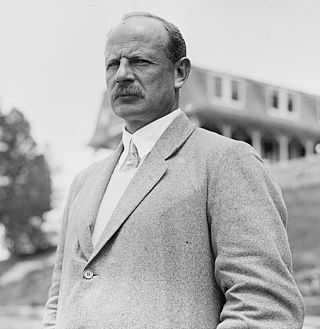Henley Royal Regatta is a rowing event held annually on the River Thames by the town of Henley-on-Thames, England. It was established on 26 March 1839. It differs from the three other regattas rowed over approximately the same course, Henley Women's Regatta, Henley Masters Regatta, and Henley Town and Visitors' Regatta, each of which is an entirely separate event.

Vesta Rowing Club is a rowing club based on the Tideway of the River Thames in Putney, London, England. It was founded in 1870.

The Thames Rowing Club (TRC) is a rowing club based on the tidal Thames as it flows through the western suburbs of London. The TRC clubhouse stands on Putney Embankment. The club was founded in 1860.
Timothy John Crooks is a former British rower who competed at the 1972 Summer Olympics and the 1976 Summer Olympics. He was seven times winner at Henley Royal Regatta and won the Wingfield Sculls three times.

Jack Beresford, CBE, born Jack Beresford-Wiszniewski, was a British rower who won five medals at five Olympic Games in succession. This record in Olympic rowing was not matched until 2000 when Sir Steve Redgrave won his sixth Olympic medal at his fifth Olympic Games.
Saint George Ashe was a British rower who competed in Rowing at the 1900 Summer Olympics in Paris winning the bronze medal in the single sculls, and won the Wingfield Sculls in 1904.
Julius Beresford (Wiszniewski) (18 July 1868 – 29 September 1959), also known as Berry or The Old Berry, was a British rower and coach. Beresford competed at the 1912 Summer Olympics in Stockholm, Sweden.

Raymond Broadley Etherington-Smith was an English doctor and rower who competed for Great Britain in the 1908 Summer Olympics.
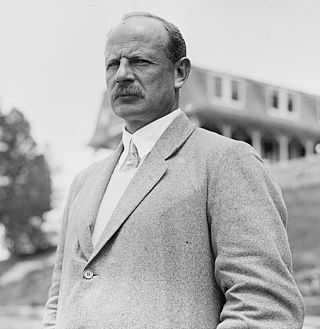
Guy Nickalls was a British rower who competed in the 1908 Summer Olympics as a member of the British eight that won gold, won 22 events at Henley Royal Regatta and won the Wingfield Sculls three times.
Donald Herbert Louis Gollan was a British rower who competed in the 1928 Summer Olympics, winning silver. He was partially deaf and communicated using British Sign Language.
The Thames is one of the main rowing rivers in Europe. Several annual competitions are held along its course, including the Henley Royal Regatta, The Boat Race and other long-distance events, called Head of the River races (Heads).

Walter Bradford Woodgate was a British barrister and oarsman who won the Wingfield Sculls three times, and various events at Henley Royal Regatta including the Silver Goblets five times and the Diamond Challenge Sculls once. He founded Vincent's Club as an undergraduate at Brasenose College, Oxford, in 1863, and in 1868 created the first coxless four by persuading Brasenose's cox to jump overboard after the start of Henley's Stewards' Challenge Cup.

University of London Boat Club is the rowing club for the University of London and its member institutions, many of which also have their own boat clubs. The club has its boathouse on the Thames in Chiswick, London, UK. It is a designated High-Performance Programme funded by British Rowing.

Alexander Alcée Casamajor was a British rower who won the Wingfield Sculls in six successive years and the Diamond Challenge Sculls at Henley Royal Regatta as well as being twice in the winning Grand Challenge Cup team.
William Fawcus was a British rower and member of Tynemouth Rowing Club. He won the Wingfield Sculls and the Diamond Challenge Sculls at Henley Royal Regatta in 1871, being the first provincial competitor to do so.
Thomas Brooks Bumpsted (1822–1917) was an English surgeon and rower who won both the Diamond Challenge Sculls and Wingfield Sculls in 1844. He later died at the age of 94 in the Chesterton district.
Thomas Anthony Fox was a doctor and rower who competed for Great Britain at the 1952 Summer Olympics and at the 1956 Summer Olympics. He won the Diamond Challenge Sculls and the Wingfield Sculls.
James Paine was an English rower who competed in the 19th century and won the Wingfield Sculls and events at Henley Royal Regatta.
The Argonaut Club was an English rowing club based on the Tideway of the River Thames that competed in the middle of the 19th century.
The Thames Club was an English rowing club based on the Tideway of the River Thames that competed in the middle of the 19th century.