
The University of Santo Tomas Manila, officially the Pontifical and Royal University of Santo Tomas, Manila or colloquially as USTè, is a private, Catholic research university in Manila, Philippines. Founded on April 28, 1611, by Spanish friar Miguel de Benavides, third Archbishop of Manila, it has the oldest extant university charter in Asia and is one of the world's largest Catholic universities in terms of enrollment found on one campus. It is the main campus of the University of Santo Tomas System that is run by the Order of Preachers.

The University of San Carlos is a private, Catholic, research, coeducational basic and higher education institution administered by the Philippine Southern Province of the Society of the Divine Word missionaries in Cebu City, Philippines, since 1935. It offers basic education and higher education. Founded originally in 1595 as Colegio de San Ildefonso which was closed upon the expulsion of the Jesuit missionaries from the Philippines in 1768. The Colegio was reopened in 1783 as Seminario-Colegio de San Carlos until the colegio was split from the seminary in 1924. The Colegio de San Carlos became university on July 1, 1948.

Cavite State University is a public university in the province of Cavite in the Philippines. Its 70-hectare (170-acre) main campus, known as the Don Severino delas Alas Campus, is located in the Municipality of Indang, Cavite about 60 km (37 mi) southwest of Manila. The educational institution has twelve other campuses spread all over the province.

The Department of Science and Technology, is the executive department of the Philippine government responsible for the coordination of science and technology-related projects in the Philippines and to formulate policies and projects in the fields of science and technology in support of national development.

The University of the Philippines Visayas is a public research university in Iloilo, Philippines. A constituent university of the University of the Philippines system, it teaches management, accountancy, marketing, economics, chemistry, applied mathematics and physics, marine science education and research, fisheries, and aquaculture. It offers regional studies programs on the preservation and enrichment of the Visayan cultural heritage.

The space program of the Philippines is currently maintained by the Philippine Space Agency (PhilSA) together with various agencies under the Department of Science and Technology (DOST). The space program includes space research and development, and is funded through the National SPACE Development Program (NSDP) by the DOST and received an initial budget of ₱1 billion in 2020.

The Philippine Space Agency (PhilSA) is the national space agency of the Philippines.

Diwata-1 also known as PHL-Microsat-1 was a Philippine microsatellite launched to the International Space Station (ISS) on March 23, 2016, and was deployed into orbit from the ISS on April 27, 2016. It was the first Philippine microsatellite and the first satellite built and designed by Filipinos. It was followed by Diwata-2, launched in 2018.

The Philippine Earth Data Resource and Observation Center, also known as the PEDRO Center is an organization tasked in operating satellite ground stations.
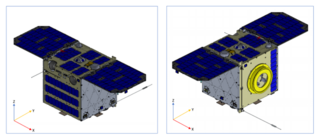
Diwata-2 or Diwata-2B is a Philippine microsatellite launched on October 29, 2018. It is the first satellite launched under the STAMINA4Space program.

The Philippine Scientific Earth Observation Microsatellite (PHL-Microsat) was a satellite program carried by the Department of Science and Technology (DOST) of the Philippines in cooperation with the Tohoku and Hokkaido Universities of Japan.

Maya-1 was a Filipino nanosatellite. It was developed under the Philippine Scientific Earth Observation Microsatellite program (PHL-Microsat) and was jointly implemented by the University of the Philippines and the Department of Science and Technology as part of the Kyushu Institute of Technology-led multinational second Joint Global Multi-nations Birds Satellite (Birds-2). Maya-1 was the first nanosatellite of the Philippines.
The Philippine government has commenced a project to develop a locally designed and manufactured Automated Guideway Transit System (AGTS) through its Department of Science and Technology (DOST). Two prototype lines has been set up by the DOST, one within the University of the Philippines Diliman campus and another in Bicutan in Taguig.

The Hybrid Electric Road Train (HERT) is a hybrid trackless train developed by the Department of Science and Technology of the Philippines for public transport. The headquarter office is located at New Clark City under the town of Capas, Tarlac, Philippines.

The Hybrid Electric Train (HET) is a hybrid electric train built by the Department of Science and Technology's Metals Industry Research and Development Center.
The Virology Science and Technology Institute of the Philippines (VSTIP), also referred to as the Virology Institute of the Philippines (VIP), is a proposed virology research facility in the Philippines.

Joel Joseph Sacro Marciano Jr. is a Filipino engineer, academic and the first and current Director General of the Philippine Space Agency, a government agency under the Office of the President in charge of the Philippines' national space program.
Maya-2 was a Filipino nanosatellite. It succeeded Maya-1, the first Filipino nanosatellite, which was deorbited in November 2020.
The Multispectral Unit for Land Assessment (MULA) is a planned Filipino satellite. Upon completion it will become the largest Filipino-made satellite.

















