
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is 7,000 km (4,350 mi) long, 200 to 700 km wide, and has an average height of about 4,000 m (13,123 ft). The Andes extend from north to south through seven South American countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina.
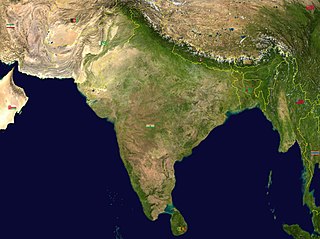
India is situated north of the equator between 8°4' north to 37°6' north latitude and 68°7' east to 97°25' east longitude. It is the seventh-largest country in the world, with a total area of 3,287,263 square kilometres (1,269,219 sq mi). India measures 3,214 km (1,997 mi) from north to south and 2,933 km (1,822 mi) from east to west. It has a land frontier of 15,200 km (9,445 mi) and a coastline of 7,516.6 km (4,671 mi).

New South Wales, is a state on the east coast of Australia. It borders Queensland to the north, Victoria to the south, and South Australia to the west. Its coast borders the Coral and Tasman Seas to the east. The Australian Capital Territory is an enclave within the state. New South Wales' state capital is Sydney, which is also Australia's most populous city. In June 2020, the population of New South Wales was over 8.1 million, making it Australia's most populous state. Just under two-thirds of the state's population, 5.3 million, live in the Greater Sydney area. The demonym for inhabitants of New South Wales is New South Welshmen.

The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch 3,000 mi (4,800 km) in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in southwestern United States. Depending on differing definitions between Canada and the United States, its northern terminus is located either in northern British Columbia's Terminal Range south of the Liard River and east of the Trench, or in the northeastern foothills of the Brooks Range/British Mountains that face the Beaufort Sea coasts between the Canning River and the Firth River across the Alaska-Yukon border. Its southernmost point is near the Albuquerque area adjacent to the Rio Grande Basin and north of the Sandia–Manzano Mountain Range. Being the easternmost portion of the North American Cordillera, the Rockies are distinct from the tectonically younger Cascade Range and Sierra Nevada, which both lie farther to its west.

Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is an island country in East Asia. The main island of Taiwan, known historically in English as Formosa, makes up 99% of the area controlled by the ROC, measuring 35,808 square kilometres (13,826 sq mi) and lying some 180 kilometres (112 mi) across the Taiwan Strait from the southeastern coast of mainland China. The East China Sea lies to the north of the island, the Philippine Sea to its east, the Luzon Strait directly to its south and the South China Sea to its southwest. The ROC also controls a number of smaller islands: some in the Taiwan Strait, and some of the South China Sea Islands.

The Himalayas, or Himalaya ; Sanskrit: IPA: [ɦɪmɐːləjɐː], himá and ā-laya, are a mountain range in South and East Asia separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has many of Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest, at the border between Nepal and China. The Himalayas include over fifty mountains exceeding 7,200 m (23,600 ft) in elevation, including ten of the fourteen 8,000-metre peaks. By contrast, the highest peak outside Asia is 6,961 m (22,838 ft) tall.

The Great Dividing Range, also known as the East Australian Cordillera or the Eastern Highlands, is a cordillera system in eastern Australia consisting of an expansive collection of mountain ranges, plateaus and rolling hills, that runs roughly parallel to the east coast of Australia and forms the fifth-longest land-based mountain chain in the world. It is mainland Australia's most substantial topographic feature and serves as the definitive watershed for the river systems in eastern Australia, hence the name.

The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before experiencing natural erosion. The Appalachian chain is a barrier to east–west travel, as it forms a series of alternating ridgelines and valleys oriented in opposition to most highways and railroads running east–west.

Lincoln County is a county located in the U.S. state of Nevada. As of the 2010 census, the population was 5,345. Its county seat is Pioche. Like many counties in Nevada, it is dry and sparsely populated, though notable for containing the Area 51 government Air Force base.

The Ikara-Flinders Ranges National Park is situated approximately 400 km north of Adelaide in the northern central part of South Australia's largest mountain range, the Flinders Ranges. The park covers an area of 912 km², northeast of the small town of Hawker. The Heysen Trail and Mawson Trails pass through the park.
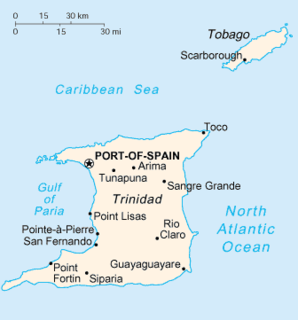
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies 11 km (6.8 mi) off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmost island in the West Indies. With an area of 5,131 km2 (1,981 sq mi), it is also the fifth largest in the West Indies.

The Blue Ridge Mountains are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Mountains range. The mountain range is located in the eastern United States, and extends 550 miles southwest from southern Pennsylvania through Maryland, West Virginia, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, and Georgia. This province consists of northern and southern physiographic regions, which divide near the Roanoke River gap. To the west of the Blue Ridge, between it and the bulk of the Appalachians, lies the Great Appalachian Valley, bordered on the west by the Ridge and Valley province of the Appalachian range.

The Vindhya Range is a complex, discontinuous chain of mountain ridges, hill ranges, highlands and plateau escarpments in west-central India.

South East Queensland (SEQ) is a bio-geographical, metropolitan, political, and administrative region of the state of Queensland in Australia, with a population of approximately 3.8 million people out of the state's population of 5.1 million. The area covered by South East Queensland varies, depending on the definition of the region, though it tends to include Queensland's three largest cities: the capital city Brisbane; the Gold Coast; and the Sunshine Coast. Its most common use is for political purposes, and covers 22,420 square kilometres (8,660 sq mi) and incorporates 11 local government areas, extending 240 kilometres (150 mi) from Noosa in the north to the Gold Coast and New South Wales border in the south, and 140 kilometres (87 mi) west to Toowoomba.

The Coast Ranges of California span 400 miles (644 km) from Del Norte or Humboldt County, California, south to Santa Barbara County. The other three coastal California mountain ranges are the Transverse Ranges, Peninsular Ranges and the Klamath Mountains.
In 1989 the U.S. Government enacted the Nevada Wilderness Bill, expanding the one existing Wilderness Area (Jarbidge) and creating thirteen new areas. The estimated total of 733,400 acres (296,800 ha) was over eleven times the area that had previously been under wilderness protection.

The Delamar Mountains are a mountain range in Lincoln County, Nevada, named after Captain Joseph Raphael De Lamar. The range extends for approximately 50 miles (80 km) in a NNE–SSW orientation with a width of about 11 miles (18 km). Surrounding ranges include the Burnt Springs Range and the Chief Range to the north, the Clover Mountains and Meadow Valley Mountains to the east and the Sheep Range and South Pahroc Range on the west. The Delamar Valley lies to the west, the Kane Springs Valley to the east and the Coyote Springs Valley lies to the south of the range.

The Gobi Desert is a large desert or brushland region in East Asia. It covers parts of Northern and Northeastern China and of Southern Mongolia. The desert basins of the Gobi are bounded by the Altai Mountains and the grasslands and steppes of Mongolia on the north, by the Taklamakan Desert to the west, by the Hexi Corridor and Tibetan Plateau to the southwest and by the North China Plain to the southeast. The Gobi is notable in history as the location of several important cities along the Silk Road.

Dry Lake Valley is a Basin and Range landform in Lincoln County within the Dry Lake Watershed between the North Pahroc Range to the west and the Black Canyon Wilderness to the east. To the south is the Delamar Valley between the South Pahroc Range to the west and the Delamar Mountains to the east.



















