
Lassen Peak, commonly referred to as Mount Lassen, is a 10,457 ft (3,187 m) lava dome volcano in Lassen Volcanic National Park in Northern California. Located in the Shasta Cascade region above the northern Sacramento Valley, it is the southernmost active volcano in the Cascade Range of the Western United States, and part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc stretching from southwestern British Columbia to northern California. It supports many flora and fauna among its diverse habitats, which reach high elevations and are subject to frequent snowfall.
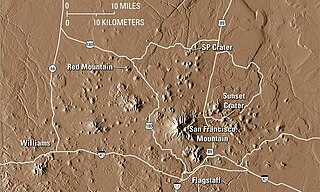
The San Francisco volcanic field is an area of volcanoes in northern Arizona, north of Flagstaff, US. The field covers 1,800 square miles (4,700 km2) of the southern boundary of the Colorado Plateau. The field contains 600 volcanoes ranging in age from nearly 6 million years old to less than 1,000 years, of which Sunset Crater is the youngest. The highest peak in the field is Humphreys Peak, at Flagstaff's northern perimeter: the peak is Arizona's highest at 12,633 feet and is a part of the San Francisco Peaks, an active stratovolcano complex.

Humphreys Peak is the highest natural point and the second most prominent peak after Mount Graham in the U.S. state of Arizona, with an elevation of 12,633 feet (3,851 m) and is located within the Kachina Peaks Wilderness in the Coconino National Forest, about 11 miles (17.7 km) north of Flagstaff, Arizona. Humphreys Peak is the highest of a group of dormant volcanic peaks known as the San Francisco Peaks.

The San Francisco Peaks are a volcanic mountain range in the San Francisco volcanic field in north central Arizona, just north of Flagstaff and a remnant of the former San Francisco Mountain. The highest summit in the range, Humphreys Peak, is the highest point in the state of Arizona at 12,633 feet (3,851 m) in elevation. The San Francisco Peaks are the remains of an eroded stratovolcano. An aquifer within the caldera supplies much of Flagstaff's water while the mountain itself is in the Coconino National Forest, a popular recreation site. The Arizona Snowbowl ski area is on the western slopes of Humphreys Peak, and has been the subject of major controversy involving several tribes and environmental groups.

A volcanic plug, also called a volcanic neck or lava neck, is a volcanic object created when magma hardens within a vent on an active volcano. When present, a plug can cause an extreme build-up of high gas pressure if rising volatile-charged magma is trapped beneath it, and this can sometimes lead to an explosive eruption. In a plinian eruption the plug is destroyed and ash is ejected.

The Coconino National Forest is a 1.856-million acre United States National Forest located in northern Arizona in the vicinity of Flagstaff, with elevations ranging from 2,600 feet to the highest point in Arizona at 12,633 feet. Originally established in 1898 as the "San Francisco Mountains National Forest Reserve", the area was designated a U.S. National Forest by Pres. Theodore Roosevelt on July 2, 1908, when the San Francisco Mountains National Forest Reserve was merged with lands from other surrounding forest reserves to create the Coconino National Forest. Today, the Coconino National Forest contains diverse landscapes, including deserts, ponderosa pine forests, flatlands, mesas, alpine tundra, and ancient volcanic peaks. The forest surrounds the towns of Sedona and Flagstaff and borders four other national forests; the Kaibab National Forest to the west and northwest, the Prescott National Forest to the southwest, the Tonto National Forest to the south, and the Apache-Sitgreaves National Forest to the southeast. The forest contains all or parts of nine designated wilderness areas, including the Kachina Peaks Wilderness, which includes the summit of the San Francisco Peaks. The headquarters are in Flagstaff. The Coconino National Forest consists of three districts: Flagstaff Ranger District, Mogollon Rim Ranger District, and Red Rock Ranger District, which have local ranger district offices in Flagstaff, Happy Jack, and Sedona.

The Sierra Blanca is an ultra-prominent range of volcanic mountains in Lincoln and Otero counties in the south-central part of the U.S. state of New Mexico. The range is about 40 miles (64 km) from north to south and 20 miles (32 km) wide.

Kendrick Peak or Kendrick Mountain is one of the highest peaks in the San Francisco volcanic field north of the city of Flagstaff in the U.S. state of Arizona and is located on the Coconino Plateau in Coconino County.

