
Rio Grande do Sul is a state in the southern region of Brazil. It is the fifth-most populous state and the ninth-largest by area. Located in the southernmost part of the country, Rio Grande do Sul is bordered clockwise by Santa Catarina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, the Uruguayan departments of Rocha, Treinta y Tres, Cerro Largo, Rivera, and Artigas to the south and southwest, and the Argentine provinces of Corrientes and Misiones to the west and northwest. The capital and largest city is Porto Alegre. The state has the highest life expectancy in Brazil, and the crime rate is relatively low compared to the Brazilian national average. Despite the high standard of living, unemployment is still high in the state, as of 2017. The state has 5.4% of the Brazilian population and it is responsible for 6.6% of the Brazilian GDP.

Pelotas is a Brazilian city and municipality (município), the fourth most populous in the southern state of Rio Grande do Sul, after Porto Alegre, Caxias do Sul and Canoas. It is located 270 km (168 mi) from Porto Alegre, the state's capital city, and 130 km (80.8 mi) from the Uruguayan border. The Lagoa dos Patos lies to the east and the São Gonçalo Channel lies to the south, separating Pelotas from the city of Rio Grande.

The Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul is a Brazilian public federal research university based in Porto Alegre, Rio Grande do Sul. UFRGS is among the largest and highest-rated universities in Brazil, having one of the largest number of scientific publications. From 2012 to 2019, the university was elected as the best federal university of Brazil. UFRGS has over 31,000 undergraduate students, over 12,000 graduate students, and more than 2,600 faculty members. As a Brazilian public federal institution, students do not pay tuition fees to enroll in courses offered by the university.

The Federal University of Santa Maria is a Brazilian public university located in Santa Maria, in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, funded by the federal government of Brazil. It was founded in 1960, by Professor José Mariano da Rocha Filho. Its campuses span over 1,837.72 ha, with a total of 386,968 m² of buildings and 28,307 students.

The Federal Center for Technological Education "Celso Suckow da Fonseca", also known as Federal Center for Technological Education of Rio de Janeiro, is one of the most traditional Brazilian federal educational institution subordinated to the Brazilian Ministry of Education.

Arroio Grande is a Brazilian municipality in the southern part of the state of Rio Grande do Sul. The population is 18,238 in an area of 2513.60 km². Its second industry is agriculture which was primary until the 1970s, it currently has more urban population (80%) than rural (20%). Much of the area is made up of plains.

Serras de Sudeste is a dissected plateau, also named Planalto Dissecado de Sudeste or Escudo Sul-Rio-Grandense, located in the southeastern portion of Rio Grande do Sul state in southernmost Brazil, near Uruguay.

The Federal Institute of São Paulo, or in full: Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology of São Paulo is an institution that offers high education and professional education by having a pluricurricular form. It is a multicampi institution, specializing in offering professional and technological education in different areas of knowledge. It was known previously as Federal Center of Technological Education of São Paulo. IFSP is one of the five Federal Colleges in São Paulo, the other ones being ITA, UFSCar, UNIFESP and UFABC.
2010 Copa FGF, also known as Copa Enio Costamilan, is the 7th edition of Copa FGF. 18 team participated in the tournament.
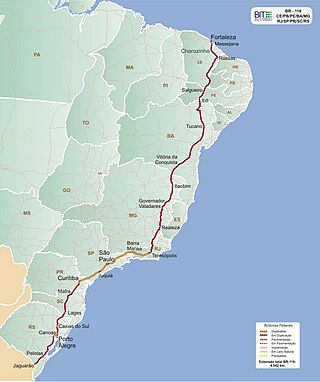
BR-116 is a federal route of highways of Brazil and the longest highway in the country, with 4,542 km (2,822 mi) of extension. The road connect Fortaleza, Ceará, one of the largest Northeast Brazil metropolises, to the southern city of Jaguarão, Rio Grande do Sul, in the border with Uruguay. It is also the longest highway in the country to be completely paved. It is considered one of the most important highways in the country, along with BR-101.

The Federal Institute of Rio Grande do Sul, or in full: Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology of Rio Grande do Sul is an institution that offers high and professional educations by having a pluricurricular form. It is an multicampi institution, especialized in offering professional and technological education in different areas of knowledge.

Sudeste Rio-Grandense is one of the seven Mesoregions of the state of Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil. It consists of 25 municipalities, grouped in four Microregions:

The Pernambuco Federal Institute of Education, Science, and Technology (Portuguese: Instituto Federal de Educação, Ciência e Tecnologia de Pernambuco, IFPE) is a Brazilian institution of higher education located in Pernambuco State, Brazil. Its rectory is headquartered in Recife, Pernambuco. The IFPE is one of the oldest and most traditional among the Federal Institutes, it has 9 campuses and offers Technical, undergraduate and postgraduate courses, as well as researches and scientific production.

The Instituto Federal de Educação, Ciência e Tecnologia de Mato Grosso (IFMT), also known as the late Centro Federal de Educação Tecnológica de Mato Grosso, is an institution that offers high and professional educations by having a pluricurricular form. It is an multicampi institution, especialized in offering professional and technological education.

Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology is a Brazilian institution of higher education with a number of campuses around Brazil. Comprising Brazil's Federal Network of Vocational, Scientific and Technological Education, it offers students a wide range of curricula, including both general education and specialized vocational and professional training in science, technology, and pedagogy.

The Instituto Federal de Educação, Ciência e Tecnologia do Acre (IFAC) is an institution that offers high and professional educations by having a pluricurricular form. It is a multicampi institution, especialized in offering professional and technological education in different areas of knowledge.

The Federal Institute of Education, Science, and Technology of Ceará(IFCE) is a Federal Institute of higher, basic, and professional education, pluricurricular and multicampus, operating in Ceará, Brazil. Specialized in offering professional and technological education in the different teaching modalities, IFCE is based on the conjugation of technical and technological knowledge with pedagogical practice and operates in all regions of the state through its 32 campuses, serving more than 33,000 students in a total installed area of over 5.9 million m2.














