage of the mere siege was surpassed by an exceptional development of military techniques, which were hardly taken any further during the Middle Ages, until the invention of firearms. The importance of siege techniques was due to the increase in the strategic role of the city to the detriment of the territory in the overall defense of the polis.















