
Hyperthyroidism is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, heat intolerance, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, hand tremor, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less severe in the elderly and during pregnancy. An uncommon but life-threatening complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature; this often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.

The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the isthmus (pl.: isthmi). The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones – triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) – and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis and growth and development in children. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which is produced by the hypothalamus.
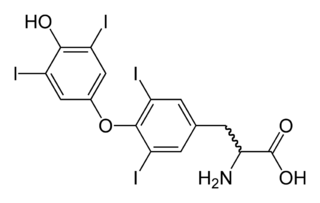
Hypothyroidism is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as poor ability to tolerate cold, extreme fatigue, muscle aches, constipation, slow heart rate, depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goitre. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome.

Congenital hypothyroidism (CH) is thyroid hormone deficiency present at birth. If untreated for several months after birth, severe congenital hypothyroidism can lead to growth failure and permanent intellectual disability. Infants born with congenital hypothyroidism may show no effects, or may display mild effects that often go unrecognized as a problem. Significant deficiency may cause excessive sleeping, reduced interest in nursing, poor muscle tone, low or hoarse cry, infrequent bowel movements, significant jaundice, and low body temperature.

Hashimoto's thyroiditis, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis and Hashimoto's disease, is an autoimmune disease in which the thyroid gland is gradually destroyed. A slightly broader term is autoimmune thyroiditis, identical other than that it is also used to describe a similar condition without a goiter.

A thyroglossal cyst or thyroglossal duct cyst is a fibrous cyst that forms from a persistent thyroglossal duct. Thyroglossal cysts can be defined as an irregular neck mass or a lump which develops from cells and tissues left over after the formation of the thyroid gland during developmental stages.

Primrose syndrome is a rare, slowly progressive genetic disorder that can vary symptomatically between individual cases, but is generally characterised by ossification of the external ears, learning difficulties, and facial abnormalities. It was first described in 1982 in Scotland's Royal National Larbert Institution by Dr D.A.A. Primrose.

Pendred syndrome is a genetic disorder leading to congenital bilateral sensorineural hearing loss and goitre with euthyroid or mild hypothyroidism. There is no specific treatment, other than supportive measures for the hearing loss and thyroid hormone supplementation in case of hypothyroidism. It is named after Vaughan Pendred (1869–1946), the British doctor who first described the condition in an Irish family living in Durham in 1896. It accounts for 7.5% to 15% of all cases of congenital deafness.

Hypoplasia is underdevelopment or incomplete development of a tissue or organ. Although the term is not always used precisely, it properly refers to an inadequate or below-normal number of cells. Hypoplasia is similar to aplasia, but less severe. It is technically not the opposite of hyperplasia. Hypoplasia is a congenital condition, while hyperplasia generally refers to excessive cell growth later in life.

The frenulumof the tongue, tongue web, lingual frenulum, frenulum linguae, or fraenulum is a small fold of mucous membrane extending from the floor of the mouth to the midline of the underside of the human tongue.
Thyroid disease is a medical condition that affects the function of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located at the front of the neck and produces thyroid hormones that travel through the blood to help regulate many other organs, meaning that it is an endocrine organ. These hormones normally act in the body to regulate energy use, infant development, and childhood development.

Thyroiditis is the inflammation of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located on the front of the neck below the laryngeal prominence, and makes hormones that control metabolism.

The sodium/iodide cotransporter, also known as the sodium/iodide symporter (NIS), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC5A5 gene. It is a transmembrane glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 87 kDa and 13 transmembrane domains, which transports two sodium cations (Na+) for each iodide anion (I−) into the cell. NIS mediated uptake of iodide into follicular cells of the thyroid gland is the first step in the synthesis of thyroid hormone.

Young–Simpson syndrome (YSS) is a rare congenital disorder with symptoms including hypothyroidism, heart defects, facial dysmorphism, cryptorchidism in males, hypotonia, intellectual disability, and postnatal growth retardation.

Paired box gene 8, also known as PAX8, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PAX8 gene.

Forkhead box protein E1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOXE1 gene.

Thyroid stimulating hormone, beta also known as TSHB is a protein which in humans is encoded by the TSHB gene.
Bamforth–Lazarus syndrome is a genetic condition that results in thyroid dysgenesis. It is due to recessive mutations in forkhead/winged-helix domain transcription factor. It is associated with FOXE1.

Salivary gland diseases (SGDs) are multiple and varied in cause. There are three paired major salivary glands in humans: the parotid glands, the submandibular glands, and the sublingual glands. There are also about 800–1,000 minor salivary glands in the mucosa of the mouth. The parotid glands are in front of the ears, one on side, and secrete mostly serous saliva, via the parotid ducts, into the mouth, usually opening roughly opposite the second upper molars. The submandibular gland is medial to the angle of the mandible, and it drains its mixture of serous and mucous saliva via the submandibular duct into the mouth, usually opening in a punctum in the floor of mouth. The sublingual gland is below the tongue, on the floor of the mouth; it drains its mostly mucous saliva into the mouth via about 8–20 ducts, which open along the plica sublingualis, a fold of tissue under the tongue.

Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disorder in which the thyroid gland fails to produce sufficient thyroid hormones. Hypothyroidism is one of the most common endocrinopathies in dogs. It is either acquired or congenital.


















