
Pachystoma, commonly known as kunai orchids or 粉口兰属 , is a genus of two species of flowering plants in the orchid family, Orchidaceae. They are deciduous, terrestrial herbs with one or two linear, pleated or veiny leaves and more or less drooping flowers which do not open widely, on a thin, wiry flowering stem. Species in this genus are found in tropical and subtropical Asia to Australia and islands of the southwest Pacific Ocean.

Crepidium, commonly known as 沼兰属 or spur orchids is a genus of about three hundred species of orchids in the family Orchidaceae. Plants in this genus are evergreen, mostly terrestrial plants with short stems lying on the ground, two or more relatively large, pleated leaves and small, non-resupinate flowers with spreading sepals and petals. The genus is widely distributed in the tropics.
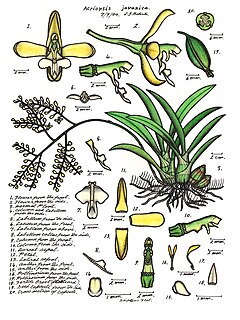
Acriopsis javanica is a species of orchid that is native to Southeast Asia, New Guinea, some Pacific islands and northern Australia. It is a clump-forming epiphyte with dark green leaves and curved, branching flower stems with many white and cream-coloured flowers with purple markings.

Cymbidium madidum, commonly known as the giant boat-lip orchid, is a plant in the orchid family and is endemic to north-eastern Australia. It is a clump-forming epiphyte or lithophyte with crowded pseudobulbs, each with between four and eight flat, strap-shaped, thin leaves and up to seventy olive green flowers with the sepals and petals curving forwards. It is found in moist habitats in eastern Queensland and north-eastern New South Wales.

Spathoglottis plicata, commonly known as the Philippine ground orchid, or large purple orchid is an evergreen, terrestrial plant with crowded pseudobulbs, three or four large, pleated leaves and up to forty resupinate, pink to purple flowers. It is found from tropical and subtropical Asia to Australia and the western Pacific including Tonga and Samoa.
Bulbophyllum boonjee commonly known as the maroon strand orchid, is a species of epiphytic orchid that is endemic to tropical North Queensland. It has crowded, flattened pseudobulbs, stiff, pale green leaves and up to four small, bell-shaped maroon flowers with darker stripes.

Bulbophyllum elisae, commonly known as the pineapple orchid, is a species of epiphytic or lithophytic orchid that is endemic to eastern Australia. It has crowded, wrinkled, pale green or yellowish clump-forming pseudobulbs, stiff, pale green to yellowish leaves and between three and twelve pale green to dark green flowers with a dark red to purple labellum. It usually grows in the tops of rainforest trees, on cliff faces or boulders.
Bulbophyllum lageniforme, commonly known as the smooth strand orchid, is a species of epiphytic or lithophytic orchid that is endemic to tropical North Queensland. It has flattened, pale green, grooved, clump-forming pseudobulbs, stiff, dark green leaves and up to four cream-coloured or pale green flowers with a pink labellum. It usually grows on shrubs, trees and rocks in highland rainforest.

Nervilia concolor, commonly known as the tall shield orchid and as Nervilia aragoana in Australia is a small terrestrial orchid found in South and Southeast Asia and in northern Australia. It has pale green, short-lived flowers with a cream-coloured or yellowish labellum and a more or less circular leaf which emerges at the base of the flowering stem after flowering.

Thelasis, commonly known as fly orchids, is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. Plants in this genus are usually epiphytes, sometimes lithophytes or rarely terrestrials. Some species have pseudobulbs with up to three leaves, whilst others have several leaves in two ranks. A large number of small, white or greenish yellow flowers are borne on a thin, arching flowering stem. There are about thirty species, distributed from tropical and subtropical Asia to the southwest Pacific.

Hetaeria oblongifolia, commonly known as the hairy jewel orchid, is a species of orchid that is native to Southeast Asia, New Guinea and Queensland. It has between four and eight egg-shaped, dark green leaves and up to forty five small, hairy green and white flowers with a deep pouch near the base of the labellum.

Goodyera rubicunda, commonly known as the giant jewel orchid, is a species of orchid that is native to parts of India, Asia, Southeast Asia, New Guinea, Queensland and some Pacific Islands where it grows in damp forest and rainforest. It has between three and six large, egg-shaped leaves and up to ten dull pink and white resupinate flowers that are hairy on the outside.
Liparis nugentiae, commonly known as the large sphinx orchid, is a plant in the orchid family and is endemic to Queensland. It is an epiphytic or lithophytic orchid which forms clumps with flattened pseudobulbs, two to four thin leaves and up to twenty greenish or pale yellow flowers. It grows in rainforest at altitudes above 600 m (2,000 ft) in tropical far North Queensland.

Pachychila pubescens, commonly known as pink kunai orchid or as 粉口兰 , is a plant in the orchid family. It is native to areas from Asia through Southeast Asia to New Guinea and northern Australia. It is a deciduous, terrestrial herb with one or two grass-like leaves and up to ten dull pink, more or less drooping flowers. It grows in wet, grassy places in forests and woodlands.

Dendrobium monophyllum, commonly known as the lily-of-the-valley orchid, is an epiphytic or lithophytic orchid in the family Orchidaceae. It has pale green to yellowish pseudobulbs with one or two leaves, and between five and twenty bell-shaped yellow flowers. It grows in rainforest in New South Wales and Queensland, Australia.
Dendrobium convexum, commonly known as the piggyback orchid, is an epiphytic orchid in the family Orchidaceae. It has a creeping, brittle root, erect pseudobulbs with a single leaf on the top and one or two cream-coloured, short-lived flowers with a red and yellow labellum. It is native to Southeast Asia, New Guinea and tropical North Queensland, Australia.

Bulbophyllum maxillare, commonly known as the red horntail orchid, is a species of epiphytic orchid with tapered grooved, dark green to yellowish pseudobulbs, each with a single large, thin leaf and a single reddish flower with yellow or white edges. The lateral sepals are much larger than the dorsal sepal which in turn is much larger than the petals. It grows on the lower branches of rainforest trees in India, New Guinea and tropical North Queensland.

Schoenorchis micrantha, commonly known as the tangled flea orchid, is a small epiphytic orchid that forms small, tangled clumps and has thin stems, many linear leaves and up to thirty small, white, bell-shaped flowers. It is found from Indochina to the south-west Pacific.
Bryobium retusum, commonly known as the Christmas Island urchin orchid, is an epiphytic clump-forming orchid that has oval, fleshy green pseudobulbs, each with two leaves and between seven and twelve short-lived, self-pollinating, pale green, hairy flowers. This orchid is found between Java and New Caledonia.

Thelasis carinata, commonly known as the triangular fly orchid, is a plant in the orchid family. It is a clump-forming epiphyte or lithophyte that lacks pseudobulbs. There are groups of between two and six erect, flattened stems each with up to six leaves that have a ridged lower surface. Up to fifteen green and white flowers are arranged on a thin but stiff flowering stem. This orchid is found from Thailand to the southwest Pacific.













