
Samphire is a name given to a number of succulent salt-tolerant plants (halophytes) that tend to be associated with water bodies.

The Salicornioideae are a subfamily of the flowering plant family Amaranthaceae. Important characters are succulent, often articulated stems, strongly reduced leaves, and flowers aggregated in thick, dense spike-shaped thyrses. These halophytic plants are distributed worldwide.

Mallee, also known as Roe Botanical District, is a biogeographic region in southern Western Australia. Located between the Esperance Plains, Avon Wheatbelt and Coolgardie regions, it has a low, gently undulating topography, a semi-arid mediterranean climate, and extensive Eucalyptus mallee vegetation. About half of the region has been cleared for intensive agriculture. Recognised as a region under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA), it was first defined by John Stanley Beard in 1980.

Lake Bryde-East Lake Bryde is a DIWA-listed freshwater wetland system located in the Great Southern region of Western Australia. The system consists of two lakes: Lake Bryde, with an area of 50 hectares ; and East Lake Bryde, with an area of about 1.4 square kilometres (0.54 sq mi). They are located at the head of a chain of lakes that extend to Lake Magenta, and ultimately form part of the Swan-Avon drainage system.

The glassworts are various succulent, annual halophytic plants, that is, plants that thrive in saline environments, such as seacoasts and salt marshes. The original English glasswort plants belong to the genus Salicornia, but today the glassworts include halophyte plants from several genera, some of which are native to continents unknown to the medieval English, and growing in ecosystems, such as mangrove swamps, never envisioned when the term glasswort was coined.
This is a list of the terrestrial flora of the Houtman Abrolhos. Only vascular plants are listed — there have been some collections of mosses, liverworts and lichens from the Houtman Abrolhos, but no information has been published on these non-vascular groups.

Tecticornia is a genus of succulent, salt tolerant plants largely endemic to Australia. Taxa in the genus are commonly referred to as samphires. In 2007, the genus Halosarcia, along with three other Australian genera was incorporated into the genus.
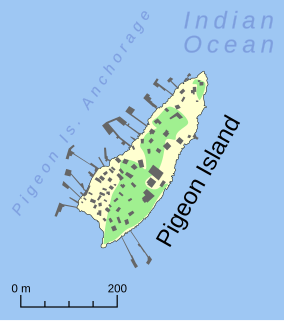
Pigeon Island is a small island located need the middle of the Wallabi Group of the Houtman Abrolhos, an archipelago off the coast of Western Australia. It is almost entirely given over to western rock lobster fishers' camps, and as a result is far more disturbed than most other islands in the archipelago. A nearby island also seasonally populated by fishers is named Little Pigeon Island, hence Pigeon Island is sometimes referred to as "Big Pigeon Island".

Tecticornia halocnemoides, commonly known as shrubby samphire or grey glasswort, is a species of succulent, salt tolerant plant endemic to Australia. It grows as a spreading or erect shrub up to fifty centimetres high. It was first published as Arthrocnemum halocnemoides in 1845, but transferred into Halosarcia in 1980, and into Tecticornia in 2007.

Tecticornia arbuscula, the shrubby glasswort or scrubby samphire, is a species of plant in the family Amaranthaceae, native to Australia. It is a shrub that grows to 2 metres in height, with a spreading habit. It has succulent swollen branchlets with small leaf lobes.

Tecticornia pergranulata is a succulent halophytic plant species in the family Chenopodiaceae, native to Australia. This plant is commonly tested in labs involving its C3 photosynthesis and its unique resistance to salinity and adversity.

The flora of Australia comprises a vast assemblage of plant species estimated to over 20,000 vascular and 14,000 non-vascular plants, 250,000 species of fungi and over 3,000 lichens. The flora has strong affinities with the flora of Gondwana, and below the family level has a highly endemic angiosperm flora whose diversity was shaped by the effects of continental drift and climate change since the Cretaceous. Prominent features of the Australian flora are adaptations to aridity and fire which include scleromorphy and serotiny. These adaptations are common in species from the large and well-known families Proteaceae (Banksia), Myrtaceae, and Fabaceae.

Lake Warden is a salt lake in the Goldfields-Esperance region of Western Australia. It and its associated wetlands are protected in a nature reserve; they were recognised as being of international importance under the Ramsar Convention through designation of the Lake Warden System on 7 June 1990 as Ramsar Site 485. The lake is also a DIWA-listed wetland.
Grevillea acacioides, is a shrub which is endemic to Western Australia.

Grevillea globosa is a shrub in the family Proteaceae. It is endemic to Western Australia, occurring in the northern wheatbelt.

Lake Newland Conservation Park is a protected area in the Australian state of South Australia located on the west coast of the Eyre Peninsula about 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) north of the town of Elliston. It was proclaimed in 1991 in order to protect Lake Newland, a hypersaline lake, and an associated wetland complex. It lies in the traditional lands of the Wirangu people.

Tecticornia indica is a species of plant that is succulent and halophyte which grows in salt marshes on tropical areas of the world. This plant belongs to the Chenopodiaceae, which are now included in family Amaranthaceae.

Lake Austin is an ephemeral salt lake located in the Mid West region of Western Australia, approximately 21 km (13 mi) south of Cue and 55 km (34 mi) north of Mount Magnet. It is named after Robert Austin, who explored the area around the lake in 1854. The abandoned town of Austin is located on an island in the lake. The Great Northern Highway passes through this island as it crosses the lake. Lake Austin is also the name of the locality surrounding it.

Lake Yealering, also known as Yealering Lakes, is an ephemeral salt lake in the Wheatbelt region of Western Australia located on the southern edge of the town of Yealering, 30 km (19 mi) north west of Wickepin and about 250 km (160 mi) south east of Perth.
Kelly Anne Shepherd is an Australian botanist, who has published some 91 names.














