Savaiʻi is the largest and highest island both in Samoa and in the Samoan Islands chain. The island is also the sixth largest in Polynesia, behind the three main islands of New Zealand and the Hawaiian Islands of Hawaii and Maui.

Palauli is a district and village of Samoa, with a population of 9,300. It consists of two sections on the southern side of Savai'i. The capital is Vailoa which is also referred to as Vailoa i Palauli.

The production of renewable energy in Scotland is a topic that has come to the fore in technical, economic, and political terms during the opening years of the 21st century. The natural resource base for renewable energy is high by European, and even global standards, with the most important potential sources being wind, wave, and tide. Renewables produced the equivalent of 97.4% of Scotland's electricity consumption in 2020, mostly from the country's wind power.

Wind power became a significant energy source within South Australia over the first two decades of the 21st century. In 2015, there was an installed capacity of 1,475 MW, which accounted for 34% of electricity production in the state. This accounted for 35% of Australia's installed wind power capacity.</ref> In 2021, there was an installed capacity of 2052.95 MW, which accounted for 42.1% of the electricity production in the state in 2020.
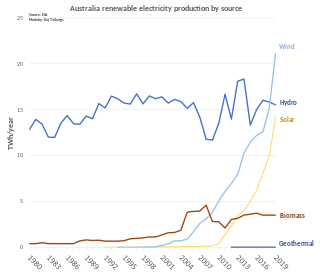
Renewable energy in Australia includes wind power, hydroelectricity, solar PV, heat pumps, geothermal, wave and solar thermal energy.

Fa'amatai is the indigenous political ('chiefly') system of Samoa, central to the organization of Samoan society. It is the traditional indigenous form of governance in both Samoas, comprising American Samoa and the Independent State of Samoa. The term comprises the prefix fa'a and the word matai.

Hydroelectric power in New Zealand has been a part of the country's energy system for over 100 years and continues to provide more than half of the country's electricity needs. Hydroelectricity is the primary source of renewable energy in New Zealand. Power is generated the most in the South Island and is used most in the North Island.
Renewable energy in Tuvalu is a growing sector of the country's energy supply. Tuvalu has committed to sourcing 100% of its electricity from renewable energy. This is considered possible because of the small size of the population of Tuvalu and its abundant solar energy resources due to its tropical location. It is somewhat complicated because Tuvalu consists of nine inhabited islands. The Tuvalu National Energy Policy (TNEP) was formulated in 2009, and the Energy Strategic Action Plan defines and directs current and future energy developments so that Tuvalu can achieve the ambitious target of 100% renewable energy for power generation by 2020. The program is expected to cost 20 million US dollars and is supported by the e8, a group of 10 electric companies from G8 countries. The Government of Tuvalu worked with the e8 group to develop the Tuvalu Solar Power Project, which is a 40 kW grid-connected solar system that is intended to provide about 5% of Funafuti’s peak demand, and 3% of the Tuvalu Electricity Corporation's annual household consumption.

Samauga is a village on the central north coast of Savai'i island in Samoa. It is situated on the central north coast of the island in the district of Gagaʻifomauga and the electoral district of Gagaʻifomauga 2. The population is 373.

The electricity sector in Sri Lanka has a national grid which is primarily powered by hydroelectric power and thermal power, with sources such as photovoltaics and wind power in early stages of deployment. Although potential sites are being identified, other power sources such as geothermal, nuclear, solar thermal and wave power are not used in the power generation process for the national grid.

India is 5th globally for installed hydroelectric power capacity. As of 31 March 2020, India's installed utility-scale hydroelectric capacity was 46,000 MW, or 12.3% of its total utility power generation capacity. Additional smaller hydroelectric power units with a total capacity of 4,683 MW have been installed. India's hydroelectric power potential is estimated at 148,700 MW at 60% load factor. In the fiscal year 2019–20, the total hydroelectric power generated in India was 156 TWh with an average capacity factor of 38.71%.

General elections were held in Samoa on 4 March 2011, in which voters elected 49 members to the Legislative Assembly for its 15th term. Unlike most neighbouring countries in the Pacific, Samoa has established party politics. The major contesting parties were that of incumbent Prime Minister Tuila'epa Sa'ilele Malielegaoi, the Human Rights Protection Party (HRPP); and the Tautua Samoa Party (TSP), a newly formed opposition party which included candidates from recently disbanded parties like the Samoa Party.

