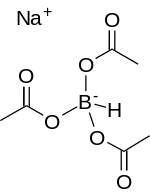
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as R−COOH or R−CO2H, sometimes as R−C(O)OH with R referring to an organyl group, or hydrogen, or other groups. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion.

In organic chemistry, an aldehyde is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure R−CH=O. The functional group itself can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are a common motif in many chemicals important in technology and biology.

Sodium borohydride, also known as sodium tetrahydridoborate and sodium tetrahydroborate, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaBH4. It is a white crystalline solid, usually encountered as an aqueous basic solution. Sodium borohydride is a reducing agent that finds application in papermaking and dye industries. It is also used as a reagent in organic synthesis.
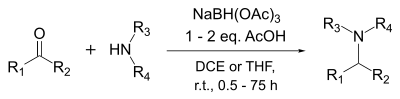
Reductive amination is a form of amination that involves the conversion of a carbonyl group to an amine via an intermediate imine. The carbonyl group is most commonly a ketone or an aldehyde. It is a common method to make amines and is widely used in green chemistry since it can be done catalytically in one-pot under mild conditions. In biochemistry, dehydrogenase enzymes use reductive amination to produce the amino acid glutamate. Additionally, there is ongoing research on alternative synthesis mechanisms with various metal catalysts which allow the reaction to be less energy taxing, and require milder reaction conditions. Investigation into biocatalysts, such as imine reductases, have allowed for higher selectivity in the reduction of chiral amines which is an important factor in pharmaceutical synthesis.

Sodium dithionite is a white crystalline powder with a sulfurous odor. Although it is stable in dry air, it decomposes in hot water and in acid solutions.
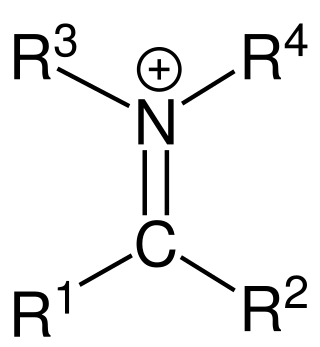
In organic chemistry, an iminium cation is a polyatomic ion with the general structure [R1R2C=NR3R4]+. They are common in synthetic chemistry and biology.

Palladium(II) acetate is a chemical compound of palladium described by the formula [Pd(O2CCH3)2]n, abbreviated [Pd(OAc)2]n. It is more reactive than the analogous platinum compound. Depending on the value of n, the compound is soluble in many organic solvents and is commonly used as a catalyst for organic reactions.

The bisulfite ion (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogensulfite) is the ion HSO−
3. Salts containing the HSO−
3 ion are also known as "sulfite lyes". Sodium bisulfite is used interchangeably with sodium metabisulfite (Na2S2O5). Sodium metabisulfite dissolves in water to give a solution of Na+HSO−
3.
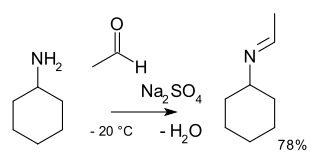
In organic chemistry, alkylimino-de-oxo-bisubstitution is the organic reaction of carbonyl compounds with amines to imines. The reaction name is based on the IUPAC Nomenclature for Transformations. The reaction is acid catalyzed and the reaction type is nucleophilic addition of the amine to the carbonyl compound followed by transfer of a proton from nitrogen to oxygen to a stable hemiaminal or carbinolamine. With primary amines water is lost in an elimination reaction to an imine. With aryl amines especially stable Schiff bases are formed.

