
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen or sulfur. More rarely still, they may contain elements such as phosphorus, chlorine, and bromine.

Aconitine is an alkaloid toxin produced by various plant species belonging to the genus Aconitum, known also commonly by the names wolfsbane and monkshood. Monkshood is notorious for its toxic properties.

Solanine is a glycoalkaloid poison found in species of the nightshade family within the genus Solanum, such as the potato, the tomato, and the eggplant. It can occur naturally in any part of the plant, including the leaves, fruit, and tubers. Solanine has pesticidal properties, and it is one of the plant's natural defenses. Solanine was first isolated in 1820 from the berries of the European black nightshade, after which it was named. It belongs to the chemical family of saponins.

A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical synthesis and have played a central role in the development of the field of organic chemistry by providing challenging synthetic targets. The term natural product has also been extended for commercial purposes to refer to cosmetics, dietary supplements, and foods produced from natural sources without added artificial ingredients.

Phytochemistry is the study of phytochemicals, which are chemicals derived from plants. Phytochemists strive to describe the structures of the large number of secondary metabolites found in plants, the functions of these compounds in human and plant biology, and the biosynthesis of these compounds. Plants synthesize phytochemicals for many reasons, including to protect themselves against insect attacks and plant diseases. The compounds found in plants are of many kinds, but most can be grouped into four major biosynthetic classes: alkaloids, phenylpropanoids, polyketides, and terpenoids.

Plant defense against herbivory or host-plant resistance (HPR) is a range of adaptations evolved by plants which improve their survival and reproduction by reducing the impact of herbivores. Plants can sense being touched, and they can use several strategies to defend against damage caused by herbivores. Many plants produce secondary metabolites, known as allelochemicals, that influence the behavior, growth, or survival of herbivores. These chemical defenses can act as repellents or toxins to herbivores or reduce plant digestibility. Another defensive strategy of plants is changing their attractiveness. To prevent overconsumption by large herbivores, plants alter their appearance by changing their size or quality, reducing the rate at which they are consumed.

Hordenine is an alkaloid of the phenethylamine class that occurs naturally in a variety of plants, taking its name from one of the most common, barley. Chemically, hordenine is the N-methyl derivative of N-methyltyramine, and the N,N-dimethyl derivative of the well-known biogenic amine tyramine, from which it is biosynthetically derived and with which it shares some pharmacological properties. As of September 2012, hordenine is widely sold as an ingredient of nutritional supplements, with the claims that it is a stimulant of the central nervous system, and has the ability to promote weight loss by enhancing metabolism. In experimental animals, given sufficiently large doses parenterally, hordenine does produce an increase in blood pressure, as well as other disturbances of the cardiovascular, respiratory, and nervous systems. These effects are generally not reproduced by oral administration of the drug in test animals, and virtually no scientific reports of the effects of hordenine in human beings have been published.

A mitotic inhibitor, microtubule inhibitor, or tubulin inhibitor, is a drug that inhibits mitosis, or cell division, and is used in treating cancer, gout, and nail fungus. These drugs disrupt microtubules, which are structures that pull the chromosomes apart when a cell divides. Mitotic inhibitors are used in cancer treatment, because cancer cells are able to grow through continuous division that eventually spread through the body (metastasize). Thus, cancer cells are more sensitive to inhibition of mitosis than normal cells. Mitotic inhibitors are also used in cytogenetics, where they stop cell division at a stage where chromosomes can be easily examined.

Chemical defense is a strategy employed by many organisms to avoid consumption by producing toxic or repellent metabolites or chemical warnings which incite defensive behavioral changes. The production of defensive chemicals occurs in plants, fungi, and bacteria, as well as invertebrate and vertebrate animals. The class of chemicals produced by organisms that are considered defensive may be considered in a strict sense to only apply to those aiding an organism in escaping herbivory or predation. However, the distinction between types of chemical interaction is subjective and defensive chemicals may also be considered to protect against reduced fitness by pests, parasites, and competitors. Repellent rather than toxic metabolites are allomones, a sub category signaling metabolites known as semiochemicals. Many chemicals used for defensive purposes are secondary metabolites derived from primary metabolites which serve a physiological purpose in the organism. Secondary metabolites produced by plants are consumed and sequestered by a variety of arthropods and, in turn, toxins found in some amphibians, snakes, and even birds can be traced back to arthropod prey. There are a variety of special cases for considering mammalian antipredatory adaptations as chemical defenses as well.
3-Alkylpyridinium (3-AP) compounds are natural chemical compounds that are found in marine sponges belonging to the order Haplosclerida. Some polymers derived from 3-APs are anticholinesterase agents and show hemolytic and cytotoxic activities. More than 70 structurally different 3-APs have been isolated from marine sponges. However, not all such sponges contain 3-AP compounds. Variation in content of 3-APs has been detected even within a single sponge species collected from different geographical area. Although 3-APs look structurally quite simple, the structure elucidation by NMR spectroscopy is complicated by the fact that most of the methylene groups in the alkyl chains show the same chemical shift. Therefore, the 3-APs are an ideal test case for a combined approach of NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry.

