
Death-associated protein 6 also known as Daxx is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DAXX gene.

The nuclear receptor 4A1 also known as Nur77, TR3, and NGFI-B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR4A1 gene.

Promyelocytic leukemia protein (PML) is the protein product of the PML gene. PML protein is a tumor suppressor protein required for the assembly of a number of nuclear structures, called PML-nuclear bodies, which form amongst the chromatin of the cell nucleus. These nuclear bodies are present in mammalian nuclei, at about 1 to 30 per cell nucleus. PML-NBs are known to have a number of regulatory cellular functions, including involvement in programmed cell death, genome stability, antiviral effects and controlling cell division. PML mutation or loss, and the subsequent dysregulation of these processes, has been implicated in a variety of cancers.

PRKC, apoptosis, WT1, regulator, also known as PAWR or Prostate apoptosis response-4 (Par-4), is a human gene coding for a tumor-suppressor protein that induces apoptosis in cancer cells, but not in normal cells.

Torsin-1A (TorA) also known as dystonia 1 protein (DYT1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TOR1A gene. TorA localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and contiguous perinuclear space, where its ATPase activity is activated by either LULL1 or LAP1, respectively.
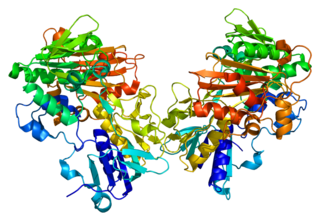
Apoptosis-inducing factor 1, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AIFM1 gene on the X chromosome. This protein localizes to the mitochondria, as well as the nucleus, where it carries out nuclear fragmentation as part of caspase-independent apoptosis.

Bcl-2-interacting killer is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BIK gene.

Zinc finger protein RFP is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRIM27 gene.

Protein kinase, interferon-inducible double stranded RNA dependent activator, also known as interferon-inducible double stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase activator A or Protein ACTivator of the interferon-induced protein kinase (PACT) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRKRA gene. PACT heterodimerizes with and activates protein kinase R. PRKRA mutations have been linked to a rare form of dystonia parkinsonism.

Tubulin beta-4A chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TUBB4A gene. Two tubulin beta-4 chain proteins are encoded in the human genome by the genes TUBB4A and TUBB4B. Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules, a key components of the cytoskeleton. It binds two molecules of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta-chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha-chain. TUBB4A is preferentially and highly expressed in the central nervous system.

Death-associated protein kinase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DAPK3 gene.

PML-RARA-regulated adapter molecule 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRAM1 gene.

Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 85B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCDC85B gene.

THAP domain-containing protein 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the THAP6 gene.

Apoptosis-inducing factor 2 (AIFM2), also known as apoptosis-inducing factor-homologous mitochondrion-associated inducer of death (AMID), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AIFM2 gene, also known as p53-responsive gene 3 (PRG3), on chromosome 10.

THAP domain-containing protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the THAP4 gene.

THAP domain-containing protein 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the THAP7 gene.

THAP domain-containing protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the THAP2 gene.

FAST kinase domain-containing protein 2 (FASTKD2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FASTKD2 gene on chromosome 2. This protein is part of the FASTKD family, which is known for regulating the energy balance of mitochondria under stress. FASTKD2 has been implicated in mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, breast cancer, and prostate cancer.

THAP domain-containing protein 3 (THAP3) is a protein that, in Homo sapiens (humans), is encoded by the THAP3 gene. The THAP3 protein is as known as MGC33488, LOC90326, and THAP domain-containing, apoptosis associated protein 3. This protein contains the Thanatos-associated protein (THAP) domain and a host-cell factor 1C binding motif. These domains allow THAP3 to influence a variety of processes, including transcription and neuronal development. THAP3 is ubiquitously expressed in H. sapiens, though expression is highest in the kidneys.






















