Related Research Articles

The gray whale, also known as the grey whale, gray back whale, Pacific gray whale, Korean gray whale, or California gray whale, is a baleen whale that migrates between feeding and breeding grounds yearly. It reaches a length of 14.9 meters (49 ft), a weight of up to 41 tonnes (90,000 lb) and lives between 55 and 70 years, although one female was estimated to be 75–80 years of age. The common name of the whale comes from the gray patches and white mottling on its dark skin. Gray whales were once called devil fish because of their fighting behavior when hunted. The gray whale is the sole living species in the genus Eschrichtius. It was formerly thought to be the sole living genus in the family Eschrichtiidae, but more recent evidence classifies members of that family in the family Balaenopteridae. This mammal is descended from filter-feeding whales that appeared during the Neogene.

The Norwegian Sea is a marginal sea in the Atlantic Ocean, northwest of Norway between the North Sea and the Greenland Sea, adjoining the Barents Sea to the northeast. In the southwest, it is separated from the Atlantic Ocean by a submarine ridge running between Iceland and the Faroe Islands. To the north, the Jan Mayen Ridge separates it from the Greenland Sea.

The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Northern Pacific Ocean. It forms, along with the Bering Strait, the divide between the two largest landmasses on Earth: Eurasia and The Americas. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves. The Bering Sea is named for Vitus Bering, a Danish navigator in Russian service, who, in 1728, was the first European to systematically explore it, sailing from the Pacific Ocean northward to the Arctic Ocean.

The Gulf of Aden is a deepwater gulf between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channel, Socotra (Yemen), Somaliland and Somalia to the south. In the northwest, it connects with the Red Sea through the Bab-el-Mandeb strait, and it connects with the Arabian Sea to the east. To the west, it narrows into the Gulf of Tadjoura in Djibouti.

The Gulf of St. Lawrence is the outlet of the North American Great Lakes via the St. Lawrence River into the Atlantic Ocean. The gulf is a semi-enclosed sea, covering an area of about 226,000 square kilometres (87,000 sq mi) and containing about 34,500 cubic kilometres (8,300 cu mi) of water, which results in an average depth of 152 metres (499 ft).

Right whales or black whales are three species of large baleen whales of the genus Eubalaena: the North Atlantic right whale, the North Pacific right whale and the Southern right whale. They are classified in the family Balaenidae with the bowhead whale. Right whales have rotund bodies with arching rostrums, V-shaped blowholes and dark gray or black skin. The most distinguishing feature of a right whale is the rough patches of skin on its head, which appear white due to parasitism by whale lice. Right whales can grow up to more than 18 m (59 ft) long with a highest-recorded length of 19.8 m (65 ft). Right whales are very robust whales, weighing 100 short tons or more. The largest known right whales can attain 20.7 m (68 ft) in length and weigh up to 135,000 kg (298,000 lb). Specimens measuring 21.3 m (70 ft) and weighing 150,000 kg (330,000 lb) are documented in whaling records but not scientifically confirmed. Their immense bulk makes right whales significantly heavier than other whales of similar or greater length such as the humpback, gray, sperm and even fin whales. In fact, right whales rank only behind the blue whale in sheer body mass. One (apocryphal) explanation for their name is that whalers identified them as the "right" whale to kill on a hunt due to the plentiful oil and baleen they could provide.

The North Pacific right whale is a very large, thickset baleen whale species that is extremely rare and endangered.

The Grand Banks of Newfoundland are a series of underwater plateaus south-east of the island of Newfoundland on the North American continental shelf. The Grand Banks are one of the world's richest fishing grounds, supporting Atlantic cod, swordfish, haddock and capelin, as well as shellfish, seabirds and sea mammals.

Cook Inlet stretches 180 miles (290 km) from the Gulf of Alaska to Anchorage in south-central Alaska. Cook Inlet branches into the Knik Arm and Turnagain Arm at its northern end, almost surrounding Anchorage. On its southern end, it merges with Shelikof Strait, Stevenson Entrance, Kennedy Entrance and Chugach Passage.

The melon-headed whale, also, less commonly, known as the electra dolphin, little killer whale, or many-toothed blackfish, is a small- to medium-sized toothed whale of the oceanic dolphin family (Delphinidae). The common name is derived from the head shape. Melon-headed whales are widely distributed throughout deep tropical/subtropical waters worldwide, however they are rarely encountered at sea. They are found near shore mostly around oceanic islands, such as Hawaii, French Polynesia, and the Philippines.

