
Bansal, Raj K. (2003). A Textbook of Organic Chemistry. New Age International Limited. p. 644. ISBN 978-81-224-1459-2.

In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. The reactants, products, and intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are modified by a sequence of chemical reactions catalyzed by enzymes. In most cases of a metabolic pathway, the product of one enzyme acts as the substrate for the next. However, side products are considered waste and removed from the cell. These enzymes often require dietary minerals, vitamins, and other cofactors to function.

Catharanthus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae. Like the genus Vinca, they are known commonly as periwinkles. There are eight known species. Seven are endemic to Madagascar, though one, C. roseus, is widely naturalized around the world. The eighth species, C. pusillus, is native to India and Sri Lanka. The name Catharanthus comes from the Greek for "pure flower".

Vinca is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, native to Europe, northwest Africa and southwest Asia. The English name periwinkle is shared with the related genus Catharanthus.

A pronucleus denotes the nucleus found in either a sperm or egg cell during the process of fertilization. The sperm cell undergoes a transformation into a pronucleus after entering the egg cell but prior to the fusion of the genetic material of both the sperm and egg. In contrast, the egg cell possesses a pronucleus once it becomes haploid, not upon the arrival of the sperm cell. Haploid cells, such as sperm and egg cells in humans, carry half the number of chromosomes present in somatic cells, with 23 chromosomes compared to the 46 found in somatic cells. It is noteworthy that the male and female pronuclei do not physically merge, although their genetic material does. Instead, their membranes dissolve, eliminating any barriers between the male and female chromosomes, facilitating the combination of their chromosomes into a single diploid nucleus in the resulting embryo, which contains a complete set of 46 chromosomes.

Vinblastine (VBL), sold under the brand name Velban among others, is a chemotherapy medication, typically used with other medications, to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes Hodgkin's lymphoma, non-small-cell lung cancer, bladder cancer, brain cancer, melanoma, and testicular cancer. It is given by injection into a vein.
Robert Laing Noble was a Canadian physician who was involved in the discovery of vinblastine.
Charles Thomas Beer was a Canadian organic chemist who helped in the discovery of vinblastine.

Catharanthus roseus, commonly known as bright eyes, Cape periwinkle, graveyard plant, Madagascar periwinkle, old maid, pink periwinkle, rose periwinkle, is a perennial species of flowering plant in the family Apocynaceae. It is native and endemic to Madagascar, but is grown elsewhere as an ornamental and medicinal plant, and now has a pantropical distribution. It is a source of the drugs vincristine and vinblastine, used to treat cancer. It was formerly included in the genus Vinca as Vinca rosea.
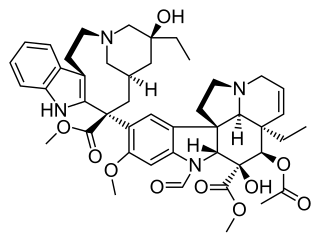
Vinca alkaloids are a set of anti-mitotic and anti-microtubule alkaloid agents originally derived from the periwinkle plant Catharanthus roseus and other vinca plants. They block beta-tubulin polymerization in a dividing cell.

Vindesine, also termed Eldisine, is a semisynthetic vinca alkaloid derived from the flowering plant Catharanthus roseus. Like the natural and semisynthetic vinca alkaloids derived from this plant, vindesine is an inhibitor of mitosis that is used as a chemotherapy drug. By inhibiting mitosis, vinedsine blocks the proliferation of cells, particularly the rapidly proliferation cells of certain types of cancer. It is used, generally in combination with other chemotherapeutic drugs, in the treatment of various malignancies such as leukaemia, lymphoma, melanoma, breast cancer, and lung cancer.

A mitotic inhibitor, microtubule inhibitor, or tubulin inhibitor, is a drug that inhibits mitosis, or cell division, and is used in treating cancer, gout, and nail fungus. These drugs disrupt microtubules, which are structures that pull the chromosomes apart when a cell divides. Mitotic inhibitors are used in cancer treatment, because cancer cells are able to grow through continuous division that eventually spread through the body (metastasize). Thus, cancer cells are more sensitive to inhibition of mitosis than normal cells. Mitotic inhibitors are also used in cytogenetics, where they stop cell division at a stage where chromosomes can be easily examined.
In enzymology, a deacetylvindoline O-acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The Fukuyama indole synthesis is a versatile tin mediated chemical reaction that results in the formation of 2,3-disubstituted indoles. A practical one-pot reaction that can be useful for the creation of disubstituted indoles. Most commonly tributyltin hydride is utilized as the reducing agent, with azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) as a radical initiator. Triethylborane can also be used as a radical initiator. The reaction can begin with either an ortho-isocyanostyrene or a 2-alkenylthioanilide derivative, both forming the indole through Radical cyclization via an α-stannoimidoyl radical. The R group can be a range of both basic and acidic sensitive functional groups such as esters, THP ethers, and β-lactams. In addition the reaction is not stereospecific, in that both the cis and trans isoform can be used to obtain the desired product.
Diffuse infantile fibromatosis is a rare condition affecting infants during the first three years of life. This condition is a multicentric infiltration of muscle fibers with fibroblasts resembling those seen in aponeurotic fibromas, presenting as lesions and tumors confined usually to the muscles of the arms, neck, and shoulder area Diffuse infantile fibromatosis is characterized by fast growing benign tumors. This disorder is known to be caused by mutations in germline variants, PDGFRB and NOTCH3, which may be generationally-inherited through autosomal dominant and recessive traits. Although diffuse infantile fibromatosis is classified as benign, it can still lead to life-threatening complications and damage other organs.

Vincoline is an alkaloid isolated from Catharanthus roseus. In a mouse model, it has been found to stimulate insulin secretion.

Tabersonine is a terpene indole alkaloid found in the medicinal plant Catharanthus roseus and also in the genus Voacanga. Tabersonine is hydroxylated at the 16 position by the enzyme tabersonine 16-hydroxylase (T16H) to form 16-hydroxytabersonine. The enzyme leading to its formation is currently unknown. Tabersonine is the first intermediate leading to the formation of vindoline one of the two precursors required for vinblastine biosynthesis.

16-Hydroxytabersonine is a terpene indole alkaloid produced by the plant Catharanthus roseus. The metabolite is an intermediate in the formation of vindoline, a precursor needed for formation of the pharmaceutically valuable vinblastine and vincristine. 16-hydroxytabersonine is formed from the hydroxylation of tabersonine by tabersonine 16-hydroxylase (T16H). Tabersonine 16-O-methyltransferase (16OMT) methylates the hydroxylated 16 position to form 16-methoxytabersonine.

Bis(cyclopentadienyl)titanium(III) chloride, also known as the Nugent–RajanBabu reagent, is the organotitanium compound which exists as a dimer with the formula [(C5H5)2TiCl]2. It is an air sensitive green solid. The complex finds specialized use in synthetic organic chemistry as a single electron reductant.
The Mukaiyama hydration is an organic reaction involving formal addition of an equivalent of water across an olefin by the action of catalytic bis(acetylacetonato)cobalt(II) complex, phenylsilane and atmospheric oxygen to produce an alcohol with Markovnikov selectivity.















