
Euglenozoa are a large group of flagellate Discoba. They include a variety of common free-living species, as well as a few important parasites, some of which infect humans. Euglenozoa are represented by four major groups, i.e., Kinetoplastea, Diplonemea, Euglenida, and Symbiontida. Euglenozoa are unicellular, mostly around 15–40 μm (0.00059–0.00157 in) in size, although some euglenids get up to 500 μm (0.020 in) long.
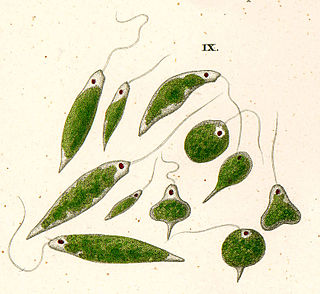
Euglenids or euglenoids are one of the best-known groups of flagellates. They are excavate eukaryotes of the phylum Euglenophyta, classified as class Euglenida or Euglenoidea. Euglenids are commonly found in freshwater, especially when it is rich in organic materials, with a few marine and endosymbiotic members. Many euglenids feed by phagocytosis, or strictly by diffusion. A monophyletic group known as Euglenophyceae have chloroplasts and produce their own food through photosynthesis. This group is known to contain the carbohydrate paramylon.

Excavata is an extensive and diverse but paraphyletic group of unicellular Eukaryota. The group was first suggested by Simpson and Patterson in 1999 and the name latinized and assigned a rank by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002. It contains a variety of free-living and symbiotic protists, and includes some important parasites of humans such as Giardia and Trichomonas. Excavates were formerly considered to be included in the now obsolete Protista kingdom. They were distinguished from other lineages based on electron-microscopic information about how the cells are arranged. They are considered to be a basal flagellate lineage.
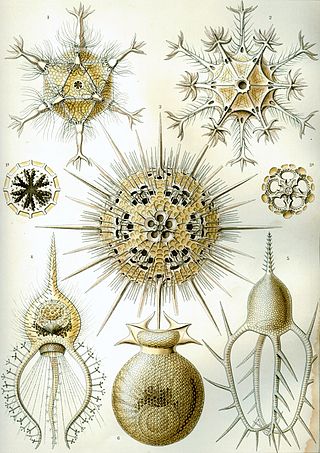
Phaeodarea or Phaeodaria is a group of amoeboid cercozoan organisms. They are traditionally considered radiolarians, but in molecular trees do not appear to be close relatives of the other groups, and are instead placed among the Cercozoa. They are distinguished by the structure of their central capsule and by the presence of a phaeodium, an aggregate of waste particles within the cell.

Labyrinthulomycetes (ICBN) or Labyrinthulea (ICZN) is a class of protists that produce a network of filaments or tubes, which serve as tracks for the cells to glide along and absorb nutrients for them. The two main groups are the labyrinthulids and thraustochytrids. They are mostly marine, commonly found as parasites on algae and seagrasses or as decomposers on dead plant material. They also include some parasites of marine invertebrates and mixotrophic species that live in a symbiotic relationship with zoochlorella.

Euglenales is an order of flagellates in the phylum Euglenozoa. The family includes the most well-known euglenoid genus, Euglena, as well as other common genera like Phacus and Lepocinclis.

Euglenaceae is a family of flagellates in the phylum Euglenozoa. The family includes the most well-known euglenoid genus, Euglena.

Ochrophytes, also known as heterokontophytes or stramenochromes, are a group of algae. They are the photosynthetic stramenopiles, a group of eukaryotes, organisms with a cell nucleus, characterized by the presence of two unequal flagella, one of which has tripartite hairs called mastigonemes. In particular, they are characterized by photosynthetic organelles or plastids enclosed by four membranes, with membrane-bound compartments called thylakoids organized in piles of three, chlorophyll a and c as their photosynthetic pigments, and additional pigments such as β-carotene and xanthophylls. Ochrophytes are one of the most diverse lineages of eukaryotes, containing ecologically important algae such as brown algae and diatoms. They are classified either as phylum Ochrophyta or Heterokontophyta, or as subphylum Ochrophytina within phylum Gyrista. Their plastids are of red algal origin.

Calkinsia is a monotypic genus of excavates comprising the single species Calkinsia aureus. It lives in low-oxygen seafloor environments. It is not classified in any of the three well-known groups of the Euglenozoa, but is placed in its own group, the Symbiontida. Some authors have classified Calkinsia alongside Postgaardi, but Postgaardi has not been studied well enough to test this hypothesis.

