
The South China Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean. It is bounded in the north by South China, in the west by the Indochinese Peninsula, in the east by the islands of Taiwan and northwestern Philippines, and in the south by the Indonesian islands of Borneo, eastern Sumatra and the Bangka Belitung Islands, encompassing an area of around 3,500,000 km2 (1,400,000 sq mi). It communicates with the East China Sea via the Taiwan Strait, the Philippine Sea via the Luzon Strait, the Sulu Sea via the straits around Palawan, and the Java Sea via the Karimata and Bangka Straits. The Gulf of Thailand and the Gulf of Tonkin are part of the South China Sea.
An exclusive mandate is a government's assertion of its legitimate authority over a certain territory, part of which another government controls with stable, de facto sovereignty. It is also known as a claim to sole representation or an exclusive authority claim. The concept was particularly important during the Cold War period when a number of states were divided on ideological grounds.

Antigius is a genus of butterflies in the family Lycaenidae. The species of this genus are found in the eastern Palearctic realm, as well as Taiwan and Myanmar.

Euaspa is a genus of butterflies in the family Lycaenidae. They are found in the Indomalayan realm ranging from the Himalayas to Vietnam. They feed on oaks.

Favonius is a Palearctic genus of butterflies in the family Lycaenidae.
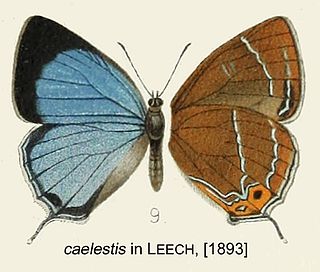
Howarthia is a genus of butterflies in the family Lycaenidae ranging from China to Laos and Myanmar. It is named after British entomologist Graham Howarth.

Japonica is an East Palearctic genus of butterfly in the family Lycaenidae.

Neozephyrus is a genus of butterflies in the family Lycaenidae. Species in this genus are mainly distributed in East Asia. The larval food plant is alder or - for Neozephyrus quercus - oak.

Cordelia is a genus of hairstreak butterflies in the family Lycaenidae. The species are endemic to temperate China.

The Republic of China (ROC), commonly known as "Nationalist China" or "Taiwan", supported South Vietnam during the Vietnam War. Both were anti-communist Asian nations fighting against rival communist regimes, the People's Republic of China and North Vietnam.
Gonerilia seraphim is a butterfly in the family Lycaenidae.

Favonius saphirinus is a butterfly in the family Lycaenidae. It is found in the Russian Far East, north-eastern China, Korea and Japan.

The history of Anglicanism in Sichuan began in 1887 when Anglican missionaries working with the China Inland Mission began to arrive from the United Kingdom. These were later joined by missionaries from the Church Missionary Society and Bible Churchmen's Missionary Society. Or according to Annals of Religion in Mianyang, in 1885, a small mission church was already founded in Mianyang by Alfred Arthur Phillips and Gertrude Emma Wells of the Church Missionary Society. Missionaries built churches, founded schools, and distributed Chinese translations of Anglican religious texts. These efforts were relatively successful and Anglicanism grew to become one of the two largest denominations of Protestant Christianity in the province, alongside Methodism.

The Protestant mission began in the Chinese province of Sichuan in 1877, when premises were rented by the China Inland Mission in Chungking. However, it grew rather slowly, it was not until the late 1980s that Protestantism experienced rapid growth. The two largest denominations in the province before 1949 were Anglicanism and Methodism.

The Canadian Methodist Mission (CMM), also known as Missionary Society of the Methodist Church in Canada, was a Canadian Methodist Christian missionary society mostly working in the province of Szechwan, which was also referred to as "West China."
The history of Adventism in Sichuan began in 1914 when American and Chinese missionaries arrived in Chongqing. Adventist missionaries in Sichuan were organized under the Szechwan Mission, later split into the East Szechwan, West Szechwan, and Tibetan Missions. Missionary activity in China generated controversy among many native Chinese and faced opposition from popular riots and the later Communist movement in China. Numerous mission properties and native Church leaders in Sichuan were respectively destroyed and killed by communists in the mid-1930s. Missionary activity ceased after the communist take over of China in 1949. Under government oppression in the 1950s, Adventist congregations and other Protestant Churches across China severed their ties with overseas Churches, and their congregations subsequently merged into the Three-Self Patriotic Church. Since 1980, their services have been provided by the China Christian Council.












