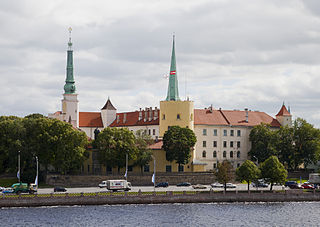Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to the southeast, and shares a maritime border with Sweden to the west. Latvia covers an area of 64,589 km2 (24,938 sq mi), with a population of 1.9 million. The country has a temperate seasonal climate. Its capital and largest city is Riga. Latvians belong to the ethnolinguistic group of the Balts and speak Latvian. Russians are the most prominent minority in the country, at almost a quarter of the population; 37.7% of the population speak Russian as their native tongue.

The history of Latvia began around 9000 BC with the end of the last glacial period in northern Europe. Ancient Baltic peoples arrived in the area during the second millennium BC, and four distinct tribal realms in Latvia's territory were identifiable towards the end of the first millennium AD. Latvia's principal river Daugava, was at the head of an important trade route from the Baltic region through Russia into southern Europe and the Middle East that was used by the Vikings and later Nordic and German traders.

Latvia lies on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea on the level northwestern part of the rising East European platform, between Estonia and Lithuania. About 98% of the country lies under 200 m (656 ft) elevation. With the exception of the coastal plains, the ice age divided Latvia into three main regions: the morainic Western and Eastern uplands and the Middle lowlands. Latvia holds over 12,000 rivers, only 17 of which are longer than 100 km (60 mi), and over 3,000 small lakes, most of which are eutrophic. The major rivers include the Daugava, the Lielupe, the Gauja, the Venta and the Salaca. Woodlands cover around 52% of the country. Other than peat, dolomite, and limestone, natural resources are scarce. Latvia has 504 km (313 mi) of sandy coastline, and the ports of Liepāja and Ventspils provide important warm-water harbors for the Baltic coast.

Riga is the capital, the primate, and the largest city of Latvia. Home to 605,273 inhabitants, the city accounts for a third of Latvia's total population. The population of Riga metropolitan area, which stretches beyond the city limits, is estimated at 860,142. The city lies on the Gulf of Riga at the mouth of the Daugava river where it meets the Baltic Sea. Riga's territory covers 307.17 km2 (118.60 sq mi) and lies 1–10 m (3–33 ft) above sea level on a flat and sandy plain.

airBaltic, legally incorporated as AS Air Baltic Corporation, is the flag carrier of Latvia, with its head office on the grounds of Riga International Airport in Mārupe municipality near Riga. Its main hub is Riga, and it operates bases in Tallinn, Vilnius, Tampere and a seasonal base in Las Palmas launched in 2023. It is 97% owned by the Government of Latvia. It operates flights solely on Airbus A220 planes. It operates a frequent-flyer program and a buy on board menu offering food and drinks for purchase.

The United Baltic Duchy, or alternatively the Grand Duchy of Livonia, was the name of a short-lived state during World War I that was proclaimed by leaders of the local Baltic German nobility.

The Latvian Soviet Socialist Republic was de facto one of the constituent republics of the Soviet Union between 1940–1941 and 1944–1990.
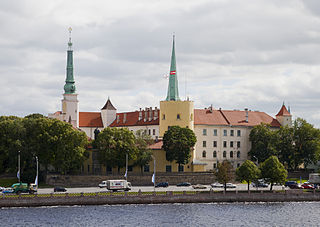
Riga Castle is a castle on the banks of River Daugava in Riga, the capital of Latvia. The castle was founded in 1330. Its structure was thoroughly rebuilt between 1497 and 1515. Upon the castle's seizure by the Swedes, they constructed spacious annexes in 1641. The fortress was continually augmented and reconstructed between the 17th and 19th centuries. Sometime in the 1930s, some renovation work was done by architect Eižens Laube. The Latvian government declared the castle its residence in 1938. Today it is the official residence of the President of Latvia as well as home to several museums.

Bertolt Martin Flick is a German businessman, the former president and CEO of airBaltic airline.

