
George O. Poinar Jr. is an American entomologist and writer. He is known for popularizing the idea of extracting DNA from insects fossilized in amber, an idea which received widespread attention when adapted by Michael Crichton for the book and movie Jurassic Park.

Dominican amber is amber from the Dominican Republic derived from resin of the extinct tree Hymenaea protera.

The Chrysomelinae are a subfamily of leaf beetles (Chrysomelidae), commonly known as broad-bodied leaf beetles or broad-shouldered leaf beetles. It includes some 3,000 species around the world.
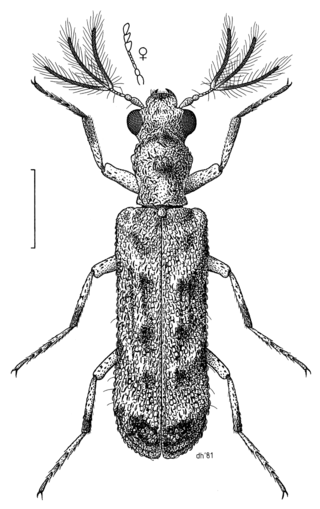
The Bostrichidae are a family of beetles with more than 700 described species. They are commonly called auger beetles, false powderpost beetles, or horned powderpost beetles. The head of most auger beetles cannot be seen from above, as it is downwardly directed and hidden by the thorax. Exceptions are the powderpost beetles, and members of the subfamily Psoinae.

Lepicerus is a genus of myxophagan beetles containing three described species in the family Lepiceridae; it is the only extant genus in the family, with another genus, Lepiceratus only known from fossils. Extant species occur in the Neotropics, from Mexico south to Venezuela and Ecuador. Fossils referrable to the genus are known from the early Late Cretaceous of Southeast Asia.

Lutzomyia adiketis is an extinct species of sandfly in the moth fly subfamily Phlebotominae. L. adiketis is a vector of the extinct Paleoleishmania neotropicum and both species are solely known from early Miocene Burdigalian stage Dominican amber deposits on the island of Hispaniola.

Paleoleishmania is an extinct genus of kinetoplastids, a monophyletic group of unicellular parasitic flagellate protozoa. At present it is placed in the family Trypanosomatidae. The genus contains two species, the type species Paleoleishmania proterus and the later described Paleoleishmania neotropicum.
Tertiapatus is an extinct genus of supposed onychophoran known from Dominican amber deposits. The only known species described is Tertiapatus dominicanus. Other authors have doubted its status as an onchyophoran, due to its arthropodized antennae and articulated exoskeleton, which suggests that it is likely an arthropod.
Succinipatopsis is an extinct genus, originally described as an onychophoran known from Eocene-aged Baltic amber. The only known species is Succinipatopsis balticus. However, other authors have doubted its status as an onchyophoran, due to its skin not closely resembling that of onchyophorans, and lacking any diagnostic characters of the group.

Vetufebrus is an extinct genus of haemospororida in the family Plasmodiidae. At the time of its description the new genus comprised a single species Vetufebrus ovatus known from a single Miocene Dominican amber fossil found on Hispaniola. V. ovatus was vectored by Enischnomyia stegosoma, the first fossil streblid bat fly described from a fossil, and the only member of the subfamily Nycterophiliinae described from Hispaniola. V. ovatus is the first instance of a Streblidae bat fly as a host for a malarial parasite.
Termitaradus protera is an extinct species of termite bug in the family Termitaphididae known from several Late Oligocene to Early Miocene fossils found in Mexico. T. protera is the only species in the extant genus Termitaradus to have been described from fossils found in Mexican amber and is one of four species from new world amber; the others are Termitaradus avitinquilinus, Termitaradus dominicanus and Termitaradus mitnicki. T. protera was also the first termite bug described from the fossil record.

Eucnemidae, or false click beetles, are a family of elateroid beetles including about 1700 species distributed worldwide.
Acanthognathus poinari is an extinct species of ant in the subfamily Myrmicinae known from a single possibly Miocene fossil found on Hispaniola. A. poinari is the first species of the ant genus Acanthognathus to have been described from fossils found in Dominican amber and is one of several species of Acanthognathus found in the Greater Antillas.
The La Toca Formation is a geologic formation in the northern and eastern part of the Dominican Republic. The formation, predominantly an alternating sequence of marls and turbiditic sandstones, breccias and conglomerates, is renowned for the preservation of insects and other arthropods in amber, known as Dominican amber. The formation is dated to the Burdigalian to Langhian stages of the Miocene period.

Formicodiplogaster is an extinct form genus of nematodes in the family Diplogasteridae which currently includes a single described species Formicodiplogaster myrmenema. The species is known from early Miocene fossils found on Hispaniola. F. myrmenema has been preserved in association with Azteca alpha, one of only two known fossil species in the ant genus Azteca.

Azteca alpha is an extinct species of ant in the subfamily Dolichoderinae known from possibly Miocene fossils found on Hispaniola. A. alpha is one of only two species in the genus Azteca to have been described from fossils, both found in Dominican amber. It is the host for a fossil nematode, and has been preserved with scale insects.
Baris grossacavis is a species of extinct beetle in the genus Baris of the family Curculionidae.

Enischnomyia is an extinct genus of bat fly in the family Streblidae. At the time of its description the new genus comprised a single species, Enischnomyia stegosoma, known from a single Miocene fossil found on Hispaniola. E. stegosoma was the first fossil streblid bat fly described from a fossil, and the only member of the subfamily Nycterophiliinae described from Hispaniola. The species is host for the plasmodiid Vetufebrus ovatus preserved in its salivary glands and midgut.
Megarididae is a family of true bugs in the superfamily Pentatomoidea. The family consists of a single extant genus Megaris with about 16 species restricted to the Neotropical Realm and a fossil is known from Dominican amber.
This paleoentomology list records new fossil insect taxa that were described during the year 2014, as well as notes other significant paleoentomology discoveries and events which occurred during that year.