The Beaufort Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of the Northwest Territories, the Yukon, and Alaska, and west of Canada's Arctic islands. The sea is named after Sir Francis Beaufort, a hydrographer. The Mackenzie River, the longest in Canada, empties into the Canadian part of the Beaufort Sea west of Tuktoyaktuk, which is one of the few permanent settlements on the sea's shores.

Baffin Bay, located between Baffin Island and the west coast of Greenland, is defined by the International Hydrographic Organization as a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is sometimes considered a sea of North Atlantic Ocean. It is connected to the Atlantic via Davis Strait and the Labrador Sea. The narrower Nares Strait connects Baffin Bay with the Arctic Ocean. The bay is not navigable most of the year because of the ice cover and high density of floating ice and icebergs in the open areas. However, a polynya of about 80,000 km2 (31,000 sq mi), known as the North Water, opens in summer on the north near Smith Sound. Most of the aquatic life of the bay is concentrated near that region.
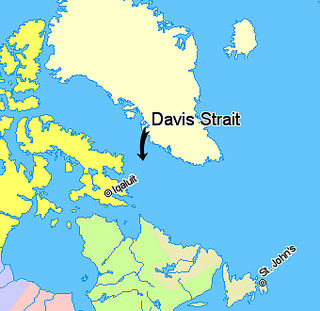
Davis Strait is a northern arm of the Atlantic Ocean that lies north of the Labrador Sea. It lies between mid-western Greenland and Baffin Island in Nunavut, Canada. To the north is Baffin Bay. The strait was named for the English explorer John Davis (1550–1605), who explored the area while seeking a Northwest Passage. By the 1650s it was used for whale hunting.

The Bedford Institute of Oceanography (BIO) is a major Government of Canada ocean research facility located in Dartmouth, Nova Scotia. BIO is the largest ocean research station in Canada. Established in 1962 as Canada's first, and currently largest, federal centre for oceanographic research, BIO derives its name from the Bedford Basin, an inland bay comprising the northern part of Halifax Harbour, upon which it is located.

Foxe Basin is a shallow oceanic basin north of Hudson Bay, in Nunavut, Canada, located between Baffin Island and the Melville Peninsula. For most of the year, it is blocked by sea ice and drift ice made up of multiple ice floes.

The Gulf of Mannar Marine National Park is a protected area of India consisting of 21 small islands (islets) and adjacent coral reefs in the Gulf of Mannar in the Indian Ocean. It lies 1 to 10 km away from the east coast of Tamil Nadu, India for 160 km between Thoothukudi (Tuticorin) and Dhanushkodi. It is the core area of the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve which includes a 10 km buffer zone around the park, including the populated coastal area. The park has a high diversity of plants and animals in its marine, intertidal and near shore habitats. Public access inside the park is limited to glass-bottom boat rides.

The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately 14,060,000 km2 (5,430,000 sq mi) and is also known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Mediterranean Sea. It has been described approximately as an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It is also seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing World Ocean.
The Irving Whale is a Canadian barge that sank off the north coast of Prince Edward Island, while en route from Halifax, Nova Scotia to Bathurst, New Brunswick, with a cargo of Bunker C oil in a rich fishing area. It is "one of Canada's most notorious nautical disasters". The barge, owned by J.D. Irving Ltd., had carried oil for JDI from 1967 until it sank in 1970. It was refloated in 1996, re-fitted as a deck barge, re-activated, and renamed ATL 2701 in 2001 and renamed again in 2009, as Atlantic Sea Lion. Since the accident, it only transports dry cargo.
Whaling in Canada encompasses both aboriginal and commercial whaling, and has existed on all three Canadian oceans, Atlantic, Pacific, and Arctic. The indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast have whaling traditions dating back millennia, and the hunting of cetaceans continues by Inuit. Commercial whaling was one of the stimuli for Europeans to explore the sub-Arctic and Arctic, possibly as early as the 14th century. By the late 20th century, watching whales was a more profitable enterprise than hunting them.

Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) are zones within Canadian waters where the marine environment enjoys a high level of environmental protection. Marine Protected Areas are governed by the Oceans Act of 1996 and administered by Fisheries and Oceans Canada.
References
- ↑ Government of Canada, Fisheries and Oceans Canada (2010-04-01). "The Gully". www.inter.dfo-mpo.gc.ca. Retrieved 2019-04-15.
- ↑ https://www.thestreet.com/story/14193950/1/oil-and-gas-platforms-dont-belong-in-the-laurentian-channel.html [ dead link ]