
The Arctic National Wildlife Refuge is a national wildlife refuge in northeastern Alaska, United States. It consists of 19,286,722 acres (78,050.59 km2) in the Alaska North Slope region. It is the largest national wildlife refuge in the country, slightly larger than the Yukon Delta National Wildlife Refuge. The refuge is administered from offices in Fairbanks. ANWR includes a large variety of species of plants and animals, such as polar bears, grizzly bears, black bears, moose, caribou, wolves, eagles, lynx, wolverine, marten, beaver and migratory birds, which rely on the refuge.

An oil platform, offshore platform, or offshore drilling rig is a large structure with facilities for well drilling to explore, extract, store, and process petroleum and natural gas that lies in rock formations beneath the seabed. Many oil platforms will also contain facilities to accommodate their workforce. Most commonly, oil platforms engage in activities on the continental shelf, though they can also be used in lakes, inshore waters, and inland seas. Depending on the circumstances, the platform may be fixed to the ocean floor, consist of an artificial island, or float. Remote subsea wells may also be connected to a platform by flow lines and by umbilical connections. These sub-sea solutions may consist of one or more subsea wells or of one or more manifold centres for multiple wells.

The Beaufort Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of the Northwest Territories, the Yukon, and Alaska, and west of Canada's Arctic islands. The sea is named after Sir Francis Beaufort, a hydrographer. The Mackenzie River, the longest in Canada, empties into the Canadian part of the Beaufort Sea west of Tuktoyaktuk, which is one of the few permanent settlements on the sea's shores.

Chukchi Sea, sometimes referred to as the Chuuk Sea, Chukotsk Sea or the Sea of Chukotsk, is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is bounded on the west by the Long Strait, off Wrangel Island, and in the east by Point Barrow, Alaska, beyond which lies the Beaufort Sea. The Bering Strait forms its southernmost limit and connects it to the Bering Sea and the Pacific Ocean. The principal port on the Chukchi Sea is Uelen in Russia. The International Date Line crosses the Chukchi Sea from northwest to southeast. It is displaced eastwards to avoid Wrangel Island as well as the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug on the Russian mainland.

Hibernia is an oil field in the North Atlantic Ocean, approximately 315 kilometres (196 mi) east-southeast of St. John's, Newfoundland, Canada, in 80 m of water.

CCGS Terry Fox is a Canadian Coast Guard heavy icebreaker. She was originally built by Burrard-Yarrows Corporation in Canada in 1983 as part of an Arctic drilling system developed by BeauDril, the drilling subsidiary of Gulf Canada Resources. After the offshore oil exploration in the Beaufort Sea ended in the early 1990s, she was first leased and then sold to the Canadian Coast Guard.
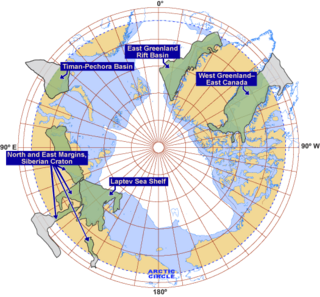
The exploration of the Arctic for petroleum is considered to be quite technically challenging. However, recent technological developments, as well as relatively high oil prices, have allowed for exploration. As a result, the region has received significant interest from the petroleum industry.

Offshore drilling is a mechanical process where a wellbore is drilled below the seabed. It is typically carried out in order to explore for and subsequently extract petroleum which lies in rock formations beneath the seabed. Most commonly, the term is used to describe drilling activities on the continental shelf, though the term can also be applied to drilling in lakes, inshore waters and inland seas.

Canada's early petroleum discoveries took place near population centres or along lines of penetration into the frontier.

Northstar Island is a 5-acre (20,000 m2) artificial island in the Beaufort Sea, 12 miles (19 km) northwest of Prudhoe Bay, Alaska and 6 miles (9.7 km) north of the Alaska coast. The island was created to develop the Northstar Oil Pool, which is located approximately 12,500 feet (3,800 m) below the seabed. The oil pool was discovered on January 30, 1984 by Royal Dutch Shell.

Vladimir Ignatyuk is a Russian icebreaking anchor handling tug supply vessel. She was built by Burrard-Yarrows Corporation in Canada in 1983 as Kalvik as part of an Arctic drilling system developed by BeauDril, the drilling subsidiary of Gulf Canada Resources. After the offshore oil exploration in the Beaufort Sea ended in the early 1990s, she was sold to the Canadian shipping company Fednav in 1997 and renamed Arctic Kalvik. In 2003, she was purchased by Murmansk Shipping Company and transferred to Russia.
Mount Elbert Methane Hydrate Site

Aiviq is an American icebreaking anchor handling tug supply vessel (AHTS) owned by Edison Chouest Offshore (ECO). The $200 million vessel was built in 2012 by North American Shipbuilding in Larose, Louisiana and LaShip in Houma, Louisiana. She has been chartered by Royal Dutch Shell to support oil exploration and drilling in the Chukchi Sea off Alaska. The primary task of the vessel is towing and laying anchors for drilling rigs, but she is also equipped for oil spill response.

Kulluk was an ice-strengthened drill barge that was used for oil exploration in the Arctic waters. She was constructed by Mitsui Engineering & Shipbuilding in Japan in 1983 and operated in the Canadian Arctic until 1993 when she was mothballed for over a decade. In 2005, she was purchased and extensively refurbished by Royal Dutch Shell for drilling off the Alaska North Slope.

Protests against Arctic drilling began in Seattle in 2015 in response to the news that the Port of Seattle authority made an agreement with Royal Dutch Shell to berth offshore drillships and semi-submersibles at the Port's Terminal 5 (T5) during the off-season of oil exploration in Alaskan waters of the Arctic. Hundreds of protesters took to Elliott Bay in kayaks, rafts, and other small boats, both as a demonstration and to interrupt docking of Shell's Polar Pioneer semi-submersible drilling vessel at Terminal 5. The waterborne demonstrators were dubbed kayaktivists by social and news media.
Robert LeMeur was an icebreaking platform supply vessel used to support oil exploration in the Beaufort Sea. Built in 1982 by Burrard Yarrows Corporation in Vancouver, British Columbia, she was part of the fleet of Canadian icebreakers, drillships and support vessels operated by Canadian Marine Drilling (Canmar), the drilling subsidiary of Dome Petroleum and later Amoco Canada Petroleum Company.
Miscaroo was an icebreaking anchor handling tug supply vessel built by Vancouver Shipyards for BeauDril, the drilling subsidiary of Gulf Canada Resources, in 1983. She was part of a fleet of Canadian icebreakers used to support offshore oil exploration in the Beaufort Sea. In the 1990s, the vessel was acquired by Canadian Marine Drilling (Canmar) and renamed Canmar Miscaroo. In 1998, she was purchased by Smit International and served in the Sakhalin oil fields as Smit Sakhalin until 2017 when the 34-year-old icebreaker was sold for scrapping in China.
Ikaluk is an icebreaking anchor handling tug supply vessel built by Nippon Kōkan K. K. Tsurumi Shipyard in Japan for BeauDril, the drilling subsidiary of Gulf Canada Resources, in 1983. She was part of a fleet of Canadian icebreakers used to support offshore oil exploration in the Beaufort Sea. In the 1990s, the vessel was acquired by Canadian Marine Drilling (Canmar) and renamed Canmar Ikaluk. In 1998, she was purchased by Smit International and served in the Sakhalin oil fields as Smit Sibu. Since 2009, she was owned by FEMCO Management and in 2012 was given back her original name. Ikaluk was sold to China in February 2018 and later renamed Beijing Ocean Leader.

Kigoriak is a Russian icebreaking anchor handling tug supply vessel. Built by Saint John Shipbuilding & Dry Dock Company for Canadian Marine Drilling (Canmar) in 1979 as Canmar Kigoriak, she was the first commercial icebreaking vessel developed to support offshore oil exploration in the Beaufort Sea.
Tagiuk Provider, formerly Arctic Endeavor, is a 205 ft (62 m) 1500-ton ice-class flat-topped deck cargo barge adapted to being a clam-shell crane scoop mining platform for placer gold mining in the Bering Sea off Nome, Alaska, United States. The barge, a gold dredge, is owned by Tagiuk Gold, which previously ran scuba-diver-operated suction dredges for seafloor gold mining in the area. Tagiuk Gold is run by miner Andrew Lee, whose business running the barge is partially crowdfunded. Tagiuk Provider was profiled in an episode of Bering Sea Gold, at which time, it was the largest scoop dredge operating off Nome.













