Related Research Articles

The endocrine system is a messenger system comprising feedback loops of the hormones released by internal glands of an organism directly into the circulatory system, regulating distant target organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neural control center for all endocrine systems. In humans, the major endocrine glands are the thyroid gland and the adrenal glands. The study of the endocrine system and its disorders is known as endocrinology.

Hyperthyroidism is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. It is noted that thyrotoxicosis is related to hyper-kinetic movement disorders including chorea and myoclonus. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, heat intolerance, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, hand tremor, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less severe in the elderly and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.

The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thyroid is located at the front of the neck, below the Adam's apple. Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones – triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) – and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis, and in children, growth and development. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which is produced by the hypothalamus.
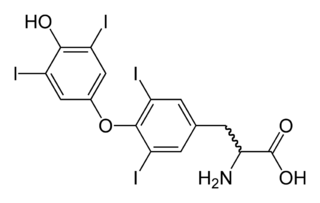
Hypothyroidism is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as poor ability to tolerate cold, a feeling of tiredness, constipation, slow heart rate, depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goiter. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome.

Parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands in the neck of humans and other tetrapods. Humans usually have four parathyroid glands, located on the back of the thyroid gland in variable locations. The parathyroid gland produces and secretes parathyroid hormone in response to a low blood calcium, which plays a key role in regulating the amount of calcium in the blood and within the bones.

Thyroid follicular cells are the major cell type in the thyroid gland, and are responsible for the production and secretion of the thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). They form the single layer of cuboidal epithelium that makes up the outer structure of the almost spherical thyroid follicle.
Pentagastrin is a synthetic polypeptide that has effects like gastrin when given parenterally. It stimulates the secretion of gastric acid, pepsin, and intrinsic factor, and has been used as a diagnostic aid as the pentagastrin-stimulated calcitonin test.

Endocrine glands are ductless glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, hypothalamus and adrenal glands. The hypothalamus and pituitary glands are neuroendocrine organs.
In medicine or biology, a diverticulum is an outpouching of a hollow structure in the body. Depending upon which layers of the structure are involved, diverticula are described as being either true or false.

An oncocytoma is a tumor made up of oncocytes, epithelial cells characterized by an excessive amount of mitochondria, resulting in an abundant acidophilic, granular cytoplasm. The cells and the tumor that they compose are often benign but sometimes may be premalignant or malignant.
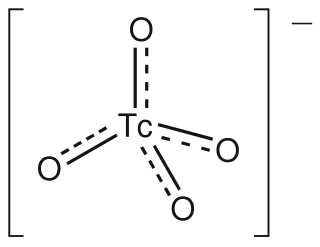
The pertechnetate ion is an oxoanion with the chemical formula TcO−
4. It is often used as a convenient water-soluble source of isotopes of the radioactive element technetium (Tc). In particular it is used to carry the 99mTc isotope which is commonly used in nuclear medicine in several nuclear scanning procedures.

Thyroid disease is a medical condition that affects the function of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located at the front of the neck and produces thyroid hormones that travel through the blood to help regulate many other organs, meaning that it is an endocrine organ. These hormones normally act in the body to regulate energy use, infant development, and childhood development.
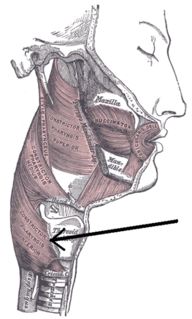
The Inferior pharyngeal constrictor, the thickest of the three constrictors, arises from the sides of the cricoid and thyroid cartilage. Similarly to the superior and middle pharyngeal constrictor muscles, it is innervated by the vagus nerve, specifically, by branches from the pharyngeal plexus and by neuronal branches from the recurrent laryngeal nerve.

Thyroiditis is the inflammation of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located on the front of the neck below the laryngeal prominence, and makes hormones that control metabolism.

The superior thyroid artery arises from the external carotid artery just below the level of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone and ends in the thyroid gland.
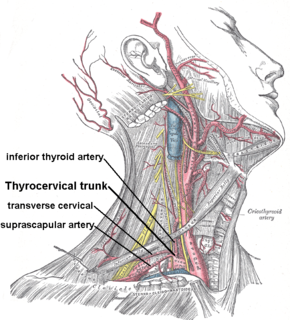
The inferior thyroid artery is an artery in the neck. It arises from the thyrocervical trunk and passes upward, in front of the vertebral artery and longus colli muscle. It then turns medially behind the carotid sheath and its contents, and also behind the sympathetic trunk, the middle cervical ganglion resting upon the vessel.

The thyroid ima artery is an artery of the head and neck. It is an anatomical variant that, when present, supplies blood to the thyroid gland primarily, or the trachea, the parathyroid gland and the thymus gland in rare cases. It has also been reported to be a compensatory artery when one or both of the inferior thyroid arteries are absent, and in a few cases the only source of blood to the thyroid gland. Furthermore, it varies in origin, size, blood supply, and termination, and occurs in around 3.8% of the population and is 4 times more common in adults than in fetuses. Because of the variations and rarity, it may lead to surgical complications.
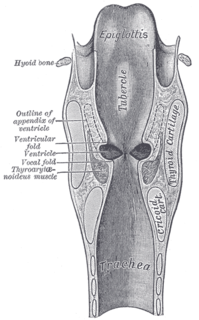
The laryngeal ventricle, is a fusiform fossa, situated between the vestibular and vocal folds on either side, and extending nearly their entire length. There is also a sinus of Morgagni in the pharynx.

Thyroid dysgenesis is a cause of congenital hypothyroidism where the thyroid is missing, ectopic, or severely underdeveloped.It should not be confused with iodine deficiency, or with other forms of congenital hypothyroidism, such as thyroid dyshormonogenesis, where the thyroid is present but not functioning correctly.
The fetal endocrine system is one of the first systems to develop during prenatal development.
References
- ↑ "Endocrine Glands". Archived from the original on March 14, 2008.
- ↑ "The thyroid gland".