The Brantas is the longest river in East Java, Indonesia. It has a length of 320 km, and drains an area of over 11,000 km2 from the southern slope of Mount Kawi-Kelud-Butak, Mount Wilis, and the northern slopes of Mount Liman-Limas, Mount Welirang, and Mount Anjasmoro. Its course is semi-circular or spiral in shape: at its source, the river heads southeast, but gradually curves south, then southwest, west, then north, and finally it flows generally eastward at the point where it branches off to become the Kalimas and Porong River.

The Asahan River is one of the principal rivers in North Sumatra, Indonesia, that begins in Porsea, Toba Regency near the southeast corner of Lake Toba.

The Indragiri River is a river in Sumatra, in the Indonesian province of Riau, about 800 km northwest of the capital Jakarta. Formed by the union of the Ombilin River and the Sinamar River, the Indragiri empties into the Strait of Malacca. The middle part that flows in the Kuantan Singingi Regency is called Batang Kuantan.
The Bohorok River is a river of the Langkat Regency in North Sumatra province, Indonesia, about 1,400 km northwest of the capital Jakarta. It is a tributary of Wampu River.

Melawi River is a river in north-western Borneo, Indonesia, about 900 km northeast of the capital Jakarta. It is a tributary of the Kapuas River.

The Mina River is a river of Timor, in the province of East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia, about 2000 km east of the capital Jakarta. Above this river also stretches the Noelmina Bridge which connects Kupang with the South Central Timor Regency.

Asem River is a river in northern West Java province on Java island, Indonesia. The river rises on Mount Tangkuban Perahu and discharges into the Bay of Ciasem, Java Sea, traversing Ciasem, Subang Regency, around 90 km east of the capital Jakarta.
Pemali River is a river in northern Central Java, Indonesia, about 250 km east of the capital Jakarta.
The Porong River is a river flowing through Sidoarjo, East Java, Indonesia, about 700 km east of the capital Jakarta. It is one of the main distributaries of the Brantas River that discharges into the Bali Sea, close to the Madura Strait, and is the main outlet for the Lusi mudflow.
Barumun River is a Sumatran river that begins in Siraisan, Padang Lawas Regency in the southeastern North Sumatra, Indonesia, about 1,200 km northwest of the capital Jakarta.
Mandau River is a river in Riau province of central Sumatra island, Indonesia, about 1,000 km northwest of the capital Jakarta. It is a tributary of the Siak River.

The Ombilin River is a river in West Sumatra, Indonesia, about 900 km northwest of the capital Jakarta.
The Merangin River is a river in Jambi province, Sumatra island, Indonesia, about 600 km northwest of the capital Jakarta. It is a tributary of the Batang Hari River, through Tembesi River.

Rokan River is a river in Riau province, central-eastern Sumatra, Indonesia, about 1,100 km northwest of the capital Jakarta.

The Wampu River is a river in North Sumatra, Indonesia, about 1500 km northwest of the capital Jakarta.
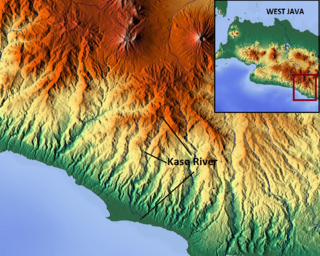
The Kaso River, also Ci Kaso, is a river in the Garut Regency of West Java, Indonesia, about 190 km southeast of the capital Jakarta. Coal-bearing sandstones, clays and limestones are typical geological traits of the Bandung area of southern Java. The river flow merges with the Cipalebuh River, near the center of Pameungpeuk, southern coastal area of Garut, West Java.
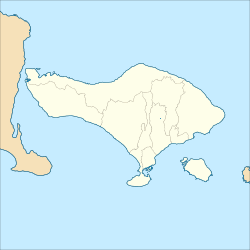
The Telaga Waja is a river which is situated in eastern Bali, Indonesia. It rises on the slope of Mount Abang and passes through towns and wilderness slopes along the region of Rendang Village, reaching the sea in Klungkung Regency.

The Tabalong River is a river traversing Tabalong Regency, in the province of South Kalimantan, Indonesia. The river flows into the Negara River. It is a confluence of two tributaries: the Left Tabalong and Right Tabalong rivers.

Sambas River, or specifically referred to Big Sambas River, is a river in Sambas Regency, West Kalimantan, Indonesia. The upstream is located in Kabupaten Bengkayang, flowing through the city of Sambas, continuing to Pemangkat where it discharges into South China Sea.
The Simpang-kanan River is a river in southern Sumatra, Indonesia, about 600 km northwest of the capital Jakarta. It is a tributary of the Rawas River.