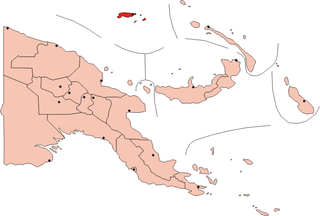
The Admiralty Islands are an archipelago group of 18 islands in the Bismarck Archipelago, to the north of New Guinea in the South Pacific Ocean. These are also sometimes called the Manus Islands, after the largest island.

The Bismarck Archipelago is a group of islands off the northeastern coast of New Guinea in the western Pacific Ocean and is part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. Its area is about 50,000 square km.
The Schouten Islands are an island group of Papua province, eastern Indonesia in the Cenderawasih Bay 50 km off the north-western coast of the island of New Guinea. The group consists of the main islands of Biak, Supiori and Numfor, and numerous smaller islands, mostly covered in rain forest.
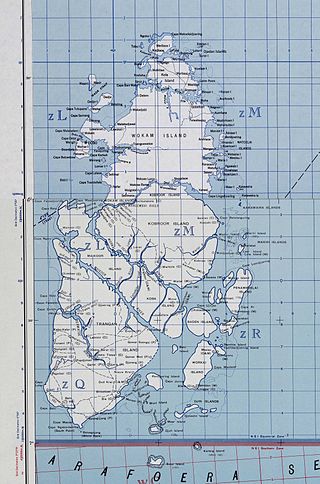
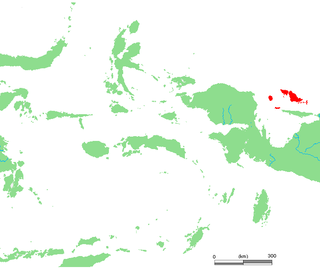
The Aru Islands Regency is a group of about 95 low-lying islands in the Maluku Islands of eastern Indonesia. It also forms a regency of Maluku Province, with a land area of 6,426.77 square kilometres. At the 2011 Census the Regency had a population of 84,138; the 2020 Census produced a total of 102,237. Some sources regard the archipelago as part of Asia, while others regard it as part of Melanesia.

West Papua, formerly Irian Jaya Barat, is a province of Indonesia. It covers the two western peninsulas of the island of New Guinea, the eastern half of the Bird's Head Peninsula and the Bomberai Peninsula, along with nearby smaller islands. The province is bordered to the north by the Pacific Ocean, to the west by the Halmahera Sea and the Ceram Sea, to the south by the Banda Sea, and to the east by the province of Central Papua and the Cenderawasih Bay. Manokwari is the province's capital and largest city. West Papua is the second-least populous province in Indonesia. It had a population of 1,134,068 at the 2020 Census, and the official estimate for mid 2022 was 1,183,307. However the total area and population will be reduced by the Parliamentary decision on 17 November 2022 to create a 38th province of Indonesia, comprising Sorong city and the regencies of Sorong, South Sorong, Raja Ampat, Maybrat and Tambrauw. The reduced West Papua Province will thus have a mid-2022 population estimated at only 561,403.

Biak is an island located in Cenderawasih Bay near the northern coast of Papua, an Indonesian province, and is just northwest of New Guinea. Biak is the largest island in its small archipelago, and has many atolls, reefs, and corals.

Western New Guinea, also known as Papua, Indonesian New Guinea, or Indonesian Papua, is the western, Indonesian half of the island of New Guinea. Since the island is alternatively named as Papua, the region is also called West Papua.

Yapen is an island of Papua, Indonesia. The Yapen Strait separates Yapen and the Biak Islands to the north. It is in Cenderawasih Bay off the north-western coast of the island of New Guinea. To the west is Mios Num Island across the Mios Num Strait, and to the east Kurudu Island. Off the southeast coast of Yapen are the Amboi Islands and to the southwest are the Kuran Islands. Together these islands form the Yapen Islands Regency within the province of Papua. It is populated with communities of Yobi, Randowaya, Serui, and Ansus. Its highest point is 1,496 metres.

Waigeo is an island in Southwest Papua province of eastern Indonesia. The island is also known as Amberi, or Waigiu. It is the largest of the four main islands in the Raja Ampat Islands archipelago, between Halmahera and about 65 kilometres to the north-west coast of New Guinea. The Dampier Strait separates it from Batanta, and the Bougainville Strait from the Kawe Islands to its north-west. The "inner sea" that nearly cleaves the island in two is Mayalibit Bay, also known as the Majoli Gulf.
Jorge de Menezes was a Portuguese explorer, who in 1526–27 landed on the islands of Biak, whilst he awaited the passing of the monsoon season, and on the northern coasts of the Bird's Head Peninsula, calling the region Ilhas dos Papuas. He is thus credited with the European discovery of New Guinea.

Blup Blup Island is a small forested island off the northern coast of Papua New Guinea about 30 km offshore from Cape Girgir and is considered part of the Schouten Islands. It is located at latitude S 3°30'46" and longitude E 144°35'16". The island has a small population and is theoretically part of the Papuan province of East Sepik, although officially it is still a protectorate.

Cenderawasih Bay, also known as Sarera Bay and formerly Geelvink Bay, is a large bay in northern Province of Papua, Central Papua and West Papua, New Guinea, Indonesia.

The Biak glider is a species of marsupial in the family Petauridae. It is endemic to the Schouten Islands in the western region of Papua Province, Indonesia. It was formerly considered to be a subspecies of Petaurus breviceps ; there is still uncertainty regarding its status as a distinct species.

Numfor is one of the Schouten Islands in Papua province, northeastern Indonesia.

Aua is an island in the Bismarck Archipelago. It is part of the Western Islands, region and Manus Province of northern Papua New Guinea.

New Guinea is the world's second-largest island, with an area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi). Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the 150-kilometre wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east.

Biak Numfor Regency is one of the regencies (kabupaten) in Papua Province of Western New Guinea in northeastern Indonesia.
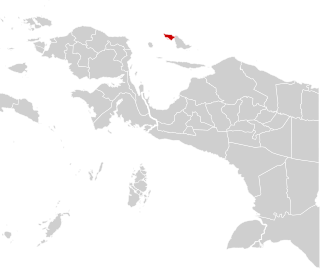
Supiori Regency is a regency in the Indonesian province of Papua. The Regency has an area of 634.24 km2 including the Aruri Islands group to the south, and had a population of 15,874 at the 2010 Census and 22,547 at the 2020 Census. Until 8 January 2004, this area was part of the Biak Numfor Regency, from which it was split off in accordance with the Law dated 18 December 2003.

The Treaty of Zaragoza, also called the Capitulation of Zaragoza was a peace treaty between Castile and Portugal, signed on 22 April 1529 by King John III of Portugal and the Castilian emperor Charles V, in the Aragonese city of Zaragoza. The treaty defined the areas of Castilian and Portuguese influence in Asia, in order to resolve the "Moluccas issue", which had arisen because both kingdoms claimed the Maluku Islands for themselves, asserting that they were within their area of influence as specified in 1494 by the Treaty of Tordesillas. The conflict began in 1520, when expeditions of both kingdoms reached the Pacific Ocean, because no agreed meridian of longitude had been established in the Orient.


