Sodium bis(2-methoxyethoxy)aluminium hydride (SMEAH; trade names Red-Al, Synhydrid, Vitride) is a hydride reductant with the formula NaAlH2(OCH2CH2OCH3)2. The trade name Red-Al refers to its being a reducing aluminium compound. It is used predominantly as a reducing agent in organic synthesis. The compound features a tetrahedral aluminium center attached to two hydride and two alkoxide groups, the latter derived from 2-methoxyethanol. Commercial solutions are colorless/pale yellow and viscous. At low temperatures (below -60°C), the solution solidifies to a glassy pulverizable substance with no sharp melting point.
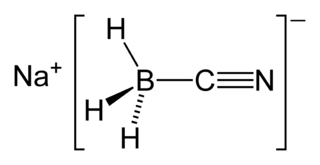
Sodium cyanoborohydride is a chemical compound with the formula Na[BH3(CN)]. It is a colourless salt used in organic synthesis for chemical reduction including that of imines and carbonyls. Sodium cyanoborohydride is a milder reductant than other conventional reducing agents.

Borohydride refers to the anion [BH4]−, which is also called tetrahydridoborate, and its salts. Borohydride or hydroborate is also the term used for compounds containing [BH4−nXn]−, where n is an integer from 0 to 3, for example cyanoborohydride or cyanotrihydroborate [BH3(CN)]− and triethylborohydride or triethylhydroborate [BH(CH2CH3)3]−. Borohydrides find wide use as reducing agents in organic synthesis. The most important borohydrides are lithium borohydride and sodium borohydride, but other salts are well known. Tetrahydroborates are also of academic and industrial interest in inorganic chemistry.

Lithium borohydride (LiBH4) is a borohydride and known in organic synthesis as a reducing agent for esters. Although less common than the related sodium borohydride, the lithium salt offers some advantages, being a stronger reducing agent and highly soluble in ethers, whilst remaining safer to handle than lithium aluminium hydride.
Luche reduction is the selective organic reduction of α,β-unsaturated ketones to allylic alcohols. The active reductant is described as "cerium borohydride", which is generated in situ from NaBH4 and CeCl3(H2O)7.
In nitrile reduction a nitrile is reduced to either an amine or an aldehyde with a suitable chemical reagent.

Aluminium borohydride, also known as aluminium tetrahydroborate, is the chemical compound with the formula Al(BH4)3. It is a volatile pyrophoric liquid which is used as a reducing agent in laboratories. Unlike most other metal–borohydrides, which are ionic structures, aluminium borohydride is a covalent compound.
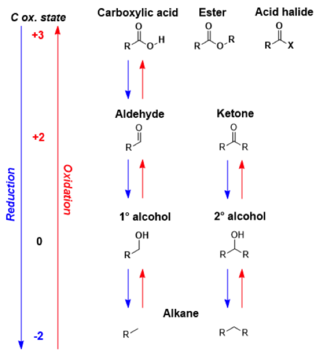
In organic chemistry, carbonyl reduction is the conversion of any carbonyl group, usually to an alcohol. It is a common transformation that is practiced in many ways. Ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, esters, amides, and acid halides - some of the most pervasive functional groups, -comprise carbonyl compounds. Carboxylic acids, esters, and acid halides can be reduced to either aldehydes or a step further to primary alcohols, depending on the strength of the reducing agent. Aldehydes and ketones can be reduced respectively to primary and secondary alcohols. In deoxygenation, the alcohol group can be further reduced and removed altogether by replacement with H.

Borane–tetrahydrofuran is an adduct derived from borane and tetrahydrofuran (THF). These solutions, which are colorless, are used for reductions and hydroboration, reactions that are useful in synthesis of organic compounds. The use of borane–tetrahydrofuran has been displaced by borane–dimethylsulfide, which has a longer shelf life and effects similar transformations.
Protonolysis is the cleavage of a chemical bond by acids. Many examples are found in organometallic chemistry since the reaction requires polar Mδ+-Rδ- bonds, where δ+ and δ- signify partial positive and negative charges associated with the bonding atoms. When compounds containing these bonds are treated with acid (HX), these bonds cleave:
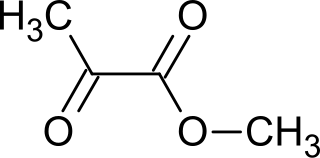
Methyl pyruvate is the organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CO2CH3. This colorless liquid is the methyl ester of pyruvic acid. It has attracted interest as a prochiral precursor to alanine and lactic acid. It is prepared by esterification of pyruvic acid.