Related Research Articles

The endocrine system is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neural control center for all endocrine systems.

The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the isthmus. Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid.
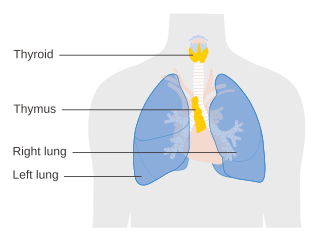
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus is located in the upper front part of the chest, in the anterior superior mediastinum, behind the sternum, and in front of the heart. It is made up of two lobes, each consisting of a central medulla and an outer cortex, surrounded by a capsule.

The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The human pituitary gland is oval shaped, about 1 cm in diameter, 0.5–1 gram (0.018–0.035 oz) in weight on average, and about the size of a kidney bean.

Parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands in the neck of humans and other tetrapods. Humans usually have four parathyroid glands, located on the back of the thyroid gland in variable locations. The parathyroid gland produces and secretes parathyroid hormone in response to low blood calcium, which plays a key role in regulating the amount of calcium in the blood and within the bones.

Calcitonin is a 32 amino acid peptide hormone secreted by parafollicular cells (also known as C cells) of the thyroid (or endostyle) in humans and other chordates in the ultimopharyngeal body. It acts to reduce blood calcium (Ca2+), opposing the effects of parathyroid hormone (PTH).

Thyroid follicular cells (also called thyroid epithelial cells or thyrocytes) are the major cell type in the thyroid gland, and are responsible for the production and secretion of the thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). They form the single layer of cuboidal epithelium that makes up the outer structure of the almost spherical thyroid follicle.

Parafollicular cells, also called C cells, are neuroendocrine cells in the thyroid. They are called C cells because the primary function of these cells is to secrete calcitonin. They are located adjacent to the thyroid follicles and reside in the connective tissue. These cells are large and have a pale stain compared with the follicular cells. In teleost and avian species these cells occupy a structure outside the thyroid gland named the ultimopharyngeal body.
A germ layer is a primary layer of cells that forms during embryonic development. The three germ layers in vertebrates are particularly pronounced; however, all eumetazoans produce two or three primary germ layers. Some animals, like cnidarians, produce two germ layers making them diploblastic. Other animals such as bilaterians produce a third layer between these two layers, making them triploblastic. Germ layers eventually give rise to all of an animal's tissues and organs through the process of organogenesis.

The endocrine system is a network of glands and organs located throughout the body. It is similar to the nervous system in that it plays a vital role in controlling and regulating many of the body's functions. Endocrine glands are ductless glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testicles, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, hypothalamus and adrenal glands. The hypothalamus and pituitary glands are neuroendocrine organs.

The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches, are transient structures seen in the embryonic development of humans and other vertebrates, that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, the arches support the gills and are known as the branchial arches, or gill arches.

In the embryonic development of vertebrates, pharyngeal pouches form on the endodermal side between the pharyngeal arches. The pharyngeal grooves form the lateral ectodermal surface of the neck region to separate the arches.
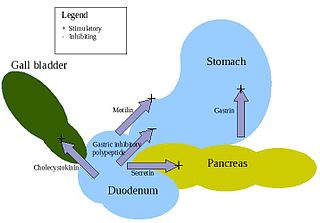
APUD cells (DNES cells) constitute a group of apparently unrelated endocrine cells, which were named by the scientist A.G.E. Pearse, who developed the APUD concept in the 1960s based on calcitonin-secreting parafollicular C cells of dog thyroid. These cells share the common function of secreting a low molecular weight polypeptide hormone. There are several different types which secrete the hormones secretin, cholecystokinin and several others. The name is derived from an acronym, referring to the following:

Human embryonic development or human embryogenesis is the development and formation of the human embryo. It is characterised by the processes of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, the development of the human body entails growth from a one-celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilization occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form the single cell zygote and the germinal stage of development commences. Human embryonic development covers the first eight weeks of development, which have 23 stages, called Carnegie stages. At the beginning of the ninth week, the embryo is termed a fetus. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features and a more complete set of developing organs.

Homeobox protein Hox-A3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HOXA3 gene.
The cranial neural crest is one of the four regions of the neural crest.
Ectopic thymus is a condition where thymus tissue is found in an abnormal location (ectopia). It usually does not cause symptoms, but may leads to a mass in the neck that may compress the trachea and the esophagus. It is thought to be the result of either a failure of descent or a failure of involution of normal thymus tissue. It may be diagnosed with radiology, such as an ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging. If it causes illness, surgery can be used to remove it. Recurrence after surgery is very unlikely.
The face and neck development of the human embryo refers to the development of the structures from the third to eighth week that give rise to the future head and neck. They consist of three layers, the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, which form the mesenchyme, neural crest and neural placodes. The paraxial mesoderm forms structures named somites and somitomeres that contribute to the development of the floor of the brain and voluntary muscles of the craniofacial region. The lateral plate mesoderm consists of the laryngeal cartilages. The three tissue layers give rise to the pharyngeal apparatus, formed by six pairs of pharyngeal arches, a set of pharyngeal pouches and pharyngeal grooves, which are the most typical feature in development of the head and neck. The formation of each region of the face and neck is due to the migration of the neural crest cells which come from the ectoderm. These cells determine the future structure to develop in each pharyngeal arch. Eventually, they also form the neurectoderm, which forms the forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain, cartilage, bone, dentin, tendon, dermis, pia mater and arachnoid mater, sensory neurons, and glandular stroma.
The fetal endocrine system is one of the first systems to develop during prenatal development of a human individual. The endocrine system arises from all three embryonic germ layers. The endocrine glands that produce the steroid hormones, such as the gonads and adrenal cortex, arise from the mesoderm. In contrast, endocrine glands that arise from the endoderm and ectoderm produce the amine, peptide, and protein hormones.
A cervical thymic cyst, also called thymopharyngeal duct cyst, is a fluid-filled mass that occurs when the thymopharyngeal duct, an embryonic structure connecting the nascent thymus with the embryonic pharynx, fails to close and disappear. A thymic cyst is typically a solitary mass on one side of the neck, and is usually found near the carotid sheath. Some cervical thymic cysts may extend into the mediastinum. It is usually asymptomatic. The diagnostic process includes differentiating between other causes of neck masses in infants and children, including branchial cleft cysts and cystic hygromas. The treatment is surgical excision. On histologic examination, the wall of the cyst includes thymic tissue, and may include parathyroid gland tissue because of the parathyroid gland's common embryonic origin with the thymus gland in the third pharyngeal pouch. Fewer than 100 cases of cervical thymic cysts have been reported in the medical literature.
References
- ↑ "Ultimobranchial bodies" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- 1 2 3 4 5 Adams A, Mankad K, Offiah C, Childs L (February 2016). "Branchial cleft anomalies: a pictorial review of embryological development and spectrum of imaging findings". Insights into Imaging. 7 (1): 69–76. doi:10.1007/s13244-015-0454-5. PMC 4729717 . PMID 26661849.
- ↑ Johansson E, Andersson L, Örnros J, Carlsson T, Ingeson-Carlsson C, Liang S, et al. (October 2015). "Revising the embryonic origin of thyroid C cells in mice and humans". Development. 142 (20): 3519–3528. doi:10.1242/dev.126581. PMC 4631767 . PMID 26395490.
- 1 2 Agathos EA, Tomos PI, Kostomitsopoulos N, Koutsoukos PG (February 2019). "Calcitonin as an anticalcification treatment for implantable biological tissues". Journal of Cardiology. New insights in treatment for heart failure. 73 (2): 179–182. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2018.07.010 . PMID 30377016. S2CID 53110929.