Related Research Articles

The Balkans, also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the whole of Bulgaria. The Balkan Peninsula is bordered by the Adriatic Sea in the northwest, the Ionian Sea in the southwest, the Aegean Sea in the south, the Turkish Straits in the east, and the Black Sea in the northeast. The northern border of the peninsula is variously defined. The highest point of the Balkans is Mount Musala, 2,925 metres (9,596 ft), in the Rila mountain range, Bulgaria.
The history of North Macedonia encompasses the history of the territory of the modern state of North Macedonia.

The Central European Free Trade Agreement (CEFTA) is an international trade agreement between countries mostly located in Southeastern Europe. Founded by representatives of Poland, Hungary and Czechoslovakia, CEFTA expanded to Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Moldova, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia and the UNMIK.

Europe, the westernmost portion of Eurasia, is often divided into regions and subregions based on geographical, cultural or historical factors. Since there is no universal agreement on Europe's regional composition, the placement of individual countries may vary based on criteria being used. For instance, the Balkans is a distinct geographic region within Europe but individual countries may alternatively be grouped into Southern Europe, Southeastern Europe, or less commonly East Central Europe.
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe (SEE) is a geographical subregion of Europe, consisting primarily of the Balkans, as well as adjacent regions and archipelagos. Sovereign states and territories that are included in the region are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Greece, Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, and the European part of Turkey. Sometimes, Moldova and Slovenia are also included. The largest cities of the region are Istanbul, Athens, Bucharest, Sofia, and Belgrade.
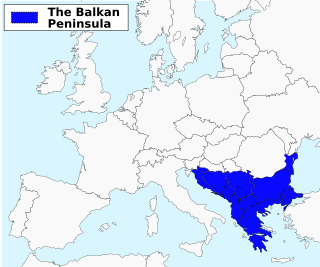
The Balkans and parts of this area are alternatively situated in Southeast, Southern, Eastern Europe and Central Europe. The distinct identity and fragmentation of the Balkans owes much to its common and often turbulent history regarding centuries of Ottoman conquest and to its very mountainous geography.
South East Europe Media Organisation (SEEMO) is a regional non-governmental, non-profit network of editors, media executives and leading journalists in Southeast, South, East and Central Europe. The organization aims to create a bridge between international media activities and the media developments in the region. It has headquarters and national committees in several countries. In total 33 member states or territories are included in SEEMO: Albania, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Estonia, Georgia, Greece, Hungary, Kazakhstan, Kosovo, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Moldova, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Poland, Romania, Russia, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Turkey, Ukraine and Uzbekistan

The South-East European Cooperation Process (SEECP) was launched on Bulgaria's initiative in 1996. At the Bulgaria-chaired meeting in Sofia, the Southeast Europe (SEE) countries laid the foundations for regional co-operation for the purposes of creating an atmosphere of trust, good neighbourly relations and stability.

The 2008 Bucharest Summit or the 20th NATO Summit was a NATO summit organized in the Palace of the Parliament, Bucharest, Romania on 2 – 4 April 2008.

The official language of North Macedonia is Macedonian, while Albanian has co-official status. Macedonian is spoken by roughly two-thirds of the population natively, and as a second language by much of the rest of the population. Albanian is the largest minority language. There are a further five national minority languages: Turkish, Romani, Serbian, Bosnian, and Aromanian. The Macedonian Sign Language is the country's official sign language.
Ohrid Summit 2008 was the name of the 15th Meeting of Presidents of Central European States that took place from 2 May to 3 May 2008 in the city of Ohrid, Republic of Macedonia. Prior to the summit, the President of the Republic of Macedonia, Branko Crvenkovski, said the Macedonians "will be especially honored as the host of the greatest political event ever organized" in his country.

Kosovo–North Macedonia relations are diplomatic relations between the Republic of Kosovo and the Republic of North Macedonia.

Gjorge Ivanov is a Macedonian politician, who served as the 4th President of North Macedonia from 2009 to 2019.

North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia. It is a landlocked country bordering Kosovo to the northwest, Serbia to the north, Bulgaria to the east, Greece to the south, and Albania to the west. It constitutes approximately the northern third of the larger geographical region of Macedonia. Skopje, the capital and largest city, is home to a quarter of the country's 1.83 million people. The majority of the residents are ethnic Macedonians, a South Slavic people. Albanians form a significant minority at around 25%, followed by Turks, Romani, Serbs, Bosniaks, Aromanians and a few other minorities.

Fatmir Besimi is a Macedonian politician and economist of Albanian ethnicity. He currently served for Minister of Finance in North Macedonia, He also served twice as Minister of Economy then Minister of Defence and after that he was Deputy Prime Minister of the Government of the Republic of Macedonia in charge of European Affairs. In 2010 he was selected as one of the top European Ministers in the group of Young Global Leaders by World Economic Forum.
Conference of Western Balkan States was a 28 August 2014 conference of heads of states and governments of Western Balkans region initiated by German chancellor Angela Merkel. An idea for organization of conference came in light of the celebration of the 100th anniversary of the beginning of World War I. It is the first conference in this framework and organizers expressed their desire to continue it in future with Vienna and Paris mentioned as a potential next hosts after Berlin. Günther Oettinger confirmed at conference that event will be organised annually with Vienna as a host city in 2015 and Paris in 2016.

A shootout which erupted during a raid between the Macedonian police and an armed group identifying itself as the National Liberation Army (NLA) occurred on 9 May 2015 in the northern Macedonian town of Kumanovo. During the shootings, eight Macedonian policemen and 10 of the militants were killed, while 37 officers were wounded and hospitalized. The shooting ended on 10 May 2015, in an operation by the Macedonian police and armed forces, in which 28 men were arrested and charged with terrorism-related charges by the Macedonian authorities.

The Berlin Process is an intergovernmental cooperation initiative linked to the future enlargement of the European Union. It started with the 2014 Berlin Conference, which was followed by the 2015 Vienna Summit, the 2016 Paris Summit, the 2017 Trieste Summit, the 2018 London Summit and the 2019 Poznań Summit. The Berlin Process was initiated in order to consolidate and maintain the dynamics of the EU integration process in light of increased euroscepticism and the five-year moratorium on enlargement announced by Commission President Jean Claude Juncker.

The Open Balkan is an economic and political zone of three member states in the Balkans, those being Albania, North Macedonia and Serbia. The zone has a total area of 131,935 km2 (50,940 sq mi) and an estimated total population of almost 12 million located in Central and Southern Europe. The official languages are Albanian, Macedonian and Serbian. Its administrative centres are the cities of Belgrade, Skopje and Tirana. With the establishment of the zone, all three member states aim to increase trade and cooperation as well as improve bilateral relations.
References
- ↑ Sitel Television - Ohrid Summit (in Macedonian)
- ↑ Nova TV - No answer from the Greek President (in Macedonian)
- ↑ Time.MK - Greek and Bulgarian President won't come to Ohrid Summit (in Macedonian)
- ↑ 24 Vesti - Albanian President won't be a part of the Ohrid Summit (in Macedonian)
- ↑ B92 News - Serbia, two more countries block Kosovo
- ↑ B92 News - Macedonia "protects dignity and integrity," cancels summit
- ↑ B92 News - EU would like Kosovo to take part in Ohrid Summit
- ↑ Time.MK - Ohrid Summit 2013