| |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.109.946 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C28H26N4O3 |
| Molar mass | 466.541 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
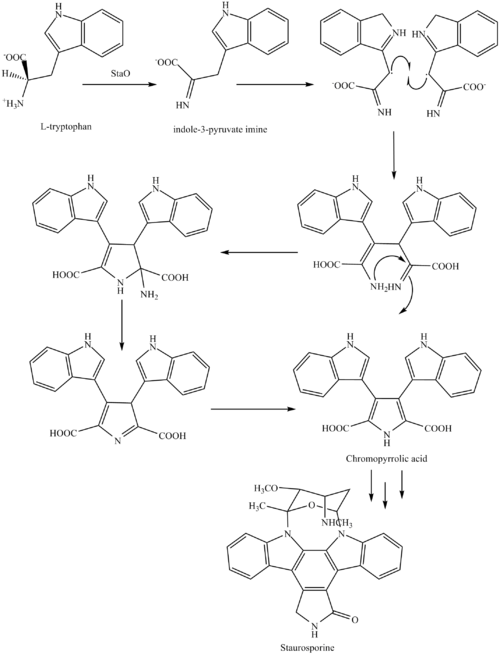
Staurosporine (antibiotic AM-2282 or STS) is a natural product originally isolated in 1977 from the bacterium Streptomyces staurosporeus . [1] It was the first of over 50 alkaloids that were discovered to share this type of bis-indole chemical structure. The chemical structure of staurosporine was elucidated by X-ray crystalography in 1994. [2]
Contents
- Biological activities
- Chemistry family
- Biosynthesis
- Research in preclinical use
- List of compounds closely related to Staurosporine
- References
Staurosporine was discovered to have biological activities ranging from anti-fungal to anti-hypertensive. [3] The interest in these activities resulted in a large investigative effort in chemistry and biology and the discovery of the potential for anti-cancer treatment.
![Structure of an indolo[2,3-a]pyrrole[3,4-c]carbazol with C-7 highlighted Structure of aIndolo(2,3-a)pyrrole(3,4-c)carbazol.svg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/9a/Structure_of_aIndolo%282%2C3-a%29pyrrole%283%2C4-c%29carbazol.svg/330px-Structure_of_aIndolo%282%2C3-a%29pyrrole%283%2C4-c%29carbazol.svg.png)