
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC)'s PDP-10, later marketed as the DECsystem-10, is a mainframe computer family manufactured beginning in 1966 and discontinued in 1983. 1970s models and beyond were marketed under the DECsystem-10 name, especially as the TOPS-10 operating system became widely used.

The PDP-1 is the first computer in Digital Equipment Corporation's PDP series and was first produced in 1959. It is famous for being the computer most important in the creation of hacker culture at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, BBN and elsewhere. The PDP-1 is the original hardware for playing history's first game on a minicomputer, Steve Russell's Spacewar!
troff, short for "typesetter roff", is the major component of a document processing system developed by Bell Labs for the Unix operating system. troff and the related nroff were both developed from the original roff.

vi is a screen-oriented text editor originally created for the Unix operating system. The portable subset of the behavior of vi and programs based on it, and the ex editor language supported within these programs, is described by the Single Unix Specification and POSIX.

A word processor is an electronic device for text, composing, editing, formatting, and printing.
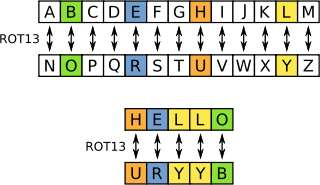
ROT13 is a simple letter substitution cipher that replaces a letter with the 13th letter after it in the latin alphabet. ROT13 is a special case of the Caesar cipher which was developed in ancient Rome.
TYPSET is an early document editor that was used with the 1964-released RUNOFF program, one of the earliest text formatting programs to see significant use.
roff is a typewriter-oriented markup language. As the first Unix text-formatting computer program, it is a predecessor of the nroff and troff document processing systems.

The Compatible Time-Sharing System (CTSS) was the first general purpose time-sharing operating system. Compatible Time Sharing referred to time sharing which was compatible with batch processing; it could offer both time sharing and batch processing concurrently.
Sporgery is the disruptive act of posting a flood of articles to a Usenet newsgroup, with the article headers falsified so that they appear to have been posted by others. The word is a portmanteau of spam and forgery, coined by German software developer, and critic of Scientology, Tilman Hausherr.
Eternal September or the September that never ended is Usenet slang for a period beginning around 1993 when Internet service providers began offering Usenet access to many new users. The flood of new users overwhelmed the existing culture for online forums and the ability to enforce existing norms. AOL followed with their Usenet gateway service in March 1994, leading to a constant stream of new users. Hence, from the early Usenet point of view, the influx of new users in September 1993 never ended.

Expensive Typewriter was a pioneering text editor program that ran on the DEC PDP-1 computer which had been delivered to MIT in the early 1960s.
The Story of Mel is an archetypical piece of computer programming folklore. Its subject, Melvin Kaye, is an exemplary "Real Programmer" whose subtle techniques fascinate his colleagues.

Alan Kotok was an American computer scientist known for his work at Digital Equipment Corporation and at the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). Steven Levy, in his book Hackers: Heroes of the Computer Revolution, describes Kotok and his classmates at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) as the first true hackers.
Peter R. Samson is an American computer scientist, best known for creating pioneering computer software for the TX-0 and PDP-1.

Colossal Typewriter by John McCarthy and Roland Silver was one of the earliest computer text editors. The program ran on the PDP-1 at Bolt, Beranek and Newman (BBN) by December 1960.
Harmony Compiler was written by Peter Samson at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). The compiler was designed to encode music for the PDP-1 and built on an earlier program Samson wrote for the TX-0 computer.
A Usenet personality was a particular kind of Internet celebrity, being an individual who gained a certain level of notoriety from posting on Usenet, a global network of computer users with a vast array of topics for discussion. The platform is usually anonymous, although users can get celebrity status, usually by being deemed different from other posters in some way.
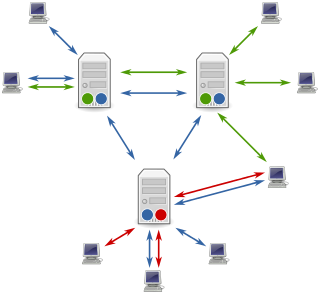
Usenet, USENET, or "in full", User’s Network, is a worldwide distributed discussion system available on computers. It was developed from the general-purpose Unix-to-Unix Copy (UUCP) dial-up network architecture. Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis conceived the idea in 1979, and it was established in 1980. Users read and post messages to one or more topic categories, known as newsgroups. Usenet resembles a bulletin board system (BBS) in many respects and is the precursor to the Internet forums that have become widely used. Discussions are threaded, as with web forums and BBSs, though posts are stored on the server sequentially.

Emacs, originally named EMACS, is a family of text editors that are characterized by their extensibility. The manual for the most widely used variant, GNU Emacs, describes it as "the extensible, customizable, self-documenting, real-time display editor". Development of the first Emacs began in the mid-1970s, and work on its direct descendant, GNU Emacs, continues actively; the latest version is 28.2, released in September 2022.












