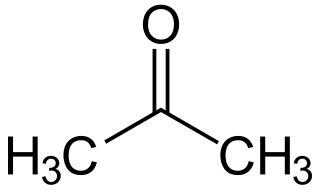
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure R−C(=O)−R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group −C(=O)−. The simplest ketone is acetone, with the formula (CH3)2CO. Many ketones are of great importance in biology and industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, and the solvent acetone.

Chloroacetic acid, industrially known as monochloroacetic acid (MCA), is the organochlorine compound with the formula ClCH2CO2H. This carboxylic acid is a useful building block in organic synthesis. It is a colorless solid. Related compounds are dichloroacetic acid and trichloroacetic acid.

Malonic acid is a dicarboxylic acid with structure CH2(COOH)2. The ionized form of malonic acid, as well as its esters and salts, are known as malonates. For example, diethyl malonate is malonic acid's diethyl ester. The name originates from the Greek word μᾶλον (malon) meaning 'apple'.

Diethyl malonate, also known as DEM, is the diethyl ester of malonic acid. It occurs naturally in grapes and strawberries as a colourless liquid with an apple-like odour, and is used in perfumes. It is also used to synthesize other compounds such as barbiturates, artificial flavourings, vitamin B1, and vitamin B6.

In organic chemistry, nitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups. The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores used globally. The nitro group is also strongly electron-withdrawing. Because of this property, C−H bonds alpha (adjacent) to the nitro group can be acidic. For similar reasons, the presence of nitro groups in aromatic compounds retards electrophilic aromatic substitution but facilitates nucleophilic aromatic substitution. Nitro groups are rarely found in nature. They are almost invariably produced by nitration reactions starting with nitric acid.
The Gabriel synthesis is a chemical reaction that transforms primary alkyl halides into primary amines. Traditionally, the reaction uses potassium phthalimide. The reaction is named after the German chemist Siegmund Gabriel.
In organic chemistry, the Knoevenagel condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction named after German chemist Emil Knoevenagel. It is a modification of the aldol condensation.
The Bouveault–Blanc reduction is a chemical reaction in which an ester is reduced to primary alcohols using absolute ethanol and sodium metal. It was first reported by Louis Bouveault and Gustave Louis Blanc in 1903. Bouveault and Blanc demonstrated the reduction of ethyl oleate and n-butyl oleate to oleyl alcohol. Modified versions of which were subsequently refined and published in Organic Syntheses.

Cyanamide is an organic compound with the formula CN2H2. This white solid is widely used in agriculture and the production of pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds. It is also used as an alcohol-deterrent drug. The molecule features a nitrile group attached to an amino group. Derivatives of this compound are also referred to as cyanamides, the most common being calcium cyanamide (CaCN2).

o-Phenylenediamine (OPD) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(NH2)2. This aromatic diamine is an important precursor to many heterocyclic compounds. OPD is a white compound although samples appear darker owing to oxidation by air. It is isomeric with m-phenylenediamine and p-phenylenediamine.

In organic chemistry, alkyl nitrites are a group of organic compounds based upon the molecular structure R−O−N=O, where R represents an alkyl group. Formally they are alkyl esters of nitrous acid. They are distinct from nitro compounds.
Stephen aldehyde synthesis, a named reaction in chemistry, was invented by Henry Stephen (OBE/MBE). This reaction involves the preparation of aldehydes (R-CHO) from nitriles (R-CN) using tin(II) chloride (SnCl2), hydrochloric acid (HCl) and quenching the resulting iminium salt ([R-CH=NH2]+Cl−) with water (H2O). During the synthesis, ammonium chloride is also produced.

Benzyl cyanide (abbreviated BnCN) is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH2CN. This colorless oily aromatic liquid is an important precursor to numerous compounds in organic chemistry. It is also an important pheromone in certain species.

2-Cyanoacetamide is an organic compound. It is an acetic amide with a nitrile functional group.
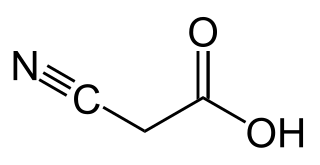
Cyanoacetic acid is an organic compound. It is a white, hygroscopic solid. The compound contains two functional groups, a nitrile (−C≡N) and a carboxylic acid. It is a precursor to cyanoacrylates, components of adhesives.
In organic chemistry, alkynylation is an addition reaction in which a terminal alkyne is added to a carbonyl group to form an α-alkynyl alcohol.

Ethyl cyanoacetate is an organic compound that contains a carboxylate ester and a nitrile. It is a colourless liquid with a pleasant odor. This material is useful as a starting material for synthesis due to its variety of functional groups and chemical reactivity.

1,3-Cyclohexanedione is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4(CO)2. It is one of three isomeric cyclohexanediones. It is a colorless compound that occurs naturally. It is the substrate for cyclohexanedione hydrolase. The compound exists mainly as the enol tautomer.

Diethyl oxomalonate is the diethyl ester of mesoxalic acid (ketomalonic acid), the simplest oxodicarboxylic acid and thus the first member (n = 0) of a homologous series HOOC–CO–(CH2)n–COOH with the higher homologues oxalacetic acid (n = 1), α-ketoglutaric acid (n = 2) and α-ketoadipic acid (n = 3) (the latter a metabolite of the amino acid lysine). Diethyl oxomalonate reacts because of its highly polarized keto group as electrophile in addition reactions and is a highly active reactant in pericyclic reactions such as the Diels-Alder reactions, cycloadditions or ene reactions. At humid air, mesoxalic acid diethyl ester reacts with water to give diethyl mesoxalate hydrate and the green-yellow oil are spontaneously converted to white crystals.

Sodium p-toluenesulfonate is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4SO3Na. It is white, water-soluble solid. It is produced by the neutralization toluenesulfonic acid with sodium hydroxide. It is also a common product from the reactions of sodium-based reagents with toluenesulfonates.















