
Apocynaceae is a family of flowering plants that includes trees, shrubs, herbs, stem succulents, and vines, commonly known as the dogbane family, because some taxa were used as dog poison. Members of the family are native to the European, Asian, African, Australian, and American tropics or subtropics, with some temperate members. The former family Asclepiadaceae is considered a subfamily of Apocynaceae and contains 348 genera. A list of Apocynaceae genera may be found here.

Catharanthus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae. Like the genus Vinca, they are known commonly as periwinkles. There are eight known species. Seven are endemic to Madagascar, though one, C. roseus, is widely naturalized around the world. The eighth species, C. pusillus, is native to India and Sri Lanka. The name Catharanthus comes from the Greek for "pure flower".
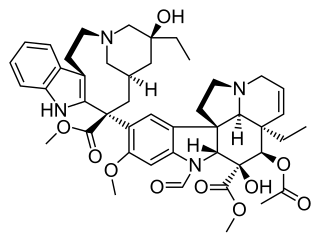
Vincristine, also known as leurocristine and marketed under the brand name Oncovin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes acute lymphocytic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, Hodgkin's disease, neuroblastoma, and small cell lung cancer among others. It is given intravenously.

Vinca is an Old World genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, The English name periwinkle is shared with the related genus Catharanthus. Some Vinca species are cultivated but have also spread invasively. Additionally, some species have medicinal uses.The most spread species is Vinca minor.

Vinorelbine (NVB), sold under the brand name Navelbine among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes breast cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. It is given by injection into a vein or by mouth.

Vinblastine (VBL), sold under the brand name Velban among others, is a chemotherapy medication, typically used with other medications, to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes Hodgkin's lymphoma, non-small-cell lung cancer, bladder cancer, brain cancer, melanoma, and testicular cancer. It is given by injection into a vein.

Catharanthus roseus, commonly known as bright eyes, Cape periwinkle, graveyard plant, Madagascar periwinkle, old maid, pink periwinkle, rose periwinkle, is a perennial species of flowering plant in the family Apocynaceae. It is native and endemic to Madagascar, but is grown elsewhere as an ornamental and medicinal plant, and now has a pantropical distribution. It is a source of the drugs vincristine and vinblastine, used to treat cancer. It was formerly included in the genus Vinca as Vinca rosea.

Vinca alkaloids are a set of anti-mitotic and anti-microtubule alkaloid agents originally derived from the periwinkle plant Catharanthus roseus and other vinca plants. They block beta-tubulin polymerization in a dividing cell.

Voacangine is an alkaloid found predominantly in the root bark of the Voacanga africana tree, as well as in other plants such as Tabernanthe iboga, Tabernaemontana africana, Trachelospermum jasminoides, Tabernaemontana divaricata and Ervatamia yunnanensis. It is an iboga alkaloid which commonly serves as a precursor for the semi-synthesis of ibogaine. It has been demonstrated in animals to have similar anti-addictive properties to ibogaine itself. It also potentiates the effects of barbiturates. Under UV-A and UV-B light its crystals fluoresce blue-green, and it is soluble in ethanol.
In enzymology, a tabersonine 16-hydroxylase (EC 1.14.13.73) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Strictosidine synthase (EC 4.3.3.2) is an enzyme in alkaloid biosynthesis that catalyses the condensation of tryptamine with secologanin to form strictosidine in a formal Pictet–Spengler reaction:

Akuammicine is a monoterpene indole alkaloid of the Vinca sub-group. It is found in the Apocynaceae family of plants including Picralima nitida, Vinca minor and the Aspidosperma.
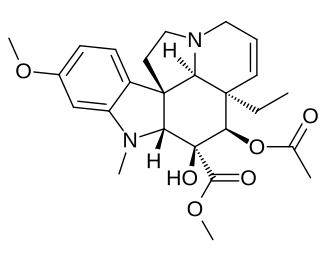
Vindoline is a chemical precursor to vinblastine. Vindoline is formed through biosynthesis from Tabersonine.