Callyspongia truncata is a species of marine sea sponge. Like all marine sponges, C. truncata is a member of phylum Porifera and is defined by its filter-feeding lifestyle and flagellated choanocytes, or collar cells, that allow for water movement and feeding. It is a species of demosponge and a member of Demospongiae, the largest class of sponges as well as the family Callyspongiidae. C. truncata is most well known for being the organism from which the polyketide Callystatin A was identified. Callystatin A is a polyketide natural product from the leptomycin family of antibiotics. It was first isolated in 1997 from this organism, which was collected from the Goto Islands in the Nagasaki Prefecture of Japan by the Kobayashi group. Recent studies have revealed numerous other bioactive compounds that have been found in this species.

Akuammicine is a monoterpene indole alkaloid of the Vinca sub-group. It is found in the Apocynaceae family of plants including Picralima nitida, Vinca minor and the Aspidosperma.

Oroidin is a bromopyrrole alkaloid, originally isolated from marine sponges in the genus Agelas. Its complex structure leads to wide biological activities, which makes Oroidin a potential drug candidate for various diseases. It also serves as chemical defense in marine sponges.

Salinispora is a genus of obligately aerobic, gram-positive, non-acid-fast bacteria belonging to the family of Micromonosporaceae. They are heterotrophic, non-motile, and obligately grow under high osmotic/ionic-strength conditions. They are the first identified genus of gram-positive bacteria which has a high osmotic/ionic-strength requirement for survival. They are widely abundant in tropical marine sediments and were first identified in 2002. This genus of bacteria has potential biotechnological significance due to their production of novel secondary metabolites which can be used pharmaceutically.
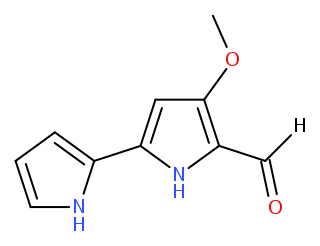
Tambjamines are a group of natural products that are structurally related to the prodiginines. They are enamine derivatives of 4-methoxy-2,2'-bipyrrole-5-carboxaldehyde (MBC).

Geodia barretti is a massive deep-sea sponge species found in the boreal waters of the North Atlantic Ocean, and is fairly common on the coasts of Norway and Sweden. It is a dominant species in boreal sponge grounds. Supported by morphology and molecular data, this species is classified in the family Geodiidae.

Apparicine is a monoterpenoid indole alkaloid. It is named after Apparicio Duarte, a Brazilian botanist who studied the Aspidosperma species from which apparicine was first isolated. It was the first member of the vallesamine group of alkaloids to be isolated and have its structure established, which was first published in 1965. It has also been known by the synonyms gomezine, pericalline, and tabernoschizine.

Aplysioviolin is a purple-colored molecule secreted by sea hares of the genera Aplysia and Dolabella to deter predators. Aplysioviolin is a chemodeterrent, serving to dispel predators on olfactory and gustatory levels as well as by temporarily blinding predators with the molecule's dark color. Aplysioviolin is an important component of secreted ink and is strongly implicated in the sea hares' predatory escape mechanism. While the ink mixture as a whole may produce dangerous hydrogen peroxide and is relatively acidic, the aplysioviolin component alone has not been shown to produce human toxicity.
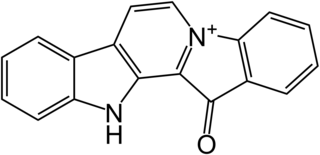
Fascaplysin is a marine alkaloid based on 12H-pyrido[1–2-a:3,4-b′]diindole ring system. It was first isolated as a red pigment from the marine sponge Fascaplysinopsis reticulata that was collected in the South Pacific near Fiji in 1988. Fascaplysin possesses a broad range of in vitro biological activities including analgesic, antimicrobial, antifungal, antiviral, antimalarial, anti-angiogenic, and antiproliferative activity against numerous cancer cell lines.


















