This article relies largely or entirely on a single source .(March 2024) |

In architecture, a spur (French griffe, German Eckblatt) is the ornament carved on the angles of the base of early columns. [1]
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source .(March 2024) |

In architecture, a spur (French griffe, German Eckblatt) is the ornament carved on the angles of the base of early columns. [1]
A spur consists of a projecting claw, which, emerging from the lower torus of the base, rests on the projecting angle of the square plinth. [1]
It is possibly to these that Pliny refers (Hist. Nat. XXVI. 42) when speaking of the lizard and frog carved on the bases (spirae) of the columns of the temples of Jupiter and Juno in the Portico of Octavius; the earliest known example is that of Diocletian's Palace at Split. [1]
In Romanesque work the oldest examples are those found on the bases in crypts, where they assumed various conventional forms; being, however, close to the eye, the spur soon developed into an elaborate leaf ornament, which in French 13th-century work and in the early English period is of great beauty; sometimes the spur takes the form of a fabulous animal, such as a griffin. [1]

A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member. The term column applies especially to a large round support with a capital and a base or pedestal, which is made of stone, or appearing to be so. A small wooden or metal support is typically called a post. Supports with a rectangular or other non-round section are usually called piers.

Pediments are a form of gable in classical architecture, usually of a triangular shape. Pediments are placed above the horizontal structure of the cornice, or entablature if supported by columns. In ancient architecture, a wide and low triangular pediment typically formed the top element of the portico of a Greek temple, a style continued in Roman temples. But large pediments were rare on other types of building before Renaissance architecture. For symmetric designs, it provides a center point and is often used to add grandness to entrances.

In architecture, a corbel is a structural piece of stone, wood or metal jutting from a wall to carry a superincumbent weight, a type of bracket. A corbel is a solid piece of material in the wall, whereas a console is a piece applied to the structure. A piece of timber projecting in the same way was called a "tassel" or a "bragger" in England.

In architecture, the capital or chapiter forms the topmost member of a column. It mediates between the column and the load thrusting down upon it, broadening the area of the column's supporting surface. The capital, projecting on each side as it rises to support the abacus, joins the usually square abacus and the usually circular shaft of the column. The capital may be convex, as in the Doric order; concave, as in the inverted bell of the Corinthian order; or scrolling out, as in the Ionic order. These form the three principal types on which all capitals in the classical tradition are based.

In architecture, an abacus is a flat slab forming the uppermost member or division of the capital of a column, above the bell. Its chief function is to provide a large supporting surface, tending to be wider than the capital, as an abutment to receive the weight of the arch or the architrave above. The diminutive of abacus, abaculus, is used to describe small mosaic tiles, also called abaciscus or tessera, used to create ornamental floors with detailed patterns of chequers or squares in a tessellated pavement.

A triforium is an interior gallery, opening onto the tall central space of a building at an upper level. In a church, it opens onto the nave from above the side aisles; it may occur at the level of the clerestory windows, or it may be located as a separate level below the clerestory. Masonry triforia are generally vaulted and separated from the central space by arcades. Early triforia were often wide and spacious, but later ones tend to be shallow, within the thickness of an inner wall, and may be blind arcades not wide enough to walk along. The outer wall of the triforium may itself have windows, or it may be solid stone. A narrow triforium may also be called a "blind-storey", and looks like a row of window frames.

A pinnacle is an architectural element originally forming the cap or crown of a buttress or small turret, but afterwards used on parapets at the corners of towers and in many other situations. The pinnacle looks like a small spire. It was mainly used in Gothic architecture.

An entablature is the superstructure of moldings and bands which lies horizontally above columns, resting on their capitals. Entablatures are major elements of classical architecture, and are commonly divided into the architrave, the frieze, and the cornice. The Greek and Roman temples are believed to be based on wooden structures, the design transition from wooden to stone structures being called petrification.

Moulding, or molding, also coving, is a strip of material with various profiles used to cover transitions between surfaces or for decoration. It is traditionally made from solid milled wood or plaster, but may be of plastic or reformed wood. In classical architecture and sculpture, the moulding is often carved in marble or other stones. In historic architecture, and some expensive modern buildings, it may be formed in place with plaster.

