
The order Pinales in the division Pinophyta, class Pinopsida, comprises all the extant conifers. The distinguishing characteristic is the reproductive structure known as a cone produced by all Pinales. All of the extant conifers, such as cedar, celery-pine, cypress, fir, juniper, larch, pine, redwood, spruce, yew and Araucaria araucana are included here. Some fossil conifers, however, belong to other distinct orders within the division Pinophyta.

The Scrophulariaceae are a family of flowering plants, commonly known as the figwort family. The plants are annual and perennial herbs, as well as shrubs. Flowers have bilateral (zygomorphic) or rarely radial (actinomorphic) symmetry. The Scrophulariaceae have a cosmopolitan distribution, with the majority found in temperate areas, including tropical mountains. The family name is based on the name of the included genus Scrophularia L.

Zosteraceae is a family of marine perennial flowering plants found in temperate and subtropical coastal waters, with the highest diversity located around Korea and Japan. Most seagrasses complete their entire life cycle under water, having filamentous pollen especially adapted to dispersion in an aquatic environment and ribbon-like leaves that lack stomata. Seagrasses are herbaceous and have prominent creeping rhizomes. A distinctive characteristic of the family is the presence of characteristic retinacules, which are present in all species except members of Zostera subgenus Zostera.

Altingiaceae is a small family of flowering plants in the order Saxifragales, consisting of wind-pollinated trees that produce hard, woody fruits containing numerous seeds. The fruits have been studied in considerable detail. They naturally occur in Central America, Mexico, eastern North America, the eastern Mediterranean, China, and tropical Asia. They are often cultivated as ornamentals and many produce valuable wood.

Tofieldiaceae is a family of flowering plants in the monocot order Alismatales. The family is divided into four genera, which together comprise 28 known species. They are small, herbaceous plants, mostly of arctic and subarctic regions, but a few extend further south, and one genus is endemic to northern South America and Florida. Tofieldia pusilla is sometimes grown as an ornamental.

Chuniophoenix is a genus of palm tree named after Chun Woon-Young, then director of the Botanical Institute, Sun Yat Sen University, Guangzhou. It contains three known species, native to southern China and Vietnam. Chuniophoenix is a member of tribe Chuniophoeniceae, a small group of palms that exhibit great morphological diversity and interesting biogeography. The tribe includes four genera: Chuniophoenix with 3 species in China and Vietnam, Kerriodoxa (monotypic) in Peninsular Malaysia and Thailand, Nannorrhops (monotypic) from Arabia to Afghanistan, and Tahina (monotypic) in Madagascar.

Satakentia liukiuensis, is a species of palm tree. They are endemic to Ishigaki Island and Iriomote Island in the Yaeyama Islands, the south-westernmost of the Ryukyu Islands, Japan. It is the only species in the genus Satakentia.
Ernst Vilhelm Østrup was a Danish botanist and phycologist, mainly working on diatoms.
Redingeria is a genus of lichenized fungi in the family Graphidaceae. It was circumscribed in 2006 by Andreas Frisch, with Redingeria leiostoma assigned as the type species. The genus name honours Karl Martin Redinger (1907–1940), an Austrian botanist.

Ecklonia is a genus of kelp belonging to the family Lessoniaceae.
Duboscquella is a genus of dinoflagellates.
Phytotaxa is a peer-reviewed scientific journal for rapid publication on any aspect of systematic botany. It publishes on a wide range of subjects, but focuses on new species, monographs, floras, revisions, reviews, and typification issues. Phytotaxa covers all plant groups covered by the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, including diatoms, fungi, algae, lichens, mosses, hornworts, liverworts, and vascular plants), both living and fossil.
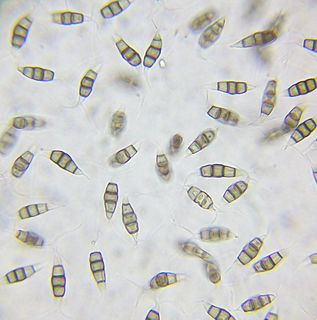
Pestalotiopsis is a genus of ascomycete fungi. Pestalotiopsis species are known as plant pathogens.

Euphronia is a genus of three species of shrubs native to northern South America and is the only genus in the family Euphroniaceae. It was previously classified in the Vochysiaceae family and elsewhere due to its unique floral features, but the APG III system of 2009 recognized Euphroniaceae as distinct and placed Euphronia in it. Based on molecular data from the rbcL gene, it is sister to the Chrysobalanaceae.

Balbisia is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Francoaceae. It is also in the Vivianiaceae subfamily.
Macbrideola is a genus of Amoebozoa in the family Stemonitidaceae. As of 2015, there are 17 species in the genus.

Brefeldia is an genus of slime molds in the family Amaurochaetaceae.

Zizkaea is a monotypic genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Bromeliaceae. It only contains one known species, Zizkaea tuerckheimii(Mez) W.Till & Barfuss
Detonula is a genus of diatoms belonging to the family Thalassiosiraceae.
Henricus (Harrie) Johannes Maria Sipman is a Dutch lichenologist. He specialises in tropical and subtropical lichens, and has authored or co-authored more than 250 scientific publications. He was the curator of the lichen herbarium at the Berlin Botanical Garden and Botanical Museum from 1983 until his retirement in 2010.













