Gamma correction or gamma is a nonlinear operation used to encode and decode luminance or tristimulus values in video or still image systems. Gamma correction is, in the simplest cases, defined by the following power-law expression:
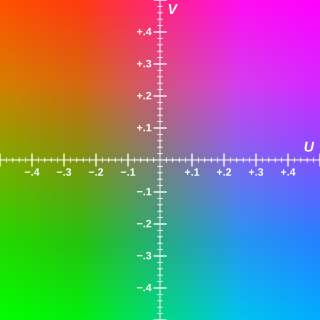
Y′UV, also written YUV, is the color model found in the PAL analogue color TV standard. A color is described as a Y′ component (luma) and two chroma components U and V. The prime symbol (') denotes that the luma is calculated from gamma-corrected RGB input and that it is different from true luminance. Today, the term YUV is commonly used in the computer industry to describe colorspaces that are encoded using YCbCr.

Composite video is an baseband analog video format that typically carries a 405, 525 or 625 line interlaced black and white or color signal, on a single channel, unlike the higher-quality S-Video and the even higher-quality YPbPr.

S-Video is an analog video signal format that carries standard-definition video, typically at 525 lines or 625 lines. It encodes video luma and chrominance on two separate channels, achieving higher image quality than composite video which encodes all video information on one channel. It also eliminates several types of visual defects such as dot crawl which commonly occur with composite video. Although it is improved over composite video, S-Video has lower color resolution than component video, which is encoded over three channels.

Chroma subsampling is the practice of encoding images by implementing less resolution for chroma information than for luma information, taking advantage of the human visual system's lower acuity for color differences than for luminance.

HSL and HSV are the two most common cylindrical-coordinate representations of points in an RGB color model. The two representations rearrange the geometry of RGB in an attempt to be more intuitive and perceptually relevant than the cartesian (cube) representation. Developed in the 1970s for computer graphics applications, HSL and HSV are used today in color pickers, in image editing software, and less commonly in image analysis and computer vision.

SMPTE color bars are a television test pattern used where the NTSC video standard is utilized, including countries in North America. The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) refers to the pattern as Engineering Guideline (EG) 1-1990. Its components are a known standard, and created by test pattern generators. Comparing it as received to the known standard gives video engineers an indication of how an NTSC video signal has been altered by recording or transmission and what adjustments must be made to bring it back to specification. It is also used for setting a television monitor or receiver to reproduce NTSC chrominance and luminance information correctly.

Hold-And-Modify, usually abbreviated as HAM, is a display mode of the Commodore Amiga computer. It uses a highly unusual technique to express the color of pixels, allowing many more colors to appear on screen than would otherwise be possible. HAM mode was commonly used to display digitized photographs or video frames, bitmap art and occasionally animation. At the time of the Amiga's launch in 1985, this near-photorealistic display was unprecedented for a home computer and it was widely used to demonstrate the Amiga's graphical capability. However, HAM has significant technical limitations which prevent it from being used as a general purpose display mode.

Dot crawl is a visual defect of color analog video standards when signals are transmitted as composite video, as in terrestrial broadcast television. It consists of moving checkerboard patterns which appear along horizontal color transitions. It results from intermodulation or crosstalk between chrominance and luminance components of the signal, which are imperfectly multiplexed in the frequency domain.

A video decoder is an electronic circuit, often contained within a single integrated circuit chip, that converts base-band analog video signals to digital video. Video decoders commonly allow programmable control over video characteristics such as hue, contrast, and saturation. A video decoder performs the inverse function of a video encoder, which converts raw (uncompressed) digital video to analog video. Video decoders are commonly used in video capture devices and frame grabbers.

ETP-1 was a test card designed and used by the Independent Broadcasting Authority (IBA). After test transmissions from the IBA's Engineering Regional Operations Centre (ROC) in Croydon from 1978 it was phased in on ITV over a period starting from 1979, replacing, in different ITV regions: Test Card F, Test Card G and full screen height EBU colour bars. After ITV went 24 hours in 1988, the card ceased to be seen on the channel. It was used for both 625-line PAL and 405-line monochrome broadcasts.

Rec. 709, also known as Rec.709, BT.709, and ITU 709, is a standard developed by ITU-R for image encoding and signal characteristics of high-definition television.

A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of color – whether such representation entails an analog or a digital representation. A color space may be arbitrary, i.e. with physically realized colors assigned to a set of physical color swatches with corresponding assigned color names, or structured with mathematical rigor. A "color space" is a useful conceptual tool for understanding the color capabilities of a particular device or digital file. When trying to reproduce color on another device, color spaces can show whether shadow/highlight detail and color saturation can be retained, and by how much either will be compromised.

The Mullard SAA5050 was a character generator chip for implementing the Teletext character set.
Composite artifact colors is a technique commonly used to address several graphic modes of some 1970s and 1980s home computers. With some machines, when connected to an NTSC TV or monitor over composite video outputs, the video signal encoding allowed for extra colors to be displayed, by manipulating the pixel position on screen, not being limited by each machine's hardware color palette.

The EBU colour bars are a television test card used to check if a video signal has been altered by recording or transmission, and what adjustments must be made to bring it back to specification. It is also used for setting a television monitor or receiver to reproduce chrominance and luminance information correctly. The EBU bars are most commonly shown arranged side-by-side in a vertical manner, though some broadcasters – such as TVP in Poland, and Gabon Télévision in Gabon – were known to have aired a horizontal version of the EBU bars.