Strictosidine is a natural chemical compound and is classified as a glucoalkaloid and a vinca alkaloid. It is formed by the Pictet–Spengler condensation reaction of tryptamine with secologanin, catalyzed by the enzyme strictosidine synthase. Thousands of strictosidine derivatives are sometimes referred to by the broad phrase of monoterpene indole alkaloids. Strictosidine is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of numerous pharmaceutically valuable metabolites including quinine, camptothecin, ajmalicine, serpentine, vinblastine, vincristine and mitragynine.

16-Hydroxytabersonine is a terpene indole alkaloid produced by the plant Catharanthus roseus. The metabolite is an intermediate in the formation of vindoline, a precursor needed for formation of the pharmaceutically valuable vinblastine and vincristine. 16-hydroxytabersonine is formed from the hydroxylation of tabersonine by tabersonine 16-hydroxylase (T16H). Tabersonine 16-O-methyltransferase (16OMT) methylates the hydroxylated 16 position to form 16-methoxytabersonine.

3-Hydroxy-16-methoxy-2,3-dihydrotabersonine is a terpene indole alkaloid produced by Catharanthus roseus. The metabolite is a substrate for 3-hydroxy-16-methoxy-2,3-dihydrotabersonine N-methyltransferase (NMT) which transfers a methyl group to the nitrogen of the indole ring forming desacetoxyvindoline. The enzyme catalyzing the formation of 3-hydroxy-16-methoxy-2,3-dihydrotabersonine from 16-methoxytabersonine is currently unknown, but is a result of hydration of the double bond connecting the 6 and 13 position carbons.
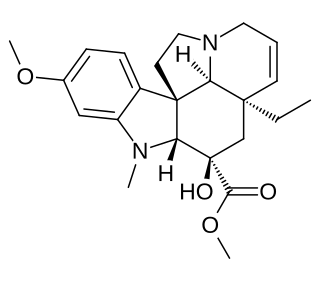
Desacetoxyvindoline is a terpene indole alkaloid produced by the plant Catharanthus roseus. Desacetoxyvindoline is a product formed by the methylation of the nitrogen on the indole ring by the enzyme 3-hydroxy-16-methoxy-2,3-dihydrotabersonine N-methyltransferase (NMT). The metabolite is a substrate for desacetoxyvindoline 4-hydroxylase (D4H) which catalyzes a hydroxylation to yield deacetylvindoline.

16-Methoxytabersonine is a terpene indole alkaloid produced by the medicinal plant Catharanthus roseus. 16-methoxytabersonine is synthesized by methylation of the hydroxyl group at the 16 position of 16-hydroxytabersonine by tabersonine 16-O-methyltransferase (16OMT). The compound is a substrate for hydration by two concerted enzymes Tabersonine-3-Oxidase (T3O) and Tabersonine-3-Reductase (T3R), which leads to the formation of 3-hydroxy-16-methoxy-2,3-dihydrotabersonine.

Deacetylvindoline is a terpene indole alkaloid produced by Catharanthus roseus. Deacetylvindoline is the product of a hydroxylation of desacetoxyvindoline by deacetoxyvindoline 4-hydroxylase (D4H). It is a substrate for deacetylvindoline O-acetyltransferase (DAT) which acetylates a hydroxy group to form vindoline, one of the two immediate precursors for the formation of the pharmacetucially valuable bisindole alkaloid vinblastine.

Catharanthine and vindoline are terpenoid indole alkaloids naturally produced within the Madagascar periwinkle plant whose dimerization produces the anti-cancer drugs vinblastine and vincristine. The precursor of catharanthine and vindoline is strictosidine, the common precursor of all indole alkaloids. The localization of catharanthine and vindoline within the plant tissue has been heavily studied in recent years with conflicting results. The dimerization of catharanthine and vindoline to form vinblastine and vincristine is catalyzed by a peroxidase and a reductase, and includes several intermediate compounds.

