Loukozoa is a proposed taxon used in some classifications of eukaryotes, consisting of the Metamonada and Malawimonadea. Ancyromonads are closely related to this group, as sister of the entire group, or as sister of the Metamonada. Amorphea may have emerged in this grouping, specifically as sister of the Malawimonads.
Rigifilida is a clade of non-ciliate phagotrophic eukaryotes. It consists of two genera: Micronuclearia and Rigifila.
Rigifila is a genus of free-living single-celled eukaryotes, or protists, containing the sole species Rigifila ramosa. It is classified within the monotypic family Rigifilidae. Along with Micronucleariidae, it is a member of Rigifilida, an order of basal eukaryotes within the CRuMs clade. It differs from Micronuclearia by having two proteic layers surrounding their cytoplasm instead of a single one, and having more irregular mitochondrial cristae, among other morphological differences.

Diplonemidae is a family of biflagellated unicellular protists that may be among the more diverse and common groups of planktonic organisms in the ocean. Although this family is currently made up of three named genera; Diplonema, Rhynchopus, and Hemistasia, there likely exist thousands of still unnamed genera. Organisms are generally colourless and oblong in shape, with two flagella emerging from a subapical pocket. They possess a large mitochondrial genome composed of fragmented linear DNA. These non-coding sequences must be massively trans-spliced, making it one of the most complicated post-transcriptional editing process known to eukaryotes.
Heteronema is a genus of phagotrophic, flagellated euglenoids that are most widely distributed in fresh water environments. This genus consists of two very distinguishable morphogroups that are phylogenetically closely related. These morphogroups are deciphered based on shape, locomotion and other ultrastructural traits. However, this genus does impose taxonomic problems due to the varying historical descriptions of Heteronema species and its similarity to the genus Paranema. The species H. exaratum, was the first heteronemid with a skidding motion to be sequenced, which led to the discovery that it was not closely related to H. scaphrum, contrary to what was previously assumed, but instead to a sister group of primary osmotrophs. This suggests that skidding heteronemids can also be distinguished phylogenetically, being more closely related to Anisoma, Dinema and Aphageae, than to other species within Heteronema.
Postgaardia is a proposed basal clade of flagellate Euglenozoa, following Thomas Cavalier-Smith. As of April 2023, the Interim Register of Marine and Nonmarine Genera treats the group as a subphylum. A 2021 review of Euglenozoa places Cavalier-Smith's proposed members of Postgaardia in the class Symbiontida. As Euglenozoans may be basal eukaryotes, the Postgaardia may be key to studying the evolution of Eukaryotes, including the incorporation of eukaryotic traits such as the incorporation of alphaproteobacterial mitochondrial endosymbionts.

Urceolus is a genus of heterotrophic flagellates belonging to the Euglenozoa, a phylum of single-celled eukaryotes or protists. Described by Russian biologist Konstantin Mereschkowsky in 1877, its type species is Urceolus alenizini. Species of this genus are characterized by deformable flask-shaped cells that exhibit at least one flagellum that is active at the tip, arising from a neck-like structure that also hosts the feeding apparatus. They are found in a variety of water body sediments across the globe. According to evolutionary studies, Urceolus belongs to a group of Euglenozoa known as peranemids, closely related to the euglenophyte algae.

Urceolus alenizini is a species of flagellates. It was described by Konstantin Mereschkowsky in 1877 as the type species of the genus Urceolus. It is a rare species only recorded by its author once in the White Sea, in northern Russia. It is distinguished by other members of the genus by the lack of spiral stripes in its cell surface.
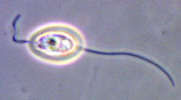
Ploeotia is a genus of heterotrophic flagellates belonging to the Euglenida, a diverse group of flagellated protists in the phylum Euglenozoa. Species of Ploeotia are composed of rigid cells exhibiting two flagella. The genus was described by Félix Dujardin in 1841.
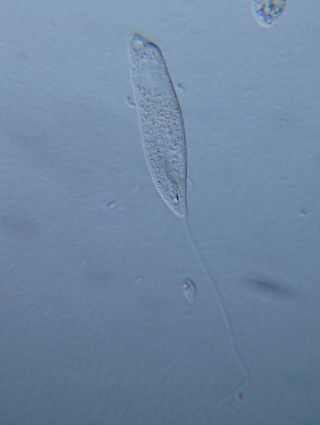
The peranemids are a group of phagotrophic flagellates, single-celled eukaryotes or protists. They belong to the Euglenida, a diverse lineage of flagellates that contains the closely related euglenophyte algae. Like these algae, peranemids have flexible cells capable of deformation or metaboly, and have one or two flagella in the anterior region of the cell. They are classified as family Peranemidae (ICZN) or Peranemataceae (ICBN) within the monotypic order Peranemida (ICZN) or Peranematales (ICBN).
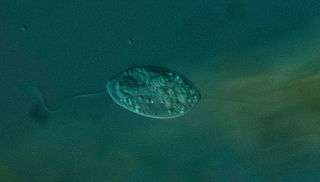
Anisonemia is a group of single-celled protists belonging to the phylum Euglenozoa, relatives of the Euglenophyceae algae. They are flagellates, with two flagella for locomotion. Anisonemia includes various phagotrophic species and a group of primary osmotrophic protists known as Aphagea.