Diamond Peak is a volcano in Klamath and Lane counties of central Oregon in the United States. It is a shield volcano, though it might also be considered a modest stratocone. Diamond Peak forms part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc, a segment of the Cascade Range in western North America extending from southern British Columbia through Oregon to Northern California. Reaching an elevation of 8,748 feet (2,666 m), the mountain is located near Willamette Pass in the Diamond Peak Wilderness within the Deschutes and Willamette national forests. Surrounded by coniferous forest and visible in the skyline from foothills near Eugene, Diamond Peak offers a few climbing routes and can be scrambled. Diamond Peak is one of Oregon's Matterhorns.
Roof Butte is a peak in the Chuska Mountains in Arizona, United States. Roof Butte is the highest peak of the Chuska Mountains which run in a north-northwest direction across the Arizona-New Mexico border. Roof Butte is a visible butte for miles around. The butte has an elevation of 9,787 feet (2,983 m). A manned-lookout tower is located on Roof Butte. Two funnel shaped explosion volcanic pipes formed the flattish summit of Roof Butte, and a low lava dome caps one nearby peak.

Mount Baldy is an extinct stratovolcano in eastern Arizona in the United States. With a summit elevation of 11,409 feet (3,477 m), the peak of Mount Baldy rises above the tree line and is left largely bare of vegetation, lending the mountain its current name. The Mount Baldy Wilderness occupies the eastern slope of the mountain and is managed by the Apache-Sitgreaves National Forest.

Chiricahua Peak is a 9,773 feet (2,979 m) peak located in the Chiricahua Mountains of southeastern Arizona, located about 35 miles (56 km) north of the United States–Mexico border. It is the highest summit in the Chiricahua Mountains and the highest point in Cochise County.

Escudilla Mountain is located in Apache County, Arizona, United States, and is part of the White Mountains. The peak is approximately 3.5 miles from the Arizona-New Mexico border. The summit is the highest point in the Escudilla Wilderness which is administered as part of the Apache-Sitgreaves National Forest. It is also the third-highest mountain peak in Arizona.

Arizona is a landlocked state situated in the southwestern region of the United States of America. It has a vast and diverse geography famous for its deep canyons, high- and low-elevation deserts, numerous natural rock formations, and volcanic mountain ranges. Arizona shares land borders with Utah to the north, the Mexican state of Sonora to the south, New Mexico to the east, and Nevada to the northwest, as well as water borders with California and the Mexican state of Baja California to the southwest along the Colorado River. Arizona is also one of the Four Corners states and is diagonally adjacent to Colorado.

Apache Peak, at 7,714 feet (2,351 m), is the highest peak in the Whetstone Mountains in Cochise County, Arizona. The summit, located in the Coronado National Forest, is a popular local hiking destination. It is located near the Kartchner Caverns State Park, the city of Benson, Interstate 10, and Arizona State Route 90.

Bill Williams Mountain is a peak and lava dome volcano located about 31 miles (50 km) west of Flagstaff and 3.5 miles (5.6 km) south of Williams, Arizona in the Kaibab National Forest. It is named for Old Bill Williams, a scout, guide, and mountain man, who lived in the 1800s. It is part of the San Francisco volcanic field.

The Pinal Mountains are a mountain range located in Gila County, Arizona. They have a maximum elevation of 7,848 ft (2,392 m) at Pinal Peak and a prominence of over 4,000 ft (1,200 m). The closest city is the Globe, Arizona/Miami, Arizona area, which is just a few miles north of the mountain range. The mountains are located within the Tonto National Forest, and their recreational facilities are maintained by the USDA's United States Forest Service. The San Carlos Indian Reservation is very close to the mountain range, with its boundaries being just a few miles east/northeast of the range. The mountains are covered with Ponderosa Pine and white fir and experience cooler weather than the Globe/Miami area, so that they are a popular recreation area in the summer. The maintained facilities include a maintained dirt road that goes all the way to the summit of Pinal Peak, a campsite and recreational area, many hiking trails, as well as some radio towers near both Pinal and Signal peaks. The mountain range covers an area of 45,760 acres.

Hoodoo Peak is a 10,571-foot-elevation (3,222-meter) mountain summit located in Park County, Wyoming, United States.

















