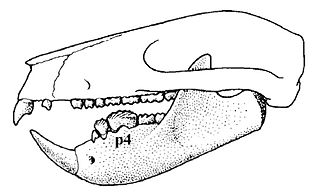
Plagiaulax is a genus of mammal from the Lower Cretaceous of Europe. It was a member of the also extinct order Multituberculata, and shared the world with dinosaurs. It is of the suborder "Plagiaulacida" and family Plagiaulacidae. The genus was named by Hugh Falconer in 1857, and was the first described multituberculate species.
Eutropis dawsoni, also known commonly as Gans's grass skink and Gans's mabuya, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to the southern Western Ghats, India.
The New Zealand catshark is a catshark of the family Scyliorhinidae in the order Carcharhiniformes. This species is endemic to in the deep waters around New Zealand. Its length is up to 45 centimetres (18 in). The New Zealand catshark is a small, little-known deep water bottom shark. It is dark brown around the top with a few widely spaced pale spots, and white below. It feeds on bottom-living crustaceans. It is also completely harmless to humans.

Lasaeidae is a family of very small saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the order Galeommatida. These bivalves are sometimes called "kelly clams", because one of the genera in this family is Kellia.
Aegialodon dawsoni is an extinct mammal from the early Cretaceous, known from fossilised teeth discovered in the Wadhurst Clay Formation near Cliff End, Hastings, East Sussex.

Amegilla dawsoni, sometimes called the Dawson's burrowing bee, is a species of bee that nests by the thousands in arid claypans in Western Australia. It is a long tongued bee, of the tribe Anthophorini and genus Amegilla, the second largest genus in Anthophorini.

Syngnathus dawsoni is a species of the pipefishes. It occurs in the central, western Atlantic in the Caribbean Sea from Puerto Rico to St. Lucia and has been recorded only from the east of the Mona Passage. It is a marine tropical demersal fish. It is ovoviviparous; the male carries the fertilized eggs in a brood pouch located under his tail. It has been captured at around 7 metres (23 ft) in shallow, inshore water but its habits and ecology are unknown.

Solaster is a genus of sea stars in the family Solasteridae.

Solaster dawsoni, the morning sun star, is a species of starfish in the family Solasteridae. It is found on either side of the northern Pacific Ocean. It has two subspecies:
Chrysotypus dawsoni is a species of moth of the family Thyrididae.

Sybra is a genus of beetles in the family Cerambycidae, containing the following species:

Sybra umbratica is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Pascoe in 1865.
Sybra uenoi is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Hayashi in 1956. It is known from Japan.

Sybra ordinata is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Henry Walter Bates in 1873.
Sybra pascoei is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Lameere in 1893.

Charles Eric "Chuck" Dawson Jr. was a Canadian-American ecologist, ichthyologist, and taxonomist. He held expertise in gobies, flatfishes, and sand stargazers, and was considered "the ultimate authority" on pipefishes in the family Syngnathidae.
Rhytiphora dawsoni is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1970.

Melanoplus dawsoni, or Dawson's grasshopper, is a species of spur-throated grasshopper in the family Acrididae. It is found in North America.
Paralomis dawsoni is a species of king crab which lives in New Caledonia, New Zealand, and the Solomon Islands at depths of 400–1,118 m (1,312–3,668 ft). It is the largest species of Paralomis in New Zealand.










