
A flatfish is a member of the order Pleuronectiformes of ray-finned demersal fishes, also called the Heterosomata, sometimes classified as a suborder of Perciformes. In many species, both eyes lie on one side of the head, one or the other migrating through or around the head during development. Some species face their left sides upward, some face their right sides upward, and others face either side upward.

"Sardine" and "pilchard" are common names used to refer to various small, oily fish in the herring family Clupeidae. The term "sardine" was first used in English during the early 15th century and may come from the Mediterranean island of Sardinia, around which sardines were once abundant.

Pison is a cosmopolitan genus of wasps within the family Crabronidae. The genus comprises 145 described species, although many species, especially in South America remain undescribed.
The southern lemon sole, also known as the New Zealand lemon sole, is a righteye flounder, the only species in the genus Pelotretis, found around New Zealand in enclosed waters such as estuaries, harbours, mudflats, and sandflats, in waters less than 385 m in depth. Their length is from 25 to 50 cm.

Palpita is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae. Members of the moth genus Stemorrhages may be very similar in appearance.

Semicassis is a genus of medium-sized predatory sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the subfamily Cassinae within the family Cassidae, the helmet snails and bonnet snails.

Echinolittorina is a genus of small sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the family Littorinidae, the winkles.

Cynoglossus is a genus of fish in the family Cynoglossidae. Most species are indigenous to the Indo-Pacific region, but they also occur in a few in warmer parts of the East Atlantic. They are commonly found in shallow waters on a muddy or sandy bottom, including estuaries and a few species are restricted to fresh water. One species Cynoglossus sinusarabici has invaded the Mediterranean Sea through the Suez Canal from the Red Sea, a process known as Lessepsian or Erythrean migration.
Hespererato is a genus of small sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Eratoidae, the false cowries or trivias.

Bankivia is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Trochidae, the top snails.

Trinectes is a genus of American soles native to the Americas. Most species are coastal, occurring in both salt and brackish water, but several may enter fresh water and one, T. hubbsbollinger, is restricted to rivers. They are fairly small, with the largest species only reaching 25 cm (9.8 in) in length.

Aesopia cornuta is a species of sole native to the Indian and western Pacific Oceans. Its common names include the unicorn sole, thickray sole, banded sole, and dark thick-rayed sole. This species grows to a standard length of 25 cm (9.8 in), and is the only known member of its genus.

Pseudaesopia japonica, the wavyband sole or Seto sole, is a species of sole native to the western Pacific Ocean, where found over sandy mud bottoms. This species is the only known member of its genus. This species grows to a length of 15 centimetres (5.9 in) SL.
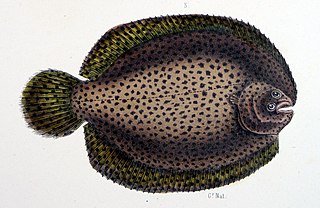
The drab sole is a brackish water-dwelling sole of the genus Achirus native to the waters of South America, the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea. The drab sole is also commonly used by humans as an aquarium fish.
Eugene G. Munroe was a Canadian entomologist who discovered numerous species of insects. He worked for the Insect Systematics and Biological Control Unit, Entomology Division in Ottawa, Canada.

The brown sole is a sole of the genus Achirus native to the eastern Pacific from central Mexico to northernmost Peru. This demersal species growth up to 23 cm (9.1 in). It is found at depths of 10–40 m on sandy and muddy grounds and may enter fresh waters in estuaries and mangroves. Its diet consists of invertebrates, small fishes, pelagic eggs and larvae.

The Mazatlan sole is a sole of the genus Achirus native to the eastern Pacific from northern Baja California and the Gulf of California to northernmost Peru. This demersal species growth up to 20 cm (7.9 in). It is found at depths of 1–60 m in coastal lagoons and fresh water. Its diet consists of crustaceans, small fishes, polychaetes, and occasionally detritus.

The network sole is a sole of the genus Achirus native to the eastern Pacific from the tip of Baja California and the southeastern Gulf of California to northern Peru. This demersal species growth up to 28 cm (11 in). It is found at depths 5–45 m in coastal lagoons and fresh water. Its diet consists of crustaceans, small fishes, polychaetes, and occasionally detritus.
The tufted sole is a species of flatfish from the family of true soles Soleidae. It is the only species in the monotypic genus Dexillus. It is found in the Indian and western Pacific Oceans.



