The Lower Se San 2 Dam is a hydroelectric dam under development on the Se San River in Stung Treng Province, northeastern Cambodia. The Se San River is a major tributary of the Mekong River. The dam site is located 25 kilometres (16 mi) east of the provincial capital, also named Stung Treng. The first turbine began producing electricity in November 2017. The dam was officially opened on December 18, 2018.
Bethlehem Hydro owns and operates two small hydro power plants situated in the Dihlabeng Local Municipality in the Free State province of South Africa. The scheme utilizes the water supplied to South Africa by the Lesotho Highlands Water Project, which releases water into the As River via a tunnel outlet near the town of Clarens. South Africa has limited potential for hydro energy due to low average annual rainfall making projects like Bethlehem Hydro rare. The project was identified in 1999 and developed by NuPlanet Project Development. The two power stations in the scheme will cut back carbon dioxide emissions by 33,000 tons per year by reducing the demand for traditional fossil-fuel power stations.

Yeo Bee Yin is a Malaysian politician from the Democratic Action Party (DAP), a component party of the Pakatan Harapan (PH) opposition coalition. She served as the Minister of Energy, Science, Technology, Environment and Climate Change in the PH administration under former Prime Minister Mahathir Mohamad from July 2018 to the collapse of the PH administration in February 2020. She has served as the Member of Parliament (MP) for Bakri since May 2018. She also served as Member of the Selangor State Legislative Assembly (MLA) for Damansara Utama from May 2013 to May 2018.

Most of Kenya's electricity is generated by renewable energy sources. On 13 December 2019, Kenya brought online a new 50 megawatt (MW) solar plant in Turkana at the cost of $129 million, bringing her renewable energy to 90% of its power mix. With an installed power capacity of 2,336 MW, Kenya generates 870 MW hydroelectric power, 706 MW geothermal power, 253.5 MW thermal power and the rest from other sources. Kenya is the largest geothermal energy producer in Africa and was also the first geothermal-producing state in Africa when Olkaria I Power Station was commissioned in 1981, generating 45 MW. Seventy three percent (73%) of Kenyan households have electricity access. Currently, Kenya is building Olkaria I Unit 6 which will produce an additional 83 MW to the grid making it the 7th largest geothermal power producer in the world. Additionally, Kenya has the largest wind farm project in Africa with the Lake Turkana Wind Project Power Project. In March 2011, Kenya became the first country in Africa to open a carbon exchange, presenting 17 projects for registration to the U.N. Kyoto Protocol’s Clean Development Mechanism executive board. Kenya is also a signatory to the Paris Agreement and targets to reduce carbon emissions by 30% below business as usual by 2030 as determined in the Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC). The Renewable Energy Directorate under the Ministry of Energy is responsible for research and development of renewable energy technologies.

Renewable energy in Afghanistan includes biomass, hydropower, solar, and wind power. Afghanistan is a landlocked country surrounded by five other countries. With a population of less than 35 million people, it is one of the lowest energy consuming countries in relation to a global standing. It holds a spot as one of the countries with a smaller ecological footprint. Hydropower is currently the main source of renewable energy due to Afghanistan's geographical location. Its large mountainous environment facilitates the siting of hydroelectric dams and other facets of hydro energy.

The Afulilo Dam is a gravity dam on the Afulilo River about 3 km (1.9 mi) south of Ta'elefaga in the district of Va'a-o-Fonoti on Upolu island of Samoa. The primary purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power generation and it supports a 4 megawatts (5,400 hp) power station. It is the largest hydroelectric power station by installed capacity in Samoa. First studied in 1980, construction on the project began in 1990 and the power station was commissioned in 1993. Funding for the US$26.6 million project was provided by the World Bank, Asian Development Bank, International Development Association, European Investment Bank, and European Economic Community loans and grants.
Concept of smart villages is a global modern approach for off-grid communities. Vision behind this concept is to assist the policy makers, donors and socio-economic planner for rural electrification worldwide.
Myanmar had a total primary energy supply (TPES) of 16.57 Mtoe in 2013. Electricity consumption was 8.71 TWh. 65% of the primary energy supply consists of biomass energy, used almost exclusively (97%) in the residential sector. Myanmar’s energy consumption per capita is one of the lowest in Southeast Asia due to the low electrification rate and a widespread poverty. An estimated 65% of the population is not connected to the national grid. Energy consumption is growing rapidly, however, with an average annual growth rate of 3.3% from 2000 to 2007.