Daugava National Stadium is a multifunctional stadium in Riga, Latvia, which was first opened in 1927. It holds football and athletics competitions. Since 1992 the Daugava Stadium has been designated as a sports facility of national importance. It is owned by the Government of Latvia.

The Vanšu Bridge in Riga is a cable-stayed bridge that crosses the Daugava river in Riga, the capital of Latvia. The word vanšu refers to the cables suspending its deck, comparing them to nautical rigging also known as shrouds in English; thus a direct translation of the name is Shroud Bridge. 595 meters in length, it is one of five bridges crossing the Daugava in Riga and passes over Ķīpsala island. It was built during the Soviet period and opened to public use on 21 July 1981 as the Gorky Bridge after Maxim Gorky street, today renamed Krišjānis Valdemārs street, which it extends across the river.

Valērijs Kargins or Valery Mikhailovich Kargin is a Latvian economist and banker was the president of Parex Banka, from 1998 to 2008. In October 2000, he and Viktor Krasovitsky had accumulated over 200 million lats together. He created the first travel agency and the first currency exchange corporation in the Soviet Union.
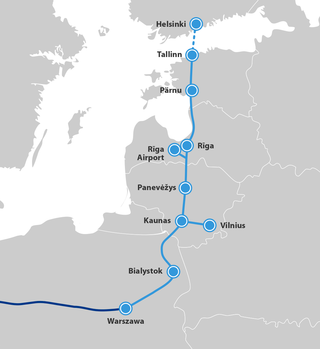
Rail Baltica is an under-construction rail infrastructure project that is intended to integrate the Baltic states in the European rail network. Its purpose is to provide passenger and freight service between participating countries and improve rail connections between Central and Northern Europe, specifically the area southeast of the Baltic Sea. It is also intended as a catalyst for building the economic corridor in Northeastern Europe. The project envisages a continuous rail link from Tallinn (Estonia) to Warsaw (Poland), consisting of links via Riga (Latvia), Kaunas, and Vilnius (Lithuania). Its total length in the Baltic States is 870 kilometres (540 mi), with 213 kilometres (132 mi) in Estonia, 265 kilometres (165 mi) in Latvia, and 392 kilometres (244 mi) in Lithuania. Rail Baltica is one of the priority projects of the European Union (EU). It is part of the North Sea–Baltic Corridor of the Trans-European Transport Networks (TEN-T).
JSC Olpha is a Latvian leading manufacturer in the chemical and pharmaceutical sector of the Baltic States.

Pauls Stradiņš Clinical University Hospital is an outpatient and hospital health care service provider in Riga, Latvia. This hospital also plays a role in medical science and medical education. It aims to become a science and a training center to residents and prospective doctors and currently is affiliated with two universities. It is named after Pauls Stradiņš.
The Baltic Coal Terminal is a special purpose company operating a specialized coal terminal in the Free port of Ventspils, Latvia.

Nils Ušakovs is a Latvian politician, former mayor of Riga and former journalist. He was the board chairman of the left-wing party alliance Harmony Centre (2005–2014) and afterwards board chairman of the Social Democratic Party "Harmony" (2014–2019). In 2009 Ušakovs was elected the Mayor of Riga, becoming the first ethnic Russian Riga Mayor since Latvia's restoration of sovereignty in 1991, a position he continuously held until his dismissal in 2019.

Ainārs Šlesers is a Latvian business oligarch and politician who was Deputy Prime Minister of Latvia, as well as Deputy Mayor of Riga. Currently he is a member of the Latvian Parliament with his political party, Latvia First, holding 9 seats in the parliament.

The Island Bridge is a bridge that crosses the Daugava river in Riga, the capital of Latvia. The bridge was built in the period from 1975 to 1977. It was called the Moscow Bridge until 1991. The bridge provides access to Zaķusala and Lucavsala.

Victory Park is a park in Riga, located on the left bank of the Daugava, in the district of Āgenskalns. The modern area of the park is 36.7 hectares.