Chlorine is a chemical element; it has symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine.
Chlordane, or chlordan, is an organochlorine compound that was used as a pesticide. It is a white solid. In the United States, chlordane was used for termite-treatment of approximately 30 million homes until it was banned in 1988. Chlordane was banned 10 years earlier for food crops like corn and citrus, and on lawns and domestic gardens.
In organochlorine chemistry, reductive dechlorination describes any chemical reaction which cleaves the covalent bond between carbon and chlorine via reductants, to release chloride ions. Many modalities have been implemented, depending on the application. Reductive dechlorination is often applied to remediation of chlorinated pesticides or dry cleaning solvents. It is also used occasionally in the synthesis of organic compounds, e.g. as pharmaceuticals.
Halocarbon compounds are chemical compounds in which one or more carbon atoms are linked by covalent bonds with one or more halogen atoms resulting in the formation of organofluorine compounds, organochlorine compounds, organobromine compounds, and organoiodine compounds. Chlorine halocarbons are the most common and are called organochlorides.
Organochlorine chemistry is concerned with the properties of organochlorine compounds, or organochlorides, organic compounds containing at least one covalently bonded atom of chlorine. The chloroalkane class includes common examples. The wide structural variety and divergent chemical properties of organochlorides lead to a broad range of names, applications, and properties. Organochlorine compounds have wide use in many applications, though some are of profound environmental concern, with TCDD being one of the most notorious.
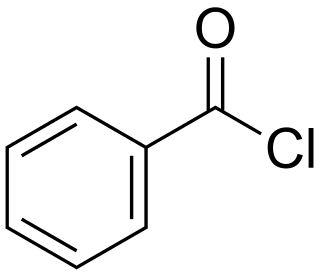
Benzoyl chloride, also known as benzenecarbonyl chloride, is an organochlorine compound with the formula C7H5ClO. It is a colourless, fuming liquid with an irritating odour, and consists of a benzene ring with an acyl chloride substituent. It is mainly useful for the production of peroxides but is generally useful in other areas such as in the preparation of dyes, perfumes, pharmaceuticals, and resins.

Dichlorine monoxide is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula Cl2O. It was first synthesised in 1834 by Antoine Jérôme Balard, who along with Gay-Lussac also determined its composition. In older literature it is often referred to as chlorine monoxide, which can be a source of confusion as that name now refers to the ClO• radical.

Chlorobenzene is an aryl chloride and the simplest of the chlorobenzenes, consisting of a benzene ring substituted with one chlorine atom. Its chemical formula is C6H5Cl. This colorless, flammable liquid is a common solvent and a widely used intermediate in the manufacture of other chemicals.
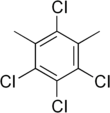
Chlorotoluenes are aryl chlorides based on toluene in which at least one aromatic hydrogen atom is replaced with a chlorine atom. They have the general formula C7H8–nCln, where n = 1–5 is the number of chlorine atoms.

β-Hexachlorocyclohexane (β-HCH) is an organochloride which is one of the isomers of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH). It is a byproduct of the production of the insecticide lindane (γ-HCH). It is typically constitutes 5–14% of technical-grade lindane, though it has not been produced or used in the United States since 1985. As of 2009, the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants classified α-hexachlorocyclohexane and β-HCH as persistent organic pollutants (POPs), due to the chemical's ability to persist in the environment, bioaccumulative, biomagnifying, and long-range transport capacity.
A chlorophenol is any organochloride of phenol that contains one or more covalently bonded chlorine atoms. There are five basic types of chlorophenols and 19 different chlorophenols in total when positional isomerism is taken into account. Chlorophenols are produced by electrophilic halogenation of phenol with chlorine.
1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene is an organochlorine compound, one of three isomers of trichlorobenzene. It is a derivative of benzene with three chloride substituents. It is a colorless liquid used as a solvent for a variety of compounds and materials.

Hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH), C
6H
6Cl
6, is any of several polyhalogenated organic compounds consisting of a six-carbon ring with one chlorine and one hydrogen attached to each carbon. This structure has nine stereoisomers, which differ by the stereochemistry of the individual chlorine substituents on the cyclohexane. It is sometimes erroneously called "benzene hexachloride" (BHC). They have been used as models for analyzing the effects of different geometric positions of the large atoms with dipolar bonds on the stability of the cyclohexane conformation. The isomers are poisonous, pesticidal, and persistent organic pollutants, to varying degrees.
Bleaching of wood pulp is the chemical processing of wood pulp to lighten its color and whiten the pulp. The primary product of wood pulp is paper, for which whiteness is an important characteristic. These processes and chemistry are also applicable to the bleaching of non-wood pulps, such as those made from bamboo or kenaf.

Pentachlorobenzene (PeCB) is an aryl chloride and a five-substituted chlorobenzene with the molecular formula C6HCl5 which is a chlorinated aromatic hydrocarbon. It consists of a benzene ring substituted with five chlorine atoms. PeCB was once used industrially for a variety of uses, but because of environmental concerns there are currently no large scale uses of PeCB. Pentachlorobenzene is a known persistent organic pollutant (POP) and banned globally by the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants in 2009.
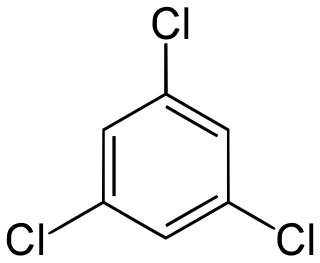
1,3,5-Trichlorobenzene is an organochlorine compound. It is one of the three isomers of trichlorobenzene. Being more symmetrical than the other isomers, it exists as colourless crystals whereas the other isomers are liquids at room temperature.

Zerovalent iron (ZVI) is jargon that describes forms of iron metal that are proposed for used in Groundwater remediation.

In the petroleum refining and petrochemical industries, the initialism BTX refers to mixtures of benzene, toluene, and the three xylene isomers, all of which are aromatic hydrocarbons. The xylene isomers are distinguished by the designations ortho –, meta –, and para – as indicated in the adjacent diagram. If ethylbenzene is included, the mixture is sometimes referred to as BTEX.
The Newbery-Vautin chlorination process is a method for extracting gold from its ore through the use of chlorination. This process was jointly developed by James Cosmo Newbery and Claude Vautin.
1,2,3-Trichlorobenzene is an organochlorine compound with the chemical formula C6H3Cl3. This is one of three isomers of trichlorobenzene; the two others are 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene and 1,3,5-Trichlorobenzene.