Tecopa is a census-designated place (CDP) in the Mojave Desert in southeast Inyo County, California, United States. Originally occupied by the Koso and Chemehuevi Indians, Pioneers began populating what would become the CDP in the late 19th century to support nearby mines. It is now better known for the natural hot springs in the northern part of the CDP.

The Death Valley pupfish, also known as Salt Creek pupfish, is a small species of fish in the family Cyprinodontidae found only in Death Valley National Park, California, United States. There are two recognized subspecies: C. s. salinus and C. s. milleri. The Death Valley pupfish is endemic to two small, isolated locations and currently classified as endangered.

The Amargosa River is an intermittent waterway, 185 miles (298 km) long, in southern Nevada and eastern California in the United States. The Amargosa River is one out of two rivers located in the California portion of the Mojave Desert with perenial flow. It drains a high desert region, the Amargosa Valley in the Amargosa Desert northwest of Las Vegas, into the Mojave Desert, and finally into Death Valley where it disappears into the ground aquifer. Except for a small portion of its route in the Amargosa Canyon in California and a small portion at Beatty, Nevada, the river flows above ground only after a rare rainstorm washes the region. A 26-mile (42 km) stretch of the river between Shoshone and Dumont Dunes is protected as a National Wild and Scenic River. At the south end of Tecopa Valley the Amargosa River Natural Area protects the habitat.

Amargosa Valley is an unincorporated town located on U.S. Route 95 in Nye County, in the U.S. state of Nevada.
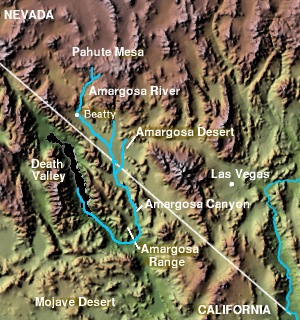
The Amargosa Valley is the valley through which the Amargosa River flows south, in Nye County, southwestern Nevada and Inyo County in the state of California. The south end is alternately called the "Amargosa River Valley'" or the "Tecopa Valley." Its northernmost point is around Beatty, Nevada and southernmost is Tecopa, California, where the Amargosa River enters into the Amargosa Canyon.

The Tecopa pupfish is an extinct subspecies of the Amargosa pupfish. The small, heat-tolerant pupfish was endemic to the outflows of a pair of hot springs in the Mojave Desert of Inyo County, California. Habitat modifications, the introduction of non-native species and hybridization with the related Amargosa River pupfish led to its extinction around 1979.

The Amargosa Range is a mountain range in Inyo County, California and Nye County, Nevada. The 110-mile (180 km) range runs along most of the eastern side of California's Death Valley, separating it from Nevada's Amargosa Desert. The U-shaped Amargosa River flows clockwise around the perimeter of the range, ending 282 feet (86 m) below sea level in the Badwater Basin.
The Shoshone pupfish is a subspecies of Cyprinodon nevadensis from California in the United States. It is characterized by large scales and a "slab-sided," narrow, slender body, with the arch of the ventral contour much less pronounced than the dorsal. It also has fewer pelvic fin rays and scales than the other subspecies of C. nevadensis.

The Kingston Range, sometimes called the Kingston Mountains, is located in Inyo and San Bernardino counties in the Mojave Desert in eastern California. The range reaches a height of 7,323 feet (2,232 m) above sea level at Kingston Peak.

The Nopah Range is a mountain range located in Inyo County, California, United States, near the eastern border with Nevada.

The Black Mountains are a mountain range located in the southeastern part of Inyo County, California, within southeastern Death Valley National Park.

The Bullfrog Hills are a small mountain range of the Mojave Desert in southern Nye County, southwestern Nevada. Bullfrog Hills was so named from a fancied resemblance of its ore to the color of a bullfrog.

The Bare Mountain Range is a mountain range in southern Nye County, Nevada, in the United States. Bare Mountain and Wildcat Peak are the high points of the range.
The Dublin Hills are a mountain range in Inyo County, California. The highest point in the Dublin Hills is 2,523 feet.
The Saratoga Springs pupfish is a subspecies of the Amargosa pupfish of the family Cyprinodontidae. The native population is endemic to Saratoga Springs, a small wetland in Death Valley National Park in the United States.

Cyprinodon nevadensis is a species of pupfish in the genus Cyprinodon. The species is also known as the Amargosa pupfish, but that name may also refer to one subspecies, Cyprinodon nevadensis amargosae. All six subspecies are or were endemic to very isolated locations in the Mojave Desert of California and Nevada.
The Tecopa Lake Beds is a Blancan Pleistocene geologic formation in the Mojave Desert in eastern California. It is in the Tecopa area, east of Death Valley, in southeastern Inyo and northeastern San Bernardino County.

The Amargosa River pupfish is a member of a pupfish species complex which inhabits the watershed of ancient Lake Manly. Currently, the species inhabits two disjunct perennial reaches of the lower Amargosa River. The upstream portion is near Tecopa and passes through the Amargosa Canyon. The lower portion is northwest of Saratoga Springs, just at the head of Death Valley, where the Amargosa River turns north to enter the valley.
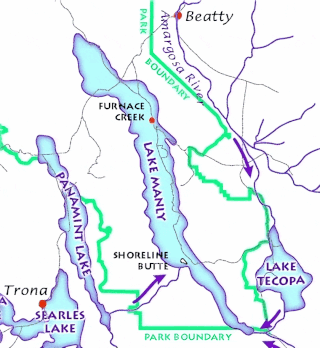
Lake Tecopa is a former lake in Inyo County, southern California. It developed during the Miocene and the Pleistocene within a tectonic basin close to the border with Nevada. Fed by the Amargosa River and some neighbouring washes, it eventually culminated to a surface area of 235 square kilometres (91 sq mi) around 186,000 years ago and left sediments. Afterwards, the Amargosa River cut a gorge out of the lake and into Death Valley with its Lake Manly, draining the lake. The present-day towns of Shoshone, California and Tecopa, California lie within the basin of the former lake.