The hypotrachelium is the upper part or groove in the shaft of a Doric column, beneath the trachelium. The Greek form is hypotrakhelion.

A dentil is a small block used as a repeating ornament in the bedmould of a cornice. Dentils are found in ancient Greek and Roman architecture, and also in later styles such as Neoclassical, Federal, Georgian Revival, Greek Revival, Renaissance Revival, Second Empire, and Beaux-Arts architecture. Dentillation refers to use of a course of dentils.

An anta, or sometimes parastas, is a term in classical architecture describing the posts or pillars on either side of a doorway or entrance of a Greek temple – the slightly projecting piers which terminate the side walls. Antae are formed either by thickening the walls or by attaching a separate strip and can serve to reinforce brick walls, as in the Heraeum of Olympia.

A crocket is a small, independent decorative element common in Gothic architecture. The name derives from the diminutive of the Old French croc, meaning "hook", due to the resemblance of a crocket to a bishop's crook-shaped crosier.

Triglyph is an architectural term for the vertically channeled tablets of the Doric frieze in classical architecture, so called because of the angular channels in them. The rectangular recessed spaces between the triglyphs on a Doric frieze are called metopes. The raised spaces between the channels themselves are called femur in Latin or meros in Greek. In the strict tradition of classical architecture, a set of guttae, the six triangular "pegs" below, always go with a triglyph above, and the pair of features are only found in entablatures of buildings using the Doric order. The absence of the pair effectively converts a building from being in the Doric order to being in the Tuscan order.
A spur is a metal instrument fastened to the heel of a horse rider.
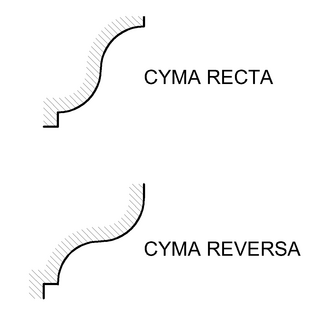
Ovolo is an Italian word that means "little egg". The ovolo or echinus is a convex decorative molding profile used in architectural ornamentation. Its profile is a quarter to a half of a more or less flattened circle.
This page is a glossary of architecture.

The fireplace mantel or mantelpiece, also known as a chimneypiece, originated in medieval times as a hood that projected over a fire grate to catch the smoke. The term has evolved to include the decorative framework around the fireplace, and can include elaborate designs extending to the ceiling. Mantelpiece is now the general term for the jambs, mantel shelf, and external accessories of a fireplace. For many centuries, the chimneypiece was the most ornamental and most artistic feature of a room, but as fireplaces have become smaller, and modern methods of heating have been introduced, its artistic as well as its practical significance has lessened.

English Gothic is an architectural style that flourished from the late 12th until the mid-17th century. The style was most prominently used in the construction of cathedrals and churches. Gothic architecture's defining features are pointed arches, rib vaults, buttresses, and extensive use of stained glass. Combined, these features allowed the creation of buildings of unprecedented height and grandeur, filled with light from large stained glass windows. Important examples include Westminster Abbey, Canterbury Cathedral and Salisbury Cathedral. The Gothic style endured in England much longer than in Continental Europe.

The Louis XIV style or Louis Quatorze, also called French classicism, was the style of architecture and decorative arts intended to glorify King Louis XIV and his reign. It featured majesty, harmony and regularity. It became the official style during the reign of Louis XIV (1643–1715), imposed upon artists by the newly established Académie royale de peinture et de sculpture and the Académie royale d'architecture. It had an important influence upon the architecture of other European monarchs, from Frederick the Great of Prussia to Peter the Great of Russia. Major architects of the period included François Mansart, Jules Hardouin-Mansart, Robert de Cotte, Pierre Le Muet, Claude Perrault, and Louis Le Vau. Major monuments included the Palace of Versailles, the Grand Trianon at Versailles, and the Church of Les Invalides (1675–1691).