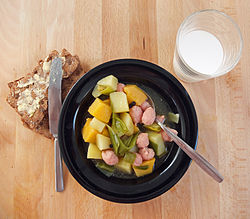
Siskonmakkara is a mild, Finnish fresh sausage made of pork, cooked before serving. The meat is soft and smooth-textured and usually squeezed from its casing when cooking. The most common dish using this sausage is siskonmakkara soup (siskonmakkarakeitto) in which the sausage is cooked in, and simultaneously flavour, the soup stock. The sausage can also be used for a stroganoff or macaroni casserole in place of minced meat. [1]
Contents
The word siskonmakkara is a partial loan translation from the Swedish compound word siskonkorv (Swedish korv and Finnish makkara meaning "sausage") whose siskon part had originally been susiskon, derived from German Sausischen and French saucisse, both meaning "small sausage". [2] As the element siskon is a homonym of the genitive form of the Finnish word sisko meaning "sister", the word siskonmakkara coincidentally appears to mean "sister’s sausage".
