
Copernicus is a lunar impact crater located in eastern Oceanus Procellarum. It was named after the astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus. It typifies craters that formed during the Copernican period in that it has a prominent ray system. It may have been created by debris from the breakup of the parent body of asteroid 495 Eulalia 800 million years ago.

Arzachel is a relatively young lunar impact crater located in the highlands in the south-central part of the visible Moon, close to the zero meridian. It lies to the south of the crater Alphonsus, and together with Ptolemaeus further north the three form a prominent line of craters to the east of Mare Nubium. The smaller Alpetragius lies to the northwest, and Thebit is to the southwest along the edge of the mare.

Fra Mauro is the worn remnant of a walled lunar plain. It is part of the surrounding Fra Mauro formation, being located to the northeast of Mare Cognitum and southeast of Mare Insularum. Attached to the southern rim are the co-joined craters Bonpland and Parry, which intrude into the formation forming inward-bulging walls. The crater is named after Italian geographer Fra Mauro.

Eratosthenes crater is a relatively deep lunar impact crater that lies on the boundary between the Mare Imbrium and Sinus Aestuum mare regions. It forms the western terminus of the Montes Apenninus mountain range. It is named after ancient Greek astronomer Eratosthenes of Cyrene, who estimated the circumference of the Earth, and the distance from the Earth to the Sun.

Bullialdus is a lunar impact crater located in the western part of the Mare Nubium. It was named after French astronomer Ismaël Boulliau. To the north by north-west is the broken-rimmed and lava-flooded crater Lubiniezky. South-west of Bullialdus lies the smaller crater König.

Wallace is the remains of a lunar impact crater that has been flooded by lava. It was named after British natural historian Alfred Russel Wallace. It lies in the southeastern part of Mare Imbrium, to the northeast of the crater Eratosthenes. The crater rim forms a somewhat polygonal outline, and is broken in the southeast. The floor is flat and devoid of significant features, but it is overlain by ray material from Copernicus to the southwest. The rim ascends to an altitude of 0.4 km above the lunar mare.

Deslandres is the heavily worn and distorted remains of a lunar impact crater. It is located to the southeast of the Mare Nubium, in the rugged southern highlands of the Moon. In dimension it is the third-largest crater formation on the visible Moon, being beaten only by Clavius and by the 303-kilometer-diameter walled plain Bailly. The northern and eastern parts of the floor display a relatively level surface, but it is pock-marked with numerous craters. There is a small region of mare material, due to basaltic lava, along the eastern interior floor.

Alpetragius is a lunar impact crater located on the eastern edge of Mare Nubium, to the southwest of the much larger crater Alphonsus. In the southeast is the prominent crater Arzachel, and to the west lies the flooded Lassell. Alpetragius is a Latinization of the name of Nur ad-Din al-Bitruji, a Spanish-Arab astronomer.

Burnham is a small crater located to the southeast of the crater Albategnius, in a relatively smooth area of the lunar surface. It was named after American astronomer Sherburne W. Burnham. To the southwest is Vogel.

Fauth is a small double-crater located at the edge of the rough southern ramparts of the prominent ray crater Copernicus on the Moon. It lies in the Mare Insularum, to the northeast of the crater Reinhold. The crater is named after German selenographer Philipp Johann Heinrich Fauth.

Aristillus is a prominent lunar impact crater that lies in the eastern Mare Imbrium. It was named after Greek astronomer Aristyllus. Directly to the south is the smaller crater Autolycus, while to the southwest is the large Archimedes. To the northeast are the craters Theaetetus and Cassini.
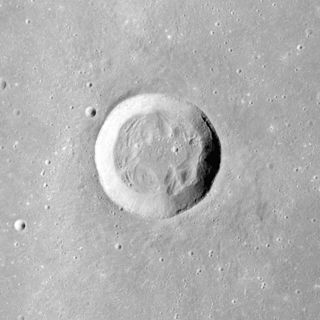
Bessel is a small lunar impact crater that is located in the southern half of the Mare Serenitatis. The crater was named after the German astronomer Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel in 1935. Despite its small size, this is the largest crater to lie entirely within the mare. It lies to the north-northeast of the crater Menelaus.

Descartes is a heavily worn lunar impact crater that is located in the rugged south-central highlands of the Moon. To the southwest is the crater Abulfeda. It is named after the French philosopher, mathematician and physicist René Descartes.

Gambart is a small lunar impact crater on the Mare Insularum, near the central region of the Moon. It is named after French astronomer Jean-Félix Adolphe Gambart. It can be located to the south-southeast of the prominent ray crater Copernicus. In the past, the floor of Gambart has been flooded with lava, leaving a relatively flat surface surrounded by a smooth but somewhat polygon-shaped outer rim. To the southwest of Gambart is an area of hilly terrain deposited from ejecta during the Mare Imbrium impact, known as the Fra Mauro Formation.

Julius Caesar is a lava-flooded lunar impact crater with a low, irregular, and heavily worn wall. Its diameter is 85 km. It was named after Roman statesman Julius Caesar. It is located to the west of Mare Tranquillitatis, and directly southeast of the crater Manilius on the Mare Vaporum. To the east is the rounded Sosigenes.

Pytheas is a small lunar impact crater located on the southern part of the Mare Imbrium, to the south of the crater Lambert. It was named after ancient Greek navigator and geographer Pytheas of Massalia.

Reinhold is a prominent lunar impact crater that lies to the south-southwest of the crater Copernicus, on the Mare Insularum. It was named after 16th century German astronomer and mathematician Erasmus Reinhold. To the southwest is the slightly smaller crater Lansberg.

Torricelli is a lunar impact crater in the eastern part of the Sinus Asperitatis, to the south of the Mare Tranquillitatis. It was named after Italian physicist Evangelista Torricelli. The western rim of the crater is broken open and joined to a smaller crater to the west. The entire formation has a pear-shaped appearance. Torricelli lies in the northeastern part of a circular formation of rises in the lunar mare, possibly the remains of a crater formation buried by lava.

Davy is a small lunar impact crater that is located on the eastern edge of the Mare Nubium. It was named after British physicist Humphry Davy. It overlies the lava-flooded remains of the satellite crater Davy Y to the east, a formation which contains a crater chain designated Catena Davy. To the southeast of Davy is the prominent crater Alphonsus.

Lassell is a small lunar impact crater that is located in the eastern part of the Mare Nubium. It was named after British astronomer William Lassell. It lies to the west of the crater Alpetragius and southwest of Alphonsus.






















