 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Tetrabromoethene | |
| Other names Perbromoethene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.084 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2Br4 | |
| Molar mass | 343.638 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless crystals |
| Melting point | 50 °C (122 °F; 323 K) |
| Boiling point | 226 °C (439 °F; 499 K) |
| −114.8·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
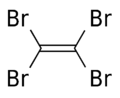
Tetrabromoethylene is an organobromine compound with the chemical formula C2Br4. Its structure is Br2C=CBr2. Under standard conditions, it exists in a form of colorless crystals. It is a brominated derivative of ethylene. Tetrabromoethylene is a potential fungicide and bactericide on fruits. [1] It was used in mineral separation. [2] It is an irritant. [3]
It is prepared from acetylene and bromine in multiple steps. [1] [4] One method involves dehydrobromination of pentabromoethane, other method involves bromination of dibromoethylene in chloroform. [1] Reaction of mercuric acetylide and bromine also gives tetrabromoethylene. [5] It can be produced by oxybrominating butane with free oxygen and bromine. [6]
Tetrabromoethylene gives tribromoacetyl bromide upon treatment with fuming nitric acid. [7]