Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ; two smaller, inhabited islands ; and several smaller, uninhabited islands, including the Aleipata Islands. Samoa is located 64 km (40 mi) west of American Samoa, 889 km (552 mi) northeast of Tonga, 1,152 km (716 mi) northeast of Fiji, 483 km (300 mi) east of Wallis and Futuna, 1,151 km (715 mi) southeast of Tuvalu, 519 km (322 mi) south of Tokelau, 4,190 km (2,600 mi) southwest of Hawaii, and 610 km (380 mi) northwest of Niue. The capital city is Apia. The Lapita people discovered and settled the Samoan Islands around 3,500 years ago. They developed a Samoan language and Samoan cultural identity.

Politics of Samoa takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic state whereby the Prime Minister of Samoa is the head of government. Existing alongside the country's Western-styled political system is the fa'amatai chiefly system of socio-political governance and organisation, central to understanding Samoa's political system.

The Mau was a non-violent movement for Samoan independence from colonial rule during the first half of the 20th century. Mau means ‘resolute’ or ‘resolved’ in the sense of ‘opinion’, ‘unwavering’, ‘to be decided’, or ‘testimony’; also denoting ‘firm strength’ in Samoan. The motto for the Mau were the words Samoa mo Samoa. Similarly in Hawaiian Mau means to strive or persevere, and is often linked with Hawaiian poetry relating to independence and sovereignty struggles.

Savaiʻi is the largest and highest island both in Samoa and in the Samoan Islands chain. The island is also the sixth largest in Polynesia, behind the three main islands of New Zealand and the Hawaiian Islands of Hawaii and Maui.

Falealupo is a village in Samoa situated at the west end of Savai'i island 20 miles (32 km) from the International Date Line used until 29 December 2011. The village has two main settlements, Falealupo-Uta, situated inland by the main island highway and Falealupo-Tai, situated by the sea. The road to the coastal settlement is about 9 km, most of it unsealed, from the main highway. The village's population is 545.

Samoa is made up of eleven itūmālō. These are the traditional eleven districts that were established well before European arrival. Each district has its own constitutional foundation (faavae) based on the traditional order of title precedence found in each district's faalupega.

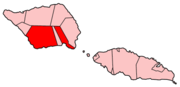
Palauli is a district and village of Samoa, with a population of 9,300. It consists of two sections on the southern side of Savai'i. The capital is Vailoa which is also referred to as Vailoa i Palauli.

Satupaʻitea is a large village district with four sub-villages on the south east coast of Savaiʻi Island in Samoa.
Dr Asiata Alaelua Va'alepa Sale'imoa Va'ai was a Samoan politician and lawyer. He was Member of Parliament for the territorial constituency of Satupa'itea and the leader of the Samoan United Independents Political Party and Samoan Democratic United Party.

Neiafu is a village on the island of Savai'i in Samoa. It is in the Alataua Sisifo electoral district and located at the south west corner of the island. The population of Neiafu Uta is 601 and Neiafu Tai is 307.

The Samoa national rugby sevens team, referred to as Samoa Sevens or Manu Samoa 7s, competes in the annual World Rugby Sevens Series. Representing the polynesian country of Samoa, with a population of about 202,000, the team competes against some of the wealthiest countries in the world. The Samoa sevens team is overseen by the Samoa Rugby Football Union, which oversees all of rugby union in Samoa.

Uale Mai Vala is a retired rugby union player who played for the country's national teams, Manu Samoa and Samoa Sevens. He is a former captain of the Samoa Sevens team which represent Samoa internationally in the IRB Sevens World Series. He was at the time of his retirement sevens rugby's most capped player, and Mai is considered one of the greats in the international sport. Mai has been one of the top points scorers in the IRB World Sevens Series.
Satapuala is a village situated on the north west coast Upolu island in Samoa. The village is part of A'ana Alofi 4 Electoral Constituency which forms part of the larger political district A'ana. It has a population of 1963.

Archaeology of Samoa began with the first systematic survey of archaeological remains on Savai'i island by Jack Golson in 1957. Since then, surveys and studies in the rest of Samoa have uncovered major findings of settlements, stone and earth mounds including star mounds, Lapita pottery remains and pre-historic artifacts.
Vailele is a village situated on the central north coast of Upolu island in Samoa.
Sili is a village on the south side of Savai'i island in Samoa. Sili is situated inland, unlike most villages in Samoa which are settlements by the sea. The village lies within the electoral constituency of Palauli 1. The population is 1071.

Piula Theological College is a Methodist training institution in Samoa. It was established in 1868 in Lufilufi on the north coast of Upolu island after its initial beginnings in 1859 at Satupa'itea on the south coast of Savai'i island. The Methodist Mission in Samoa purchased the land at the Methodist leaning district and later named their training center Piula Theological College. The name Piula is a transliteration of the biblical name Beulah which means married.

General elections were held in Western Samoa on 24 February 1973. All candidates ran as independents and voting was restricted to matai and citizens of European origin, with the matai electing 45 MPs and Europeans two. Following the election, Fiame Mata'afa became Prime Minister for a second term, having previously held the office between 1959 and 1970.

Vailoatai is a village in southwestern Tutuila, the main island of American Samoa. It is located on the eastern end of Leone Bay. The village is known for its beautiful malae nested along the island's rugged southern coast, lined by the fale tali mālō of its village chiefs.