
A cloudburst is an enormous amount of precipitation in a short period of time, sometimes accompanied by hail and thunder, which is capable of creating flood conditions. Cloudbursts can quickly dump large amounts of water, e.g. 25 mm of the precipitation corresponds to 25,000 metric tons per square kilometre. However, cloudbursts are infrequent as they occur only via orographic lift or occasionally when a warm air parcel mixes with cooler air, resulting in sudden condensation. At times, a large amount of runoff from higher elevations is mistakenly conflated with a cloudburst. The term "cloudburst" arose from the notion that clouds were akin to water balloons and could burst, resulting in rapid precipitation. Though this idea has since been disproven, the term remains in use.
Panvel is a city and taluka in Raigad district of Maharashtra, India. It is highly populated due to its closeness to Mumbai. Panvel is also governed for development purpose by the body of Mumbai Metropolitan Region. Panvel Municipal Corporation is the first Municipal Corporation in Raigad and the 27th Municipal corporation of Maharashtra State.

Raigad district, previously Colaba district, is a district in the Konkan division of Maharashtra, India. The headquarters of the district is Alibag. Other major cities in the district are Panvel, Karjat, Navi Mumbai, Khopoli, Shrivardhan and Mahad.

Mahad ( [məɦaːɖ]) is a city in Raigad district situated in the North Konkan region of Maharashtra state, India. It is located 108.5 km (67.4 mi) from District Headquarters Alibag, and 167 km (104 mi) from Mumbai. Mahad is known for Raigad Fort, the capital of the Maratha Empire in Shivaji Maharaj's era and the revolutionary Mahad Satyagraha launched by at Chavdar Tale in the wake of modern India.
The 2008 Indian floods were a series of floods in various states of India during the 2008 monsoon season. The floods mostly affected the western regions of Maharashtra state and Andhra Pradesh as well as northern Bihar. In India, the monsoon season generally lasts from June to September.

The 2009 Karachi floods in Pakistan's financial centre, Karachi, have killed at least 26 people. The death toll is expected to rise, and more than 150 people have been injured in a series of related incidents. The floods are the result of the heaviest rains in the region in thirty years.

The National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) is a specialized force in India, tasked with the responsibility of responding to natural and man-made disasters. It operates under the National Disaster Management Authority of Ministry of Home Affairs and was established in 2006 with the aim of strengthening disaster management capabilities in the country

Savitri River is one of the five rivers which originate from Mahabaleshwar in Maharashtra state in India. It originates at Savitri point near Mahabaleshwar and flows through the bankot village and directly goes to Arabian sea Raigad district and eventually meets Arabian Sea at Harehareshwar. It passes through rocky and hilly terrain of western ghats till Poladpur and further through the towns of Mahad, Mangaon and Shrivardhan Tehsil (taluka). There are a number of Shiva temples along the banks of river Savitri. Many other small rivers get merged into it at Kapade, Poladpur and Birwadi. Its major tributary is the Kal River which enters from the right (north) near Dasgaon.
This is a list of notable recorded floods that have occurred in India. Floods are the most common natural disaster in India. The heaviest southwest, the Brahmaputra, and other rivers to distend their banks, often flooding surrounding areas.

Deep Depression ARB 02 was a weak tropical cyclone which brought heavy rains and flooding to the Indian state of Gujarat in June 2015. It was the third tropical cyclone and second deep depression of the 2015 North Indian Ocean cyclone season.

The 2017 Mumbai flood occurred on 29 August 2017, following heavy rain on 29 August 2017 in Mumbai. Transport systems were unavailable through parts of the city as trains and roadways were shut. Power was shut off from various parts of the city to prevent electrocution. The International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC) called the South Asian floods one of the worst regional humanitarian crises in years. This event can be compared with the 2005 floods in Mumbai, which recorded 944 mm of rainfall within 24 hours on 26 July.
Widespread monsoon flooding occurred in the South Asian countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India, Nepal and Pakistan from July through September 2017. More than 45 million people were affected by the floods, including 16 million children.
The 2019 Indian floods were a series of floods that affected over thirteen states in late July and early August 2019, due to excessive rains. At least 200 people died and about a million people were displaced. Karnataka and Maharashtra were the most severely affected states. People died but many were rescued with the help of the Indian Navy.
Between 25–28 September 2019, Pune, India, and its division received a heavy amount of rainfall which caused flash flooding. In addition to people lost to these floods, other rain-related incidents such as collapsed compound walls of buildings have killed at least 21 people. Three NDRF teams along with the Army was deployed in the district for rescue operations.

Extremely Severe Cyclonic Storm Tauktae was a powerful, deadly and damaging tropical cyclone in the Arabian Sea that became the strongest tropical cyclone to make landfall in the Indian state of Gujarat since the 1998 Gujarat cyclone and one of the strongest tropical cyclones to ever affect the west coast of India and above all It was the strongest storm of 2021 North Indian Ocean cyclone season. The second depression, first cyclonic storm, first severe cyclonic storm, first very severe cyclonic storm, and first extremely severe cyclonic storm of the 2021 North Indian Ocean cyclone season, Tauktae originated from an area of low pressure in the Arabian Sea, which was first monitored by the India Meteorological Department on May 13. The low drifted eastward and organized into a deep depression by May 14. The storm soon took a northward turn, continuing to gradually intensify because of warm waters near the coast, and the system strengthened into a cyclonic storm and was named Tauktae later that same day. Tauktae continued intensifying into May 15, reaching severe cyclonic storm status later that day. Tauktae began to parallel the coast of the Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka, Goa and Maharashtra, before rapidly intensifying into a very severe cyclonic storm, early on May 16. Early on May 17, Tauktae intensified into an extremely severe cyclonic storm, reaching its peak intensity soon afterward. Later that same day, Tauktae underwent an eyewall replacement cycle and weakened, before restrengthening as it neared the coast of Gujarat, making landfall soon afterward.

The 2021 Mumbai landslide was a series of landslides that occurred in Chembur and Vikhroli, the suburban neighbourhood located in Mumbai, India on 18 July 2021. At least thirty-two people were killed and several others injured after they were trapped under houses that collapsed due to landslides caused by heavy rains. Prime Minister Narendra Modi expressed his grief over the loss of lives and announced ₹2 lakh ex-gratia for family of each deceased victim while a sum of ₹50,000 would be given to the injured from the Prime Minister's National Relief Fund.
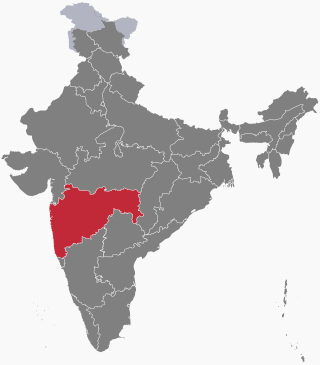
A series of floods took place across the Indian State of Maharashtra in 2021. As of 28 July 2021, around 251 people have died and over 100 are still missing due to floods and landslides. 13 districts have been affected in western Maharashtra. Damage was calculated to be Rs4,000 crore.
From January to October 2022, excessive rainfall and widespread monsoon flooding occurred in the South Asian countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. It has become the region's deadliest floods since 2020, with over 4,700 people dead.

After over 6,500 people died in flooding in 2020, monsoon floods hit South Asia again in 2021.
On 19 July 2023 at approximately 22:30 local time, a landslide occurred in Raigad, Maharashtra, India. The landslide was caused by torrential rains, and resulted in at least 26 deaths, with more than 100 estimated trapped under debris